Abstract
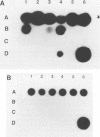
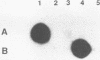
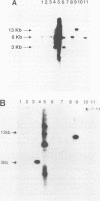
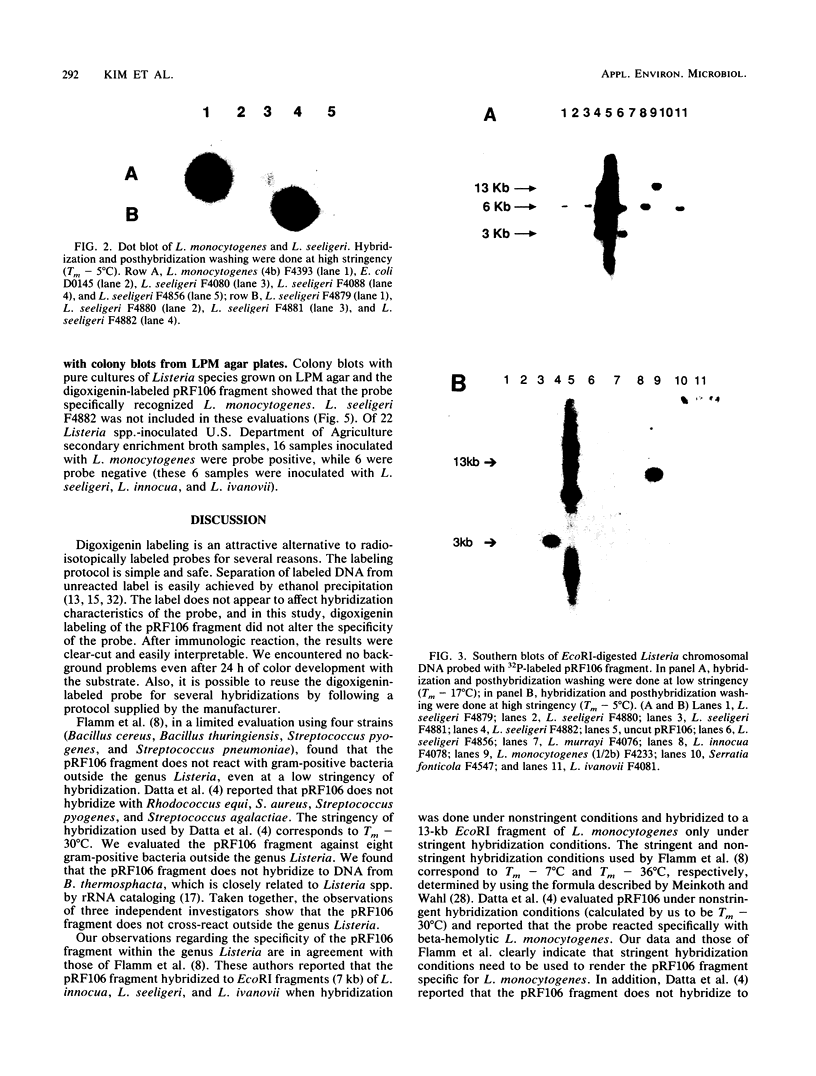
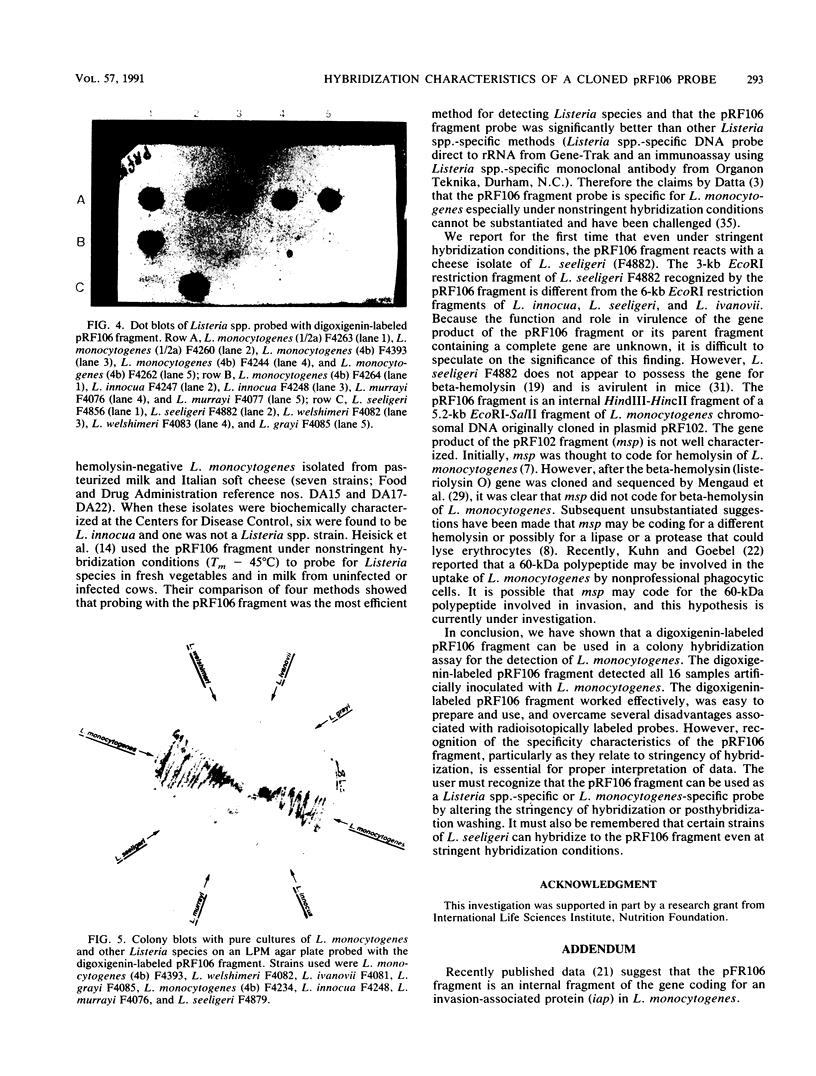
An internal fragment (pRF106 fragment, ca. 500 bp) of a gene (msp) coding for a 60-kDa protein of Listeria monocytogenes serotype 1/2a was used to develop a screening method to discriminate between L. monocytogenes and avirulent Listeria spp. on primary isolation plates. The L. monocytogenes-derived probe fragment of pRF106 hybridized to a 13-kb fragment of L. monocytogenes and a 3-kb fragment of one cheese isolate strain of Listeria seeligeri under stringent hybridization conditions (mean thermal denaturation temperature [Tm]-5 degrees C). The probe also hybridized to a 6-kb fragment of Listeria innocua, Listeria ivanovii, and L. seeligeri under less stringent hybridization conditions (Tm-17 degrees C). The pRF106 fragment was labeled with digoxigenin-11-dUTP and used to develop a colony hybridization assay. Colonies from lithium chloride-phenylethanol-moxalactam agar were blotted onto nylon membranes. The cells were pretreated with microwaves before lysis with sodium hydroxide. DNA-DNA hybridization and posthybridization washing were done at high stringency (Tm-7 degrees C). The nonisotopic colony hybridization procedure was specific for L. monocytogenes when evaluated against pure cultures of L. monocytogenes and other Listeria species, excluding the cheese isolate of L. seeligeri. Also, it was specific for L. monocytogenes when evaluated with Listeria-negative food enrichment cultures that were inoculated in the laboratory with Listeria species.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chenevert J., Mengaud J., Gormley E., Cossart P. A DNA probe specific for L. monocytogenes in the genus Listeria. Int J Food Microbiol. 1989 Jul;8(4):317–319. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(89)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. R. Probes for identifying Listeria. JAMA. 1989 Sep 22;262(12):1629–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. R., Wentz B. A., Hill W. E. Detection of hemolytic Listeria monocytogenes by using DNA colony hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2256–2259. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2256-2259.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitelson J. S., Lederberg J. Crude lysates of Staphylococcus aureus can transform Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):545–547. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamm R. K., Hinrichs D. J., Thomashow M. F. Cloning of a gene encoding a major secreted polypeptide of Listeria monocytogenes and its potential use as a species-specific probe. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2251–2256. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2251-2256.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebeyehu G., Rao P. Y., SooChan P., Simms D. A., Klevan L. Novel biotinylated nucleotide--analogs for labeling and colorimetric detection of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4513–4534. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiles H. B., Genersch E., Kessler C., Neumann R., Eggers H. J. In situ hybridization with digoxigenin-labeled DNA of human papillomaviruses (HPV 16/18) in HeLa and SiHa cells. Biotechniques. 1988 Nov-Dec;6(10):978–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington C. S., Burns J., Graham A. K., Evans M., McGee J. O. Interphase cytogenetics using biotin and digoxigenin labelled probes I: relative sensitivity of both reporter molecules for detection of HPV16 in CaSki cells. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Jun;42(6):592–600. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.6.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. The place of Listeria among gram-positive bacteria. Infection. 1988;16 (Suppl 2):S85–S88. doi: 10.1007/BF01639727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger J. D., Johnson A., Croan D., Flynn P., Whippie K., Kimball M., Lawrie J., Curiale M. Comparative studies of nucleic acid hybridization assay for Listeria in foods. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):669–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Goebel W. Identification of an extracellular protein of Listeria monocytogenes possibly involved in intracellular uptake by mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.55-61.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler S., Leimeister-Wächter M., Chakraborty T., Lottspeich F., Goebel W. The gene coding for protein p60 of Listeria monocytogenes and its use as a specific probe for Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1943–1950. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1943-1950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnan M. J., Mascola L., Lou X. D., Goulet V., May S., Salminen C., Hird D. W., Yonekura M. L., Hayes P., Weaver R. Epidemic listeriosis associated with Mexican-style cheese. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 29;319(13):823–828. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809293191303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D., Lee W. H. Development of USDA-FSIS method for isolation of Listeria monocytogenes from raw meat and poultry. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):660–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConaughy B. L., Laird C. D., McCarthy B. J. Nucleic acid reassociation in formamide. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3289–3295. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Chenevert J., Pereira J. M., Geoffroy C., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Cossart P. Expression in Escherichia coli and sequence analysis of the listeriolysin O determinant of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):766–772. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.766-772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Chakraborty T., Leimeister-Wächter M., Dufrenne J., Heuvelman K. J., Maas H., Jansen W., Wernars K., Guinee P. Specific gene probe for detection of biotyped and serotyped Listeria strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):902–906. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.902-906.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlech W. F., 3rd, Lavigne P. M., Bortolussi R. A., Allen A. C., Haldane E. V., Wort A. J., Hightower A. W., Johnson S. E., King S. H., Nicholls E. S. Epidemic listeriosis--evidence for transmission by food. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 27;308(4):203–206. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301273080407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer R., Zischler H., Epplen J. T. DNA fingerprinting using non-radioactive oligonucleotide probes specific for simple repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9344–9344. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]