Abstract
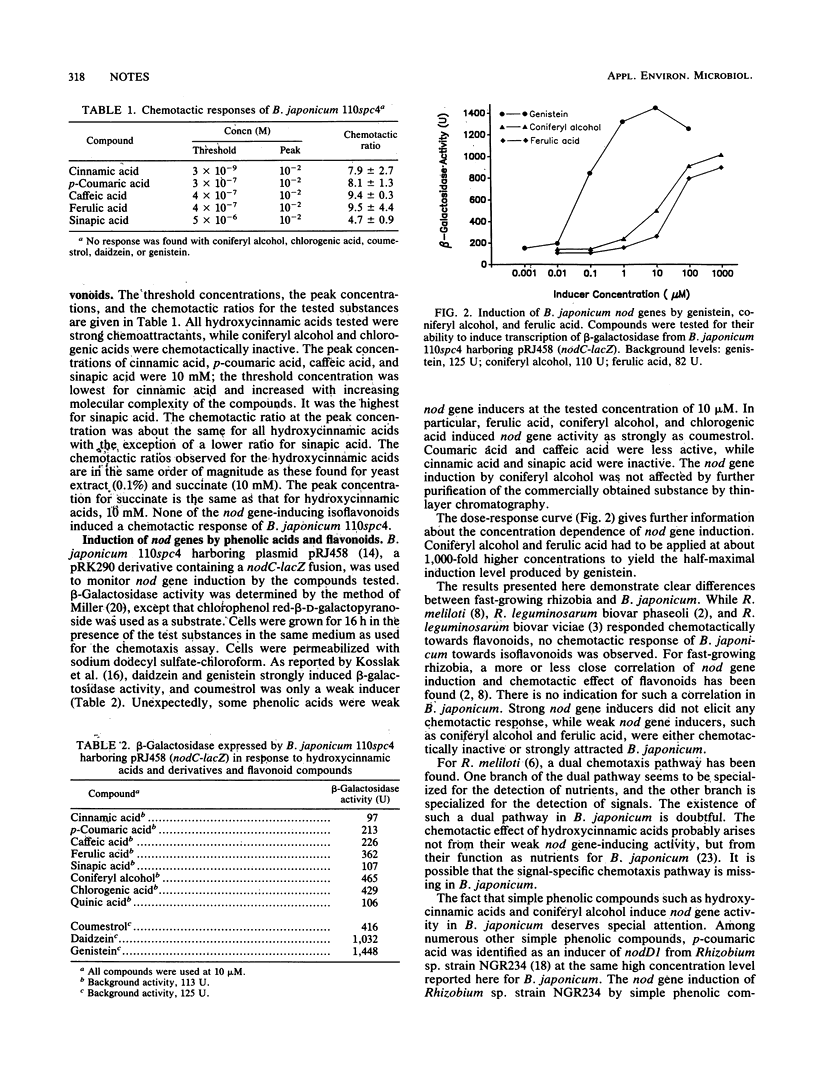
For Bradyrhizobium japonicum, the chemotactic and the nod gene-inducing effects of hydroxycinnamic acids and two of their derivatives were compared with those of isoflavonoids. Only the hydroxycinnamic acids were strong chemoattractants, while the other substances tested were chemotactically inactive. Besides the known nod gene induction by isoflavonoids, a weak nod gene induction by coniferyl alcohol, chlorogenic acid, and ferulic acid was found.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage J. P., Gallagher A., Johnston A. W. Comparison of the chemotactic behaviour of Rhizobium leguminosarum with and without the nodulation plasmid. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):743–748. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby A. M., Watson M. D., Loake G. J., Shaw C. H. Ti plasmid-specified chemotaxis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58C1 toward vir-inducing phenolic compounds and soluble factors from monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4181–4187. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4181-4187.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banfalvi Z., Nieuwkoop A., Schell M., Besl L., Stacey G. Regulation of nod gene expression in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):420–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00330475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman K., Gulash-Hoffee M., Hovestadt R. E., Larosiliere R. C., Ronco P. G., 2nd, Su L. Physiology of behavioral mutants of Rhizobium meliloti: evidence for a dual chemotaxis pathway. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3249–3254. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3249-3254.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Simon M. Bacterial chemotaxis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:501–517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caetano-Anollés G., Crist-Estes D. K., Bauer W. D. Chemotaxis of Rhizobium meliloti to the plant flavone luteolin requires functional nodulation genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3164–3169. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3164-3169.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshmane N., Stacey G. Identification of Bradyrhizobium nod genes involved in host-specific nodulation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3324–3330. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3324-3330.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttfert M., Hitz S., Hennecke H. Identification of nodS and nodU, two inducible genes inserted between the Bradyrhizobium japonicum nodYABC and nodIJ genes. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 Sep-Oct;3(5):308–316. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bookland R., Barkei J., Paaren H. E., Appelbaum E. R. Induction of Bradyrhizobium japonicum common nod genes by isoflavones isolated from Glycine max. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupski G., Götz R., Ober K., Pleier E., Schmitt R. Structure of complex flagellar filaments in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):361–366. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.361-366.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Adler J. Chemotaxis toward amino acids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):315–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.315-326.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleroni N. J. Chamber for bacterial chemotaxis experiments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Nov;32(5):729–730. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.5.729-730.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke D., Rivelli M., Ornston L. N. Chemotaxis to aromatic and hydroaromatic acids: comparison of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Rhizobium trifolii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):417–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.417-422.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Frost J. W., Long S. R. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regensburger B., Hennecke H. RNA polymerase from Rhizobium japonicum. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Aug;135(2):103–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00408017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]