Abstract
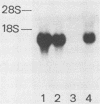
Microcystis aeruginosa is a common cyanobacterium in water blooms that appear widely in nutrient-rich, fresh, and brackish waters, and its toxic blooms cause the death of domestic animals. The administration of a crude toxic cell extract of M. aeruginosa K-139 to mice can produce tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and prompt severe physiological disturbances, especially liver damage, which can lead to death. The in vitro production of TNF-alpha by peritoneal macrophages was observed after stimulation with the cell extract or the purified toxin from K-139 cells. The expression of a TNF-alpha mRNA was also detected in spleen cells and peritoneal macrophages after stimulation with the cell extract. However, a previous injection of rabbit anti-murine TNF-alpha serum could prevent the liver damage to some extent and protect the mice from death. These findings indicate the involvement of TNF in microcystin shock.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertini R., Bianchi M., Ghezzi P. Adrenalectomy sensitizes mice to the lethal effects of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1708–1712. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Beutler B. The role of cachectin/TNF in endotoxic shock and cachexia. Immunol Today. 1988 Jan;9(1):28–31. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES E. O., GORHAM P. R., ZEHNDER A. Toxicity of a unialgal culture of Microcystis aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Jun;4(3):225–236. doi: 10.1139/m58-024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Nakano Y., Saito-Taki T., Mori N., Kojima M., Ohtake A., Shirai M. Toxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa K-139 strain. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(9):787–792. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb00964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano Y., Onozuka K., Terada Y., Shinomiya H., Nakano M. Protective effect of recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha in murine salmonellosis. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1935–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obayashi T., Tamura H., Tanaka S., Ohki M., Takahashi S., Kawai T. Endotoxin-inactivating activity in normal and pathological human blood samples. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):294–297. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.294-297.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtake A., Shirai M., Aida T., Mori N., Harada K., Matsuura K., Suzuki M., Nakano M. Toxicity of Microcystis species isolated from natural blooms and purification of the toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3202–3207. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3202-3207.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Hayflick J. S., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the cDNA for murine tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6060–6064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai M., Matumaru K., Ohotake A., Takamura Y., Aida T., Nakano M. Development of a solid medium for growth and isolation of axenic microcystis strains (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2569–2571. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2569-2571.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai M., Takamura Y., Sakuma H., Kojima M., Nakano M. Toxicity and delayed type hypersensitivity caused by Microcystis blooms from Lake Kasumigaura. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):731–735. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Espevik T. Interleukin 1 potentiates the lethal effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin in mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]