Abstract
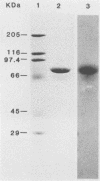
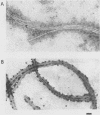
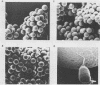
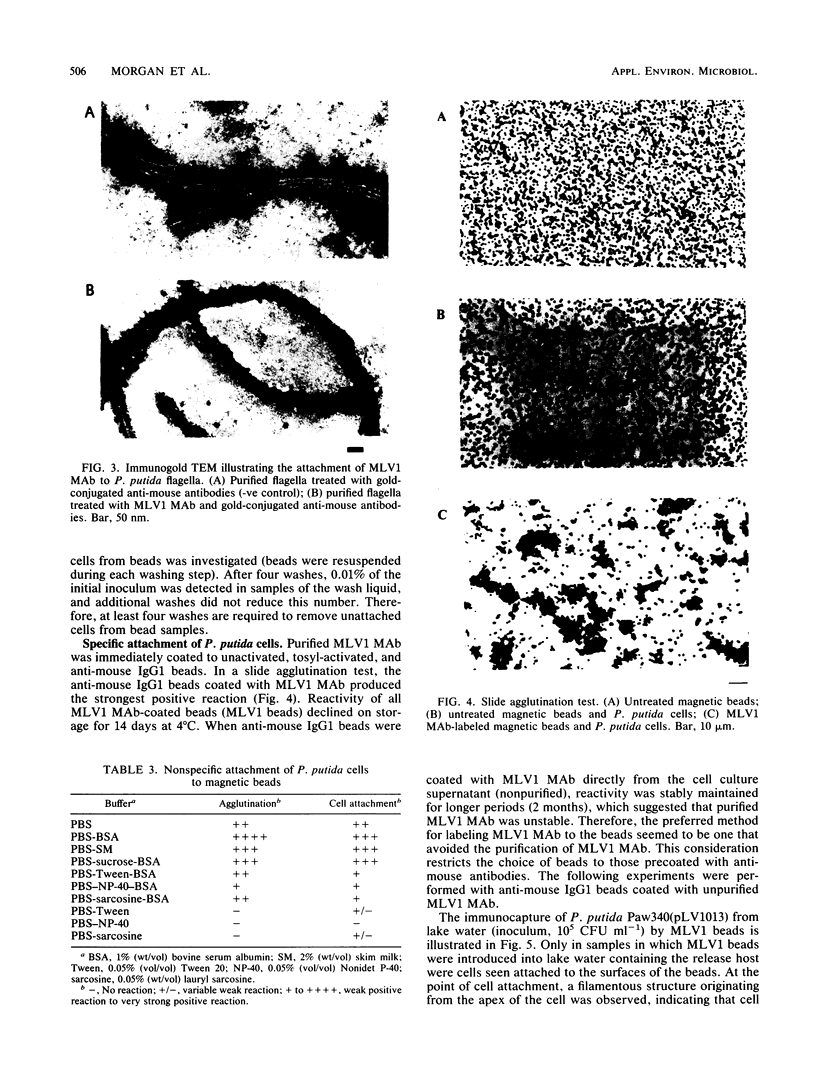
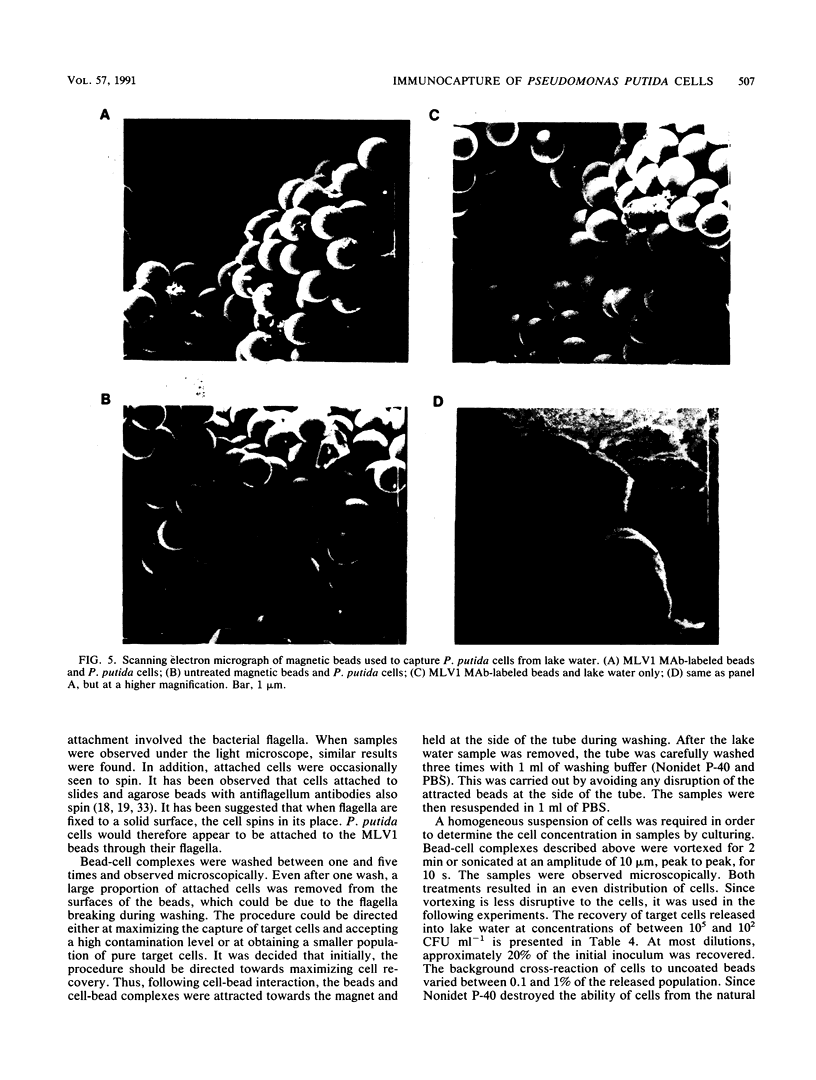
Monoclonal antibodies to Pseudomonas putida Paw340 cells were produced. In an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) against whole bacterial cells, a hybridoma cell line termed MLV1 produced a monoclonal antibody that reacted with P. putida Paw340 but showed no cross-reaction with 100 medical isolates and 150 aquatic isolates. By ELISA, immunogold electron microscopy, and Western blot (immunoblot) analysis, MLV1 antibody was found to react with purified bacterial flagella. The surfaces of magnetic polystyrene beads were coated with MLV1 antibody. By mixing MLV1 antibody-coated beads with lake water samples containing the target P. putida host, bead-cell complexes which could be recovered by attraction towards a magnet were formed. Prevention of nonspecific attachment of cells to the beads required the incorporation of detergents in the isolation protocol. These detergents affected colony-forming ability; however, the cells remained intact for direct detection. When reisolated by standard cultural methods, approximately 20% of the initial target population was recovered. Since the beads and bead-cell complexes were recovered in a magnetic field, target bacteria were separated from other lake water organisms and from particulate material which was not attracted towards the magnet and were thereby enriched. This method may now provide a useful system for recovering recombinant bacteria selectively from environmental samples.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. S., Dawson M., Drake D., Montie T. C. Electrophoretic separation and molecular weight characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa H-antigen flagellins. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):770–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.770-774.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentjen S. A., Fredrickson J. K., Van Voris P., Li S. W. Intact soil-core microcosms for evaluating the fate and ecological impact of the release of genetically engineered microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):198–202. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.198-202.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry G. R., Toranzos G. A., Bhatti A. R. Novel method for monitoring genetically engineered microorganisms in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1301–1304. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1301-1304.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng P., Sugasawara R. J., Schantz A. Identification of a common enterobacterial flagellin epitope with a monoclonal antibody. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Feb;136(2):337–342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-2-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson J. K., Bezdicek D. F., Brockman F. J., Li S. W. Enumeration of Tn5 mutant bacteria in soil by using a most- probable-number-DNA hybridization procedure and antibiotic resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):446–453. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.446-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulthorpe R. R., Wyndham R. C. Survival and activity of a 3-chlorobenzoate-catabolic genotype in a natural system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1584–1590. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1584-1590.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. R., Agabian N. A comparative structural analysis of the flagellin monomers of Caulobacter crescentus indicates that these proteins are encoded by two genes. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):925–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.925-933.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. R., Agabian N. The nucleotide sequence of the Mr = 28,500 flagellin gene of Caulobacter crescentus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7395–7401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben William E., Jansson Janet K., Chelm Barry K., Tiedje James M. DNA Probe Method for the Detection of Specific Microorganisms in the Soil Bacterial Community. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):703–711. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.703-711.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. K., Holben W. E., Tiedje J. M. Detection in soil of a deletion in an engineered DNA sequence by using DNA probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):3022–3025. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.3022-3025.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The covalent structure of the phase-1 flagellar filament protein of Salmonella typhimurium and its comparison with other flagellins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidus I. R., Welch M., Eisenbach M. Pausing of flagellar rotation is a component of bacterial motility and chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3627–3632. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3627-3632.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea T., Vartdal F., Davies C., Ugelstad J. Magnetic monosized polymer particles for fast and specific fractionation of human mononuclear cells. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(2):207–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger R. J., Charon N. W. Antiserum to the 33,000-dalton periplasmic-flagellum protein of "Treponema phagedenis" reacts with other treponemes and Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):1030–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.1030-1032.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Location of epitopes on Campylobacter jejuni flagella. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):739–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.739-745.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund A., Hellemann A. L., Vartdal F. Rapid isolation of K88+ Escherichia coli by using immunomagnetic particles. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2572–2575. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2572-2575.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONOUGH M. W. AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF ANTIGENICALLY DISTINCT SALMONELLA FLAGELLAR PROTEINS. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:342–355. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough M. W., Smith S. E. Molecular weight variation among bacterial flagellins. Microbios. 1976;16(63):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. A., Winstanley C., Pickup R. W., Jones J. G., Saunders J. R. Direct phenotypic and genotypic detection of a recombinant pseudomonad population released into lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2537–2544. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2537-2544.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba K., Yamashita I., Vonderviszt F. Structure of the core and central channel of bacterial flagella. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):648–654. doi: 10.1038/342648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton S. M., Jacob C. O., Stocker B. A. Immune response to cholera toxin epitope inserted in Salmonella flagellin. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.2468182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Charon N. W., Cook R. G., Fuentes M. D., Limberger R. J. Antigenic relatedness and N-terminal sequence homology define two classes of periplasmic flagellar proteins of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum and Treponema phagedenis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4072–4082. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4072-4082.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peel M., Donachie W., Shaw A. Physical and antigenic heterogeneity in the flagellins of Listeria monocytogenes and L. ivanovii. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Sep;134(9):2593–2598. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-9-2593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. N., Jr, McGee Z. A., Kaplan J., Hammond M. E., Larson J. K., Buchanan T. M., Schoolnik G. K. Ultrastructural localization of specific gonococcal macromolecules with antibody-gold sphere immunological probes. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):361–366. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.361-366.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiry G., Clippe A., Scarcez T., Petre J. Cloning of DNA sequences encoding foreign peptides and their expression in the K88 pili. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):984–993. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.984-993.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartdal F., Gaudernack G., Funderud S., Bratlie A., Lea T., Ugelstad J., Thorsby E. HLA class I and II typing using cells positively selected from blood by immunomagnetic isolation--a fast and reliable technique. Tissue Antigens. 1986 Nov;28(5):301–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1986.tb00500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield C., Walker S. G., Atkinson C. F., Lam J. S., MacDonald L. A., Beveridge T. J., Orskov I., Orskov F. Serotype-specific monoclonal antibodies against the H12 flagellar antigen of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jul;134(7):1747–1753. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-7-1747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstanley C., Morgan J. A., Pickup R. W., Jones J. G., Saunders J. R. Differential regulation of lambda pL and pR promoters by a cI repressor in a broad-host-range thermoregulated plasmid marker system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):771–777. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.771-777.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]