Abstract
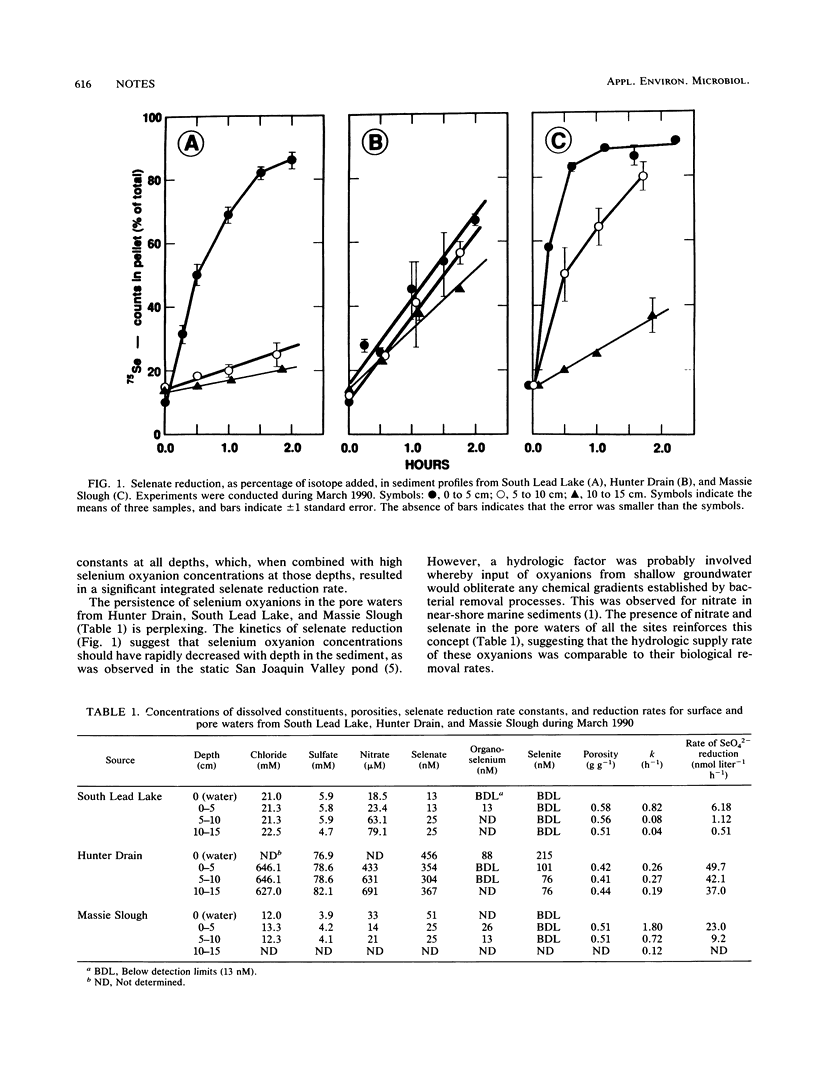
Dissimilatory in situ selenate reduction to elemental selenium in sediments from irrigated agricultural drainage regions of western Nevada was measured at ambient Se oxyanion concentrations. Selenate reduction was rapid, with turnover rate constants ranging from 0.04 to 1.8 h-1 at total Se concentrations in pore water of 13 to 455 nM. Estimates of removal rates of selenium oxyanions were 14.38, and 155 mumol m-2 day-1 for South Lead Lake, Massie Slough, and Hunter Drain, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Oremland R. S., Hollibaugh J. T., Maest A. S., Presser T. S., Miller L. G., Culbertson C. W. Selenate reduction to elemental selenium by anaerobic bacteria in sediments and culture: biogeochemical significance of a novel, sulfate-independent respiration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2333–2343. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2333-2343.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg N. A., Oremland R. S. Dissimilatory selenate reduction potentials in a diversity of sediment types. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3550–3557. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3550-3557.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



