Abstract
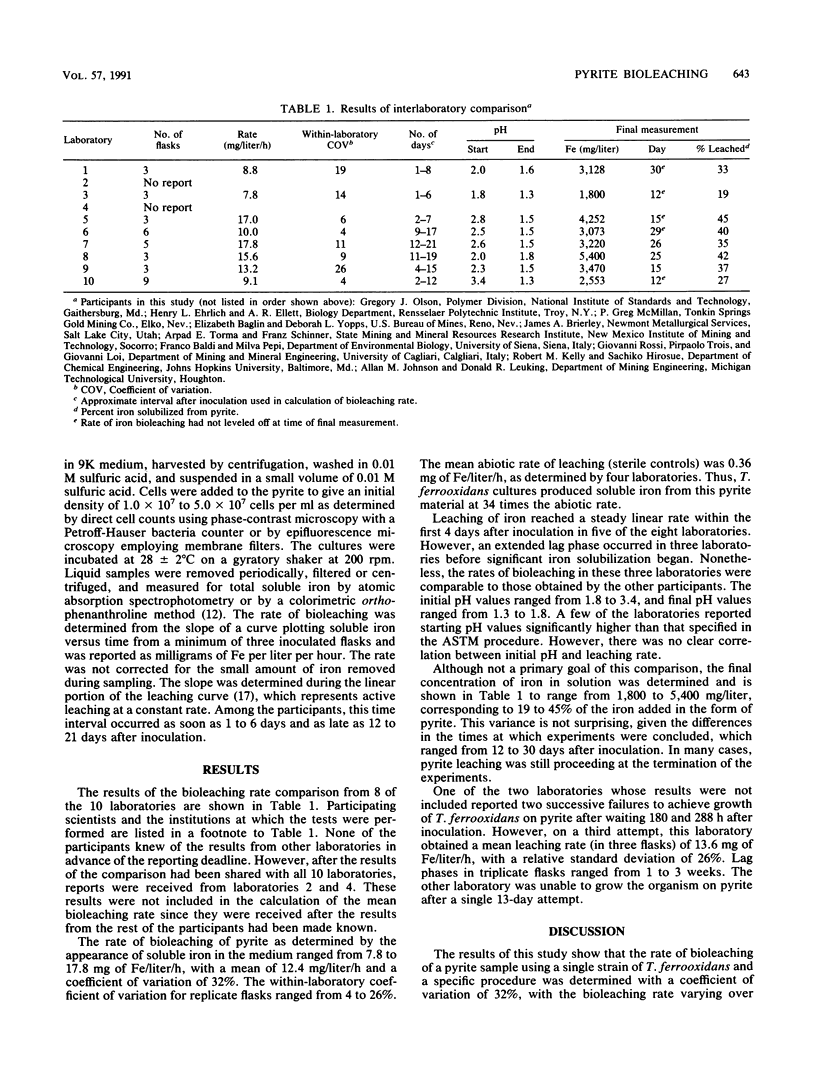
Ten laboratories participated in an interlaboratory comparison of determination of bioleaching rates of a pyrite reference material. A standardized procedure and a single strain of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans were used in this study. The mean rate of bioleaching of the pyrite reference material was 12.4 mg of Fe per liter per h, with a coefficient of variation (percent relative standard deviation) of 32% as determined by eight laboratories. These results show the precision among laboratories of the determination of rates of pyrite bioleaching when a standard test procedure and reference material are used.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Manning H. L. New medium for isolating iron-oxidizing and heterotrophic acidophilic bacteria from acid mine drainage. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1010–1016. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1010-1016.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monticello D. J., Finnerty W. R. Microbial desulfurization of fossil fuels. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:371–389. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M. P., LUNDGREN D. G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):642–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.642-647.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P. C., Stumm W. Acidic mine drainage: the rate-determining step. Science. 1970 Feb 20;167(3921):1121–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3921.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


