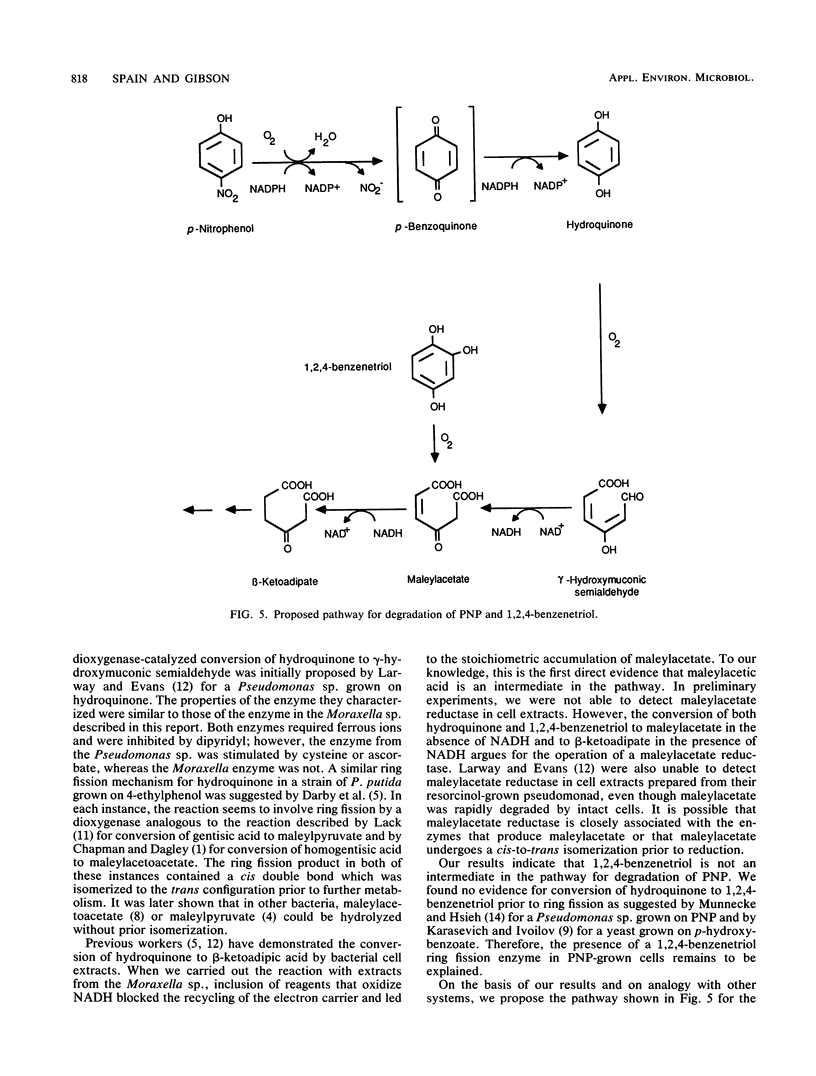
Abstract
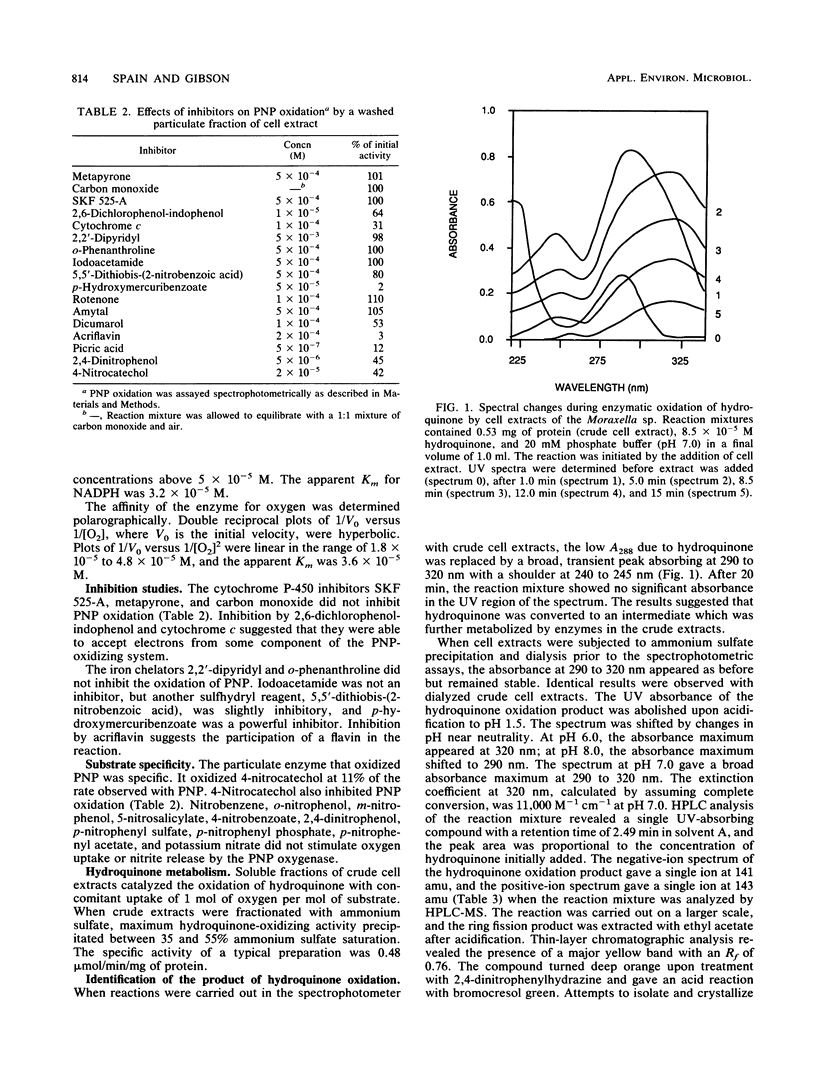
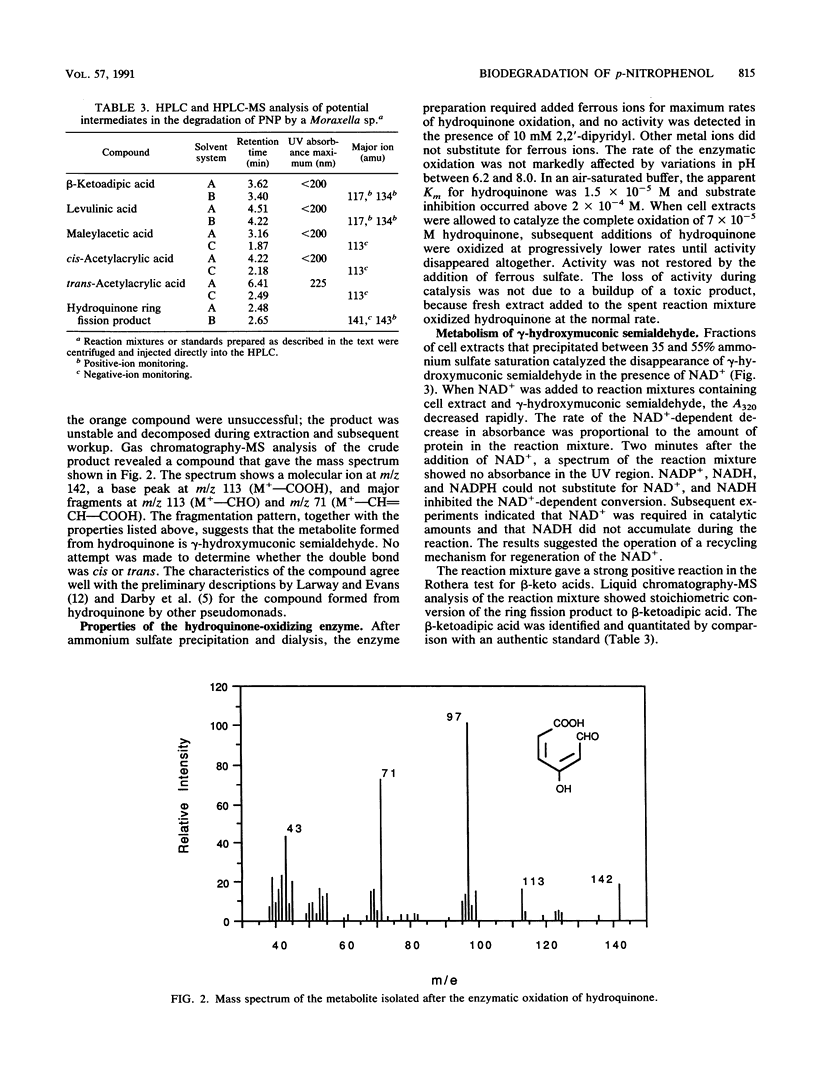
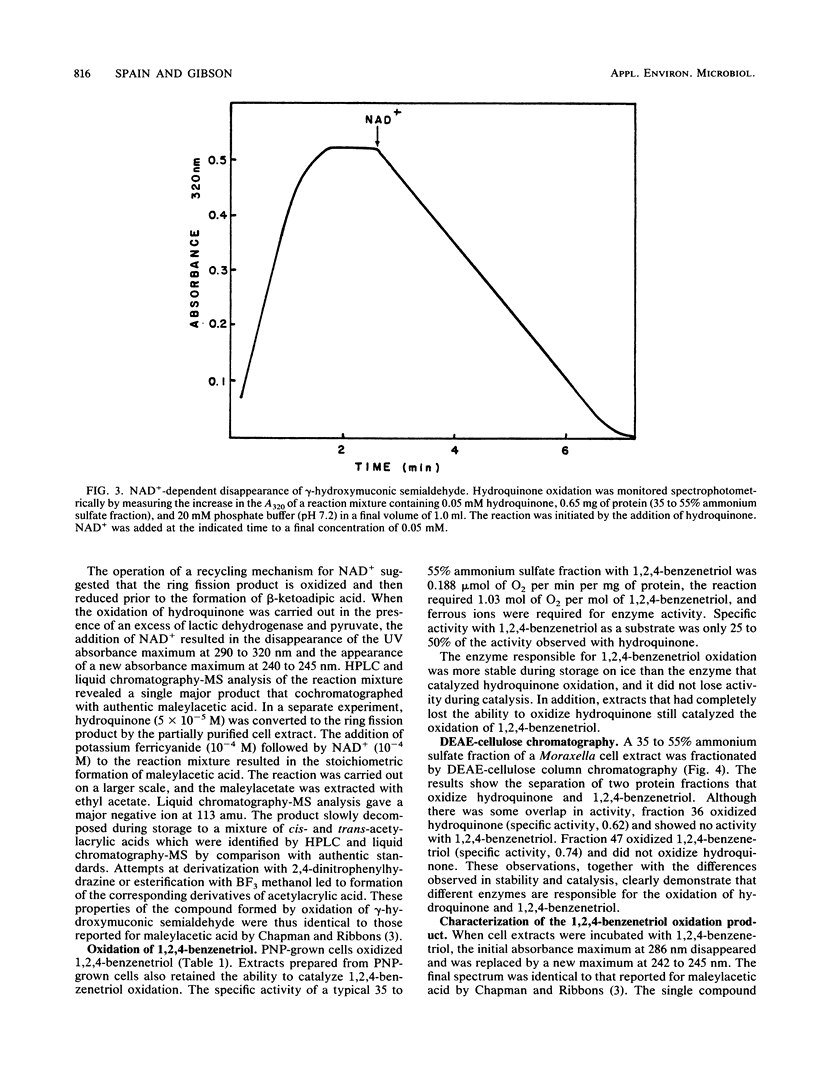
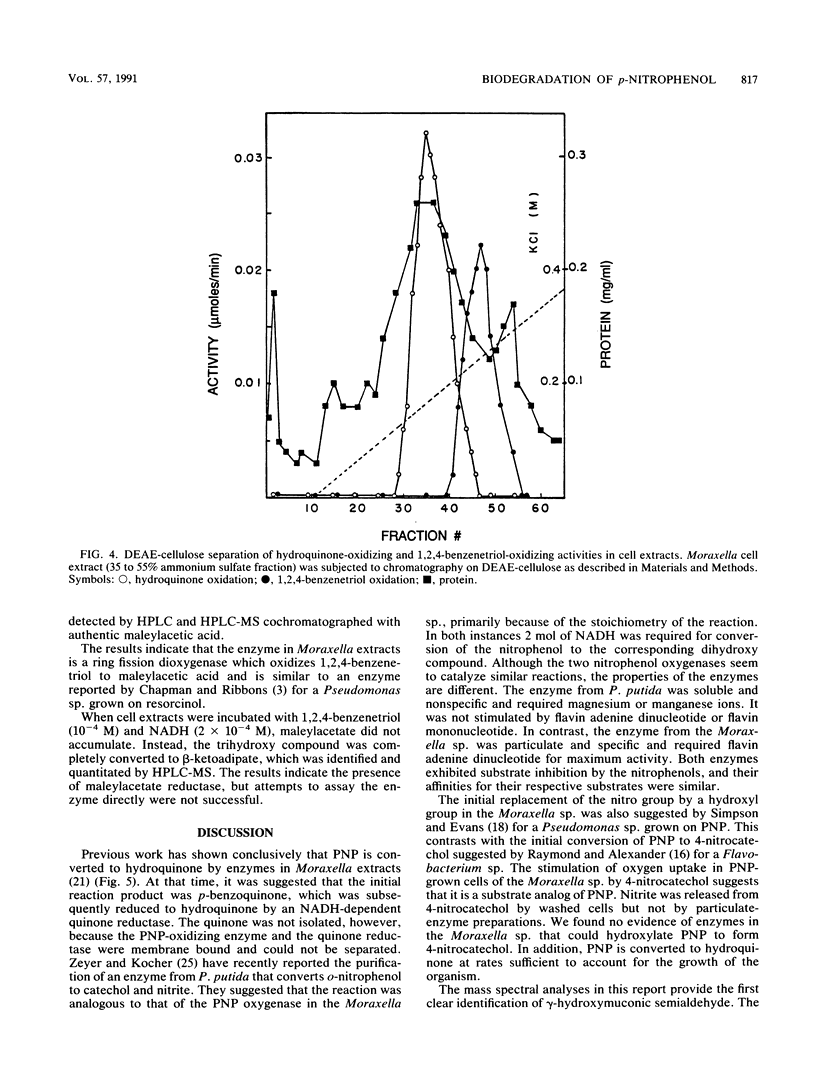
A Moraxella strain grew on p-nitrophenol with stoichiometric release of nitrite. During induction of the enzymes for growth on p-nitrophenol, traces of hydroquinone accumulated in the medium. In the presence of 2,2′-dipyridyl, p-nitrophenol was converted stoichiometrically to hydroquinone. Particulate enzymes catalyzed the conversion of p-nitrophenol to hydroquinone in the presence of NADPH and oxygen. Soluble enzymes catalyzed the conversion of hydroquinone to γ-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde, which was identified by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-mass spectroscopy. Upon addition of catalytic amounts of NAD+, γ-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde was converted to β-ketoadipic acid. In the presence of pyruvate and lactic dehydrogenase, substrate amounts of NAD were required and γ-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde was converted to maleylacetic acid, which was identified by HPLC-mass spectroscopy. Similar results were obtained when the reaction was carried out in the presence of potassium ferricyanide. Extracts prepared from p-nitrophenol-growth cells also contained an enzyme that catalyzed the oxidation of 1,2,4-benzenetriol to maleylacetic acid. The enzyme responsible for the oxidation of 1,2,4-benzenetriol was separated from the enzyme responsible for hydroquinone oxidation by DEAE-cellulose chromatography. The results indicate that the pathway for biodegradation of p-nitrophenol involves the initial removal of the nitro group as nitrite and formation of hydroquinone. 1,4-Benzoquinone, a likely intermediate in the initial reaction, was not detected. Hydroquinone is converted to β-ketoadipic acid via γ-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde and maleylacetic acid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAPMAN P. J., DAGLEY S. Oxidation of homogentistic acid by cell-free extracts of a vibrio. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jun;28:251–256. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. J., Hopper D. J. The bacterial metabolism of 2,4-xylenol. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):491–498. doi: 10.1042/bj1100491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. J., Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of resorcinylic compounds by bacteria: alternative pathways for resorcinol catabolism in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):985–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.985-998.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L. Degradation of homogentisate by strains of Bacillus and Moraxella. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Feb;22(2):276–280. doi: 10.1139/m76-037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Enzymic formation of D-malate. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):798–800. doi: 10.1042/bj1100798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILBY B. A. The formation of beta-ketoadipic acid by bacterial fission of aromatic rings. Biochem J. 1951 Oct;49(5):671–674. doi: 10.1042/bj0490671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACK L. The enzymic oxidation of gentisic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:117–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90239-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnecke D. M., Hsieh D. P. Microbial decontamination of parathion and p-nitrophenol in aqueous media. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):212–217. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.212-217.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyholm N., Lindgaard-Jørgensen P., Hansen N. Biodegradation of 4-nitrophenol in standardized aquatic degradation tests. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 1984 Oct;8(5):451–470. doi: 10.1016/0147-6513(84)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlömann M., Fischer P., Schmidt E., Knackmuss H. J. Enzymatic formation, stability, and spontaneous reactions of 4-fluoromuconolactone, a metabolite of the bacterial degradation of 4-fluorobenzoate. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5119–5129. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5119-5129.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Nishino S. F. Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1010-1019.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Van Veld P. A., Monti C. A., Pritchard P. H., Cripe C. R. Comparison of p-Nitrophenol Biodegradation in Field and Laboratory Test Systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):944–950. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.944-950.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Wyss O., Gibson D. T. Enzymatic oxidation of p-nitrophenol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):634–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudhakar-Barik, Siddaramappa R., Sethunathan N. Metabolism of nitrophenols by bacteria isolated from parathion-amended flooded soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1976;42(4):461–470. doi: 10.1007/BF00410177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeyer J., Kocher H. P. Purification and characterization of a bacterial nitrophenol oxygenase which converts ortho-nitrophenol to catechol and nitrite. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1789–1794. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1789-1794.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



