Abstract
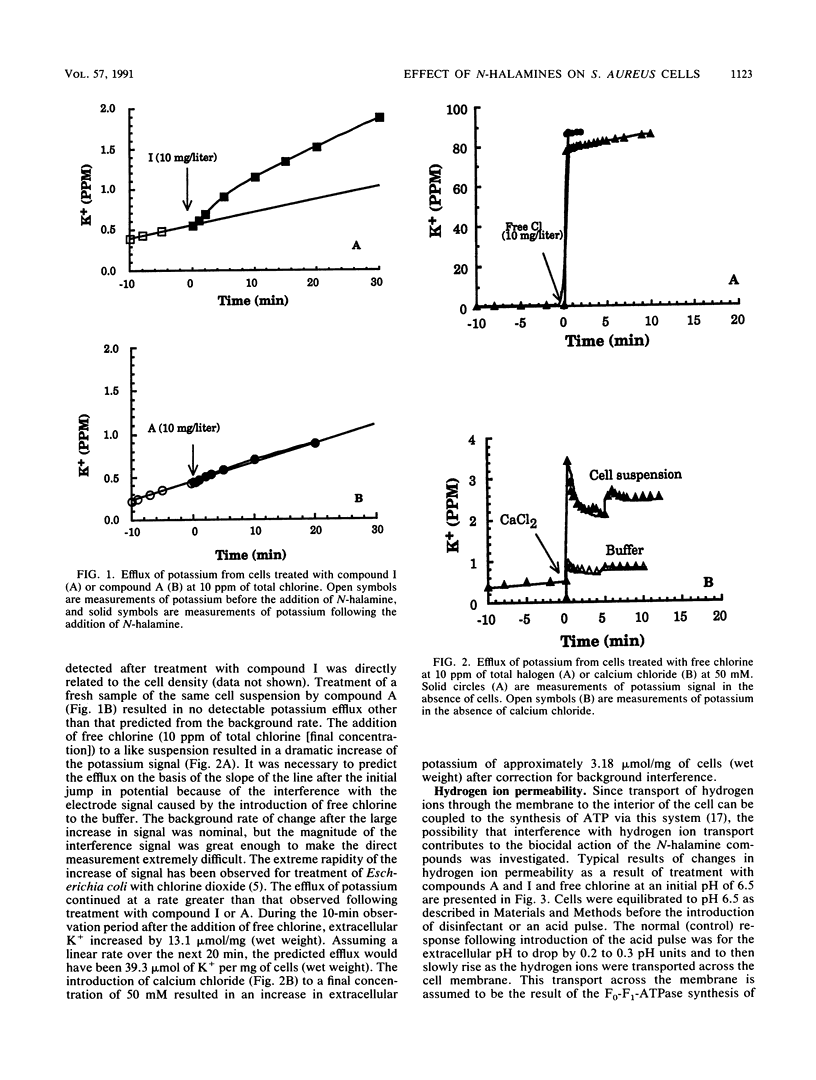
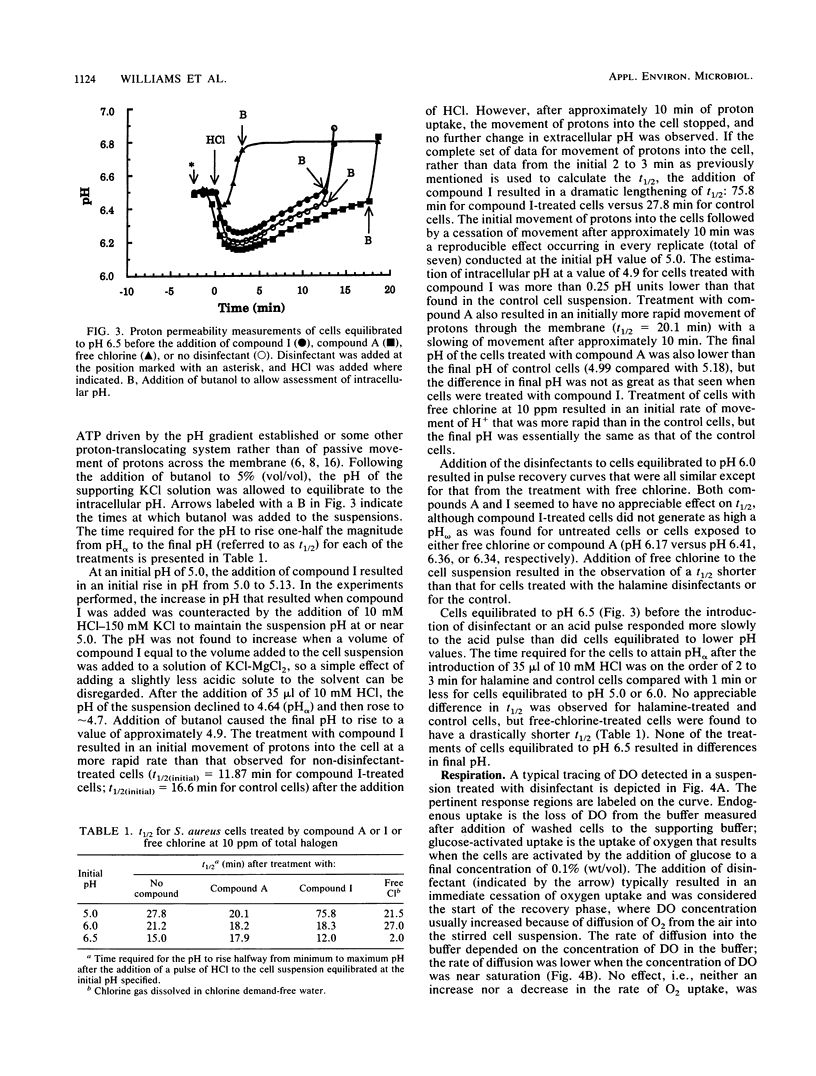
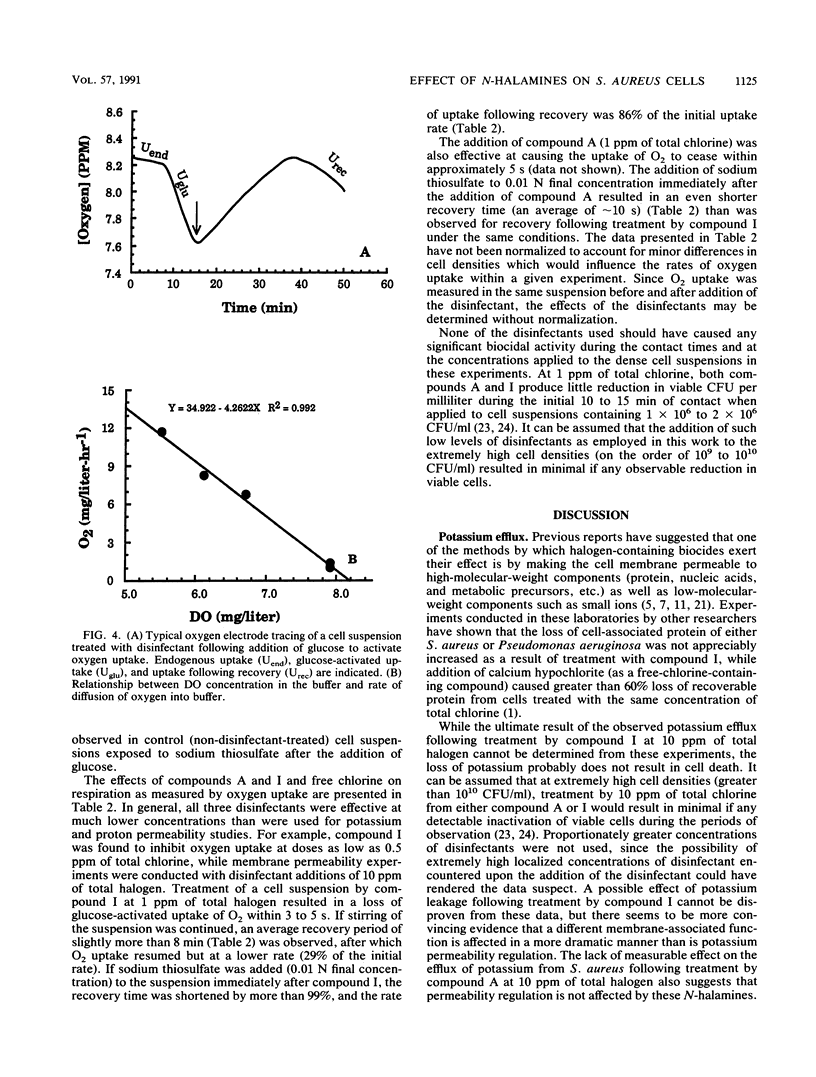
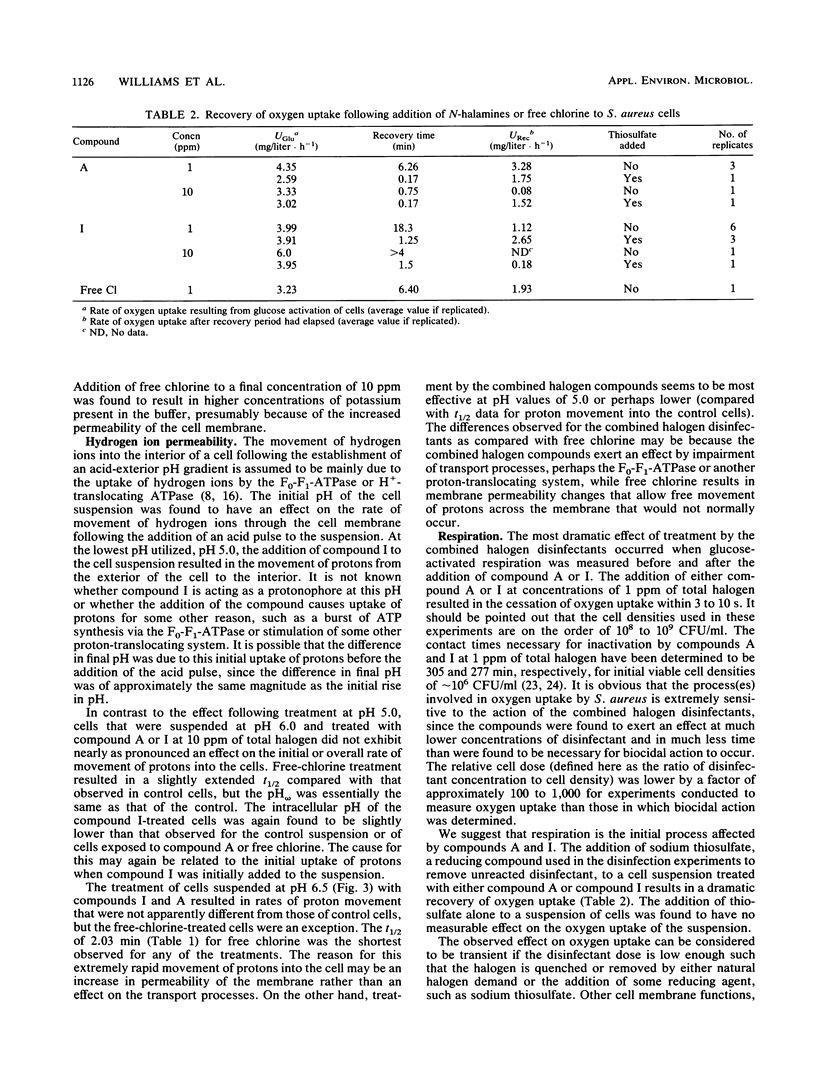
Two N-halamine compounds, 3-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-2-oxazolidinone and 1,3-dichloro-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-imidazolidinone, were compared with free chlorine as to their effects on selected membrane functions of intact Staphylococcus aureus cells. Free chlorine was found to cause a loss of permeability control, as measured by the efflux of potassium from the cells and a dramatic increase in hydrogen ion permeability, and to affect cell respiration in a nonreversible fashion, as measured by oxygen uptake. The two N-halamines were found to have very little effect on permeability to either potassium or hydrogen ions but were both found to dramatically inhibit respiration in a reversible manner. It is proposed that the first step in the disinfection process by these N-halamines is an inhibition of respiratory enzymes that, if not reversed, ultimately leads to a loss of cell viability.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnela S. B., Worley S. D., Williams D. E. Syntheses and antibacterial activity of new N-halamine compounds. J Pharm Sci. 1987 Mar;76(3):245–247. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600760314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender G. R., Sutton S. V., Marquis R. E. Acid tolerance, proton permeabilities, and membrane ATPases of oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):331–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.331-338.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. D., Roberts P. V., Matin A. Effect of chlorine dioxide on selected membrane functions of Escherichia coli. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;60(3):213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb01075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):359–378. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.359-378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIBERG L. Further quantitative studies on the reaction of chlorine with bacteria in water disinfection. II. Experimental investigations with C136 and P32. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1957;40(1):67–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas C. N., Engelbrecht R. S. Physiological alterations of vegetative microorganisms resulting form chlorination. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1980 Jul;52(7):1976–1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski J. J., Huycke M. M., Selk S. H., Bodor N., Higuchi T. N-Halo derivatives V: Comparative antimicrobial activity of soft N-chloramine systems. J Pharm Sci. 1976 Dec;65(12):1737–1742. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600651211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox W. E., Stumpf P. K., Green D. E., Auerbach V. H. The Inhibition of Sulfhydryl Enzymes as the Basis of the Bactericidal Action of Chlorine. J Bacteriol. 1948 Apr;55(4):451–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong L. I., Swango L. J., Blagburn B. L., Hendrix C. M., Williams D. E., Worley S. D. Inactivation of Giardia lamblia and Giardia canis cysts by combined and free chlorine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2580–2582. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2580-2582.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Shih K., Lederberg J. Effects of chloramine on Bacillus subtilis deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):934–945. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.934-945.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholes P., Mitchell P. Respiration-driven proton translocation in Micrococcus denitrificans. J Bioenerg. 1971 Sep;1(3):309–323. doi: 10.1007/BF01516290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swango L. J., Wilt G. R., Killen A. D., Williams D. E., Worley S. D. Inactivation of Legionella pneumophila by hypochlorite and an organic chloramine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2983–2986. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2983-2986.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., Elder E. D., Worley S. D. Is free halogen necessary for disinfection? Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2583–2585. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2583-2585.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., Worley S. D., Barnela S. B., Swango L. J. Bactericidal activities of selected organic N-halamines. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2082–2089. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2082-2089.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., Worley S. D., Wheatley W. B., Swango L. J. Bactericidal properties of a new water disinfectant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):637–643. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.637-643.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



