Abstract
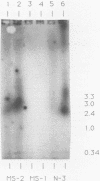
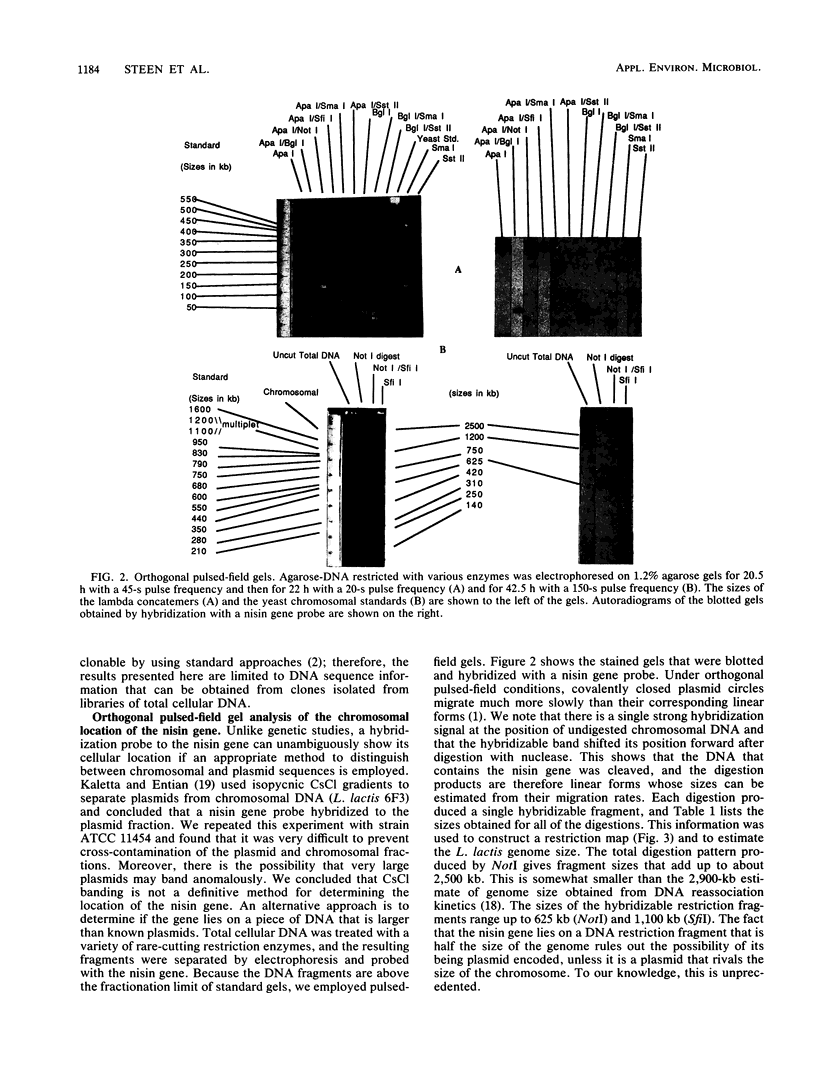
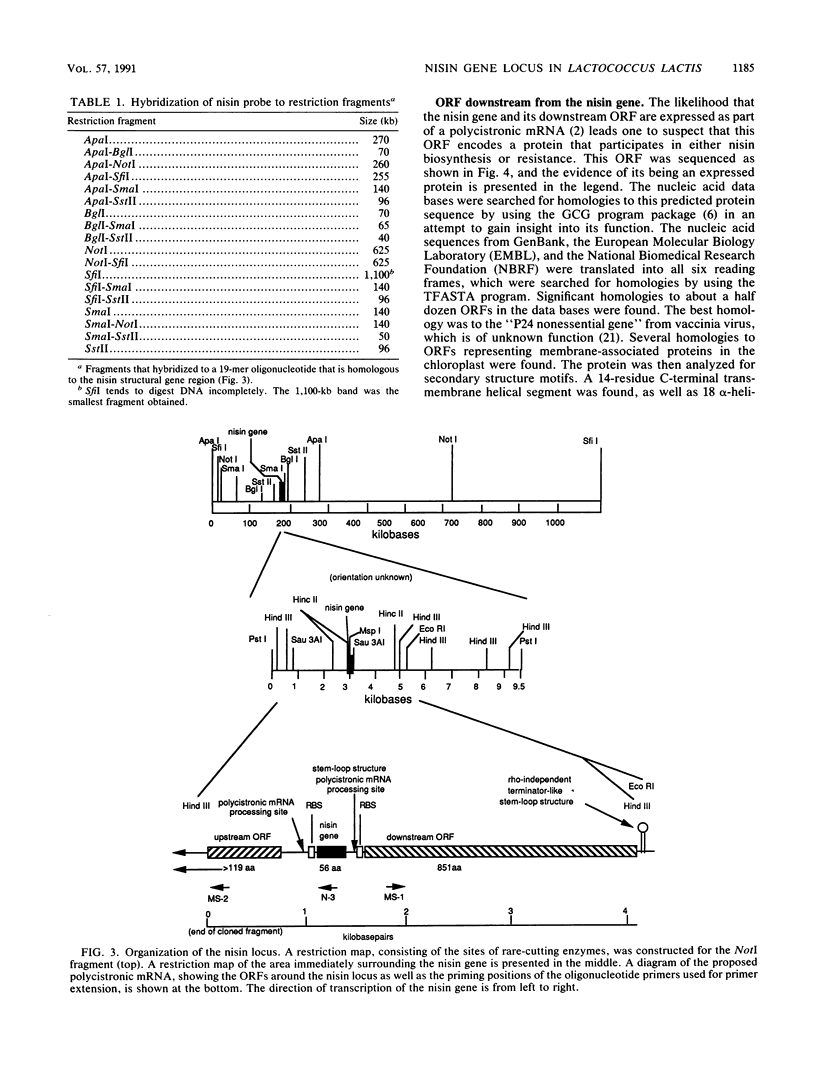
The location and organization of the nisin locus in Lactococcus lactis ATCC 11454 were studied. Primer extension of in vivo mRNA transcripts of the gene that encodes the nisin prepropeptide sequence indicated the presence of a promoter at least 4 kb upstream from the nisin gene and that the mRNA has several processing sites. Restriction fragment patterns using rare-cutting enzymes, orthogonal pulsed-field clamped homogeneous electric field (CHEF) agarose gel electrophoresis, and hybridization with nisin gene probes showed that the nisin prepropeptide gene was located on a megabase-size restriction fragment, which was taken as proof of a chromosomal location. This is contrary to earlier reports, which had indicated that genes for nisin production were located on plasmids. There was no evidence of more than one chromosomal location or more than one copy of the nisin gene. The restriction patterns indicated that the size of the L. lactis genome is about 2,500 kb. The previously observed (G. W. Buchman, S. Banerjee, and J. N. Hansen, J. Biol. Chem. 263: 16260-16266, 1988) downstream open reading frame (ORF) was fully sequenced to reveal an 851-amino-acid coding region, an upstream putative mRNA processing site, and a putative rho-independent terminator. The ORF was analyzed for secondary structural features, and the sequence data bases were searched for homologies. The ORF contained many amphipathic helices, a C-terminal transmembrane helix, and homologies to some membrane-associated proteins. It lacked an N-terminal membrane insertion sequence and accordingly appears to be associated with, and anchored to, the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. An additional ORF that possessed a ribosome-binding sequence and tandem promoters, indicating the beginning of a new operon, was identified still farther downstream. The results were consistent with the nisin gene being part of a polycistronic operon with a size greater than 8.5 kb.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beverley S. M. Characterization of the 'unusual' mobility of large circular DNAs in pulsed field-gradient electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):925–939. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman G. W., Banerjee S., Hansen J. N. Structure, expression, and evolution of a gene encoding the precursor of nisin, a small protein antibiotic. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16260–16266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassy B. M. A gentle method for the lysis of oral streptococci. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):603–608. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd H. M., Horn N., Gasson M. J. Analysis of the genetic determinant for production of the peptide antibiotic nisin. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Mar;136(3):555–566. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-3-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Weiss R. M., Terwilliger T. C. The helical hydrophobic moment: a measure of the amphiphilicity of a helix. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):371–374. doi: 10.1038/299371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froseth B. R., Herman R. E., McKay L. L. Cloning of nisin resistance determinant and replication origin on 7.6-kilobase EcoRI fragment of pNP40 from Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis DRC3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):2136–2139. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.2136-2139.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. G., Zajdel J., Dobrzański W. T. Possible plasmid nature of the determinant for production of the antibiotic nisin in some strains of Streptococcus lactis. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):189–192. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S. Transfer of Sucrose-Fermenting Ability and Nisin Production Phenotype among Lactic Streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):627–633. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.627-633.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Malpartida F., Kieser H. M., Ikeda H., Duncan J., Fujii I., Rudd B. A., Floss H. G., Omura S. Production of 'hybrid' antibiotics by genetic engineering. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):642–644. doi: 10.1038/314642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A. Biosynthesis of the antibiotic nisin by whole Streptococcus lactus organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Aug;44(2):209–220. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. C. Synthesis of the antibiotic nisin: formation of lanthionine and beta-methyl-lanthionine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;184(1):216–219. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W., Jarvis B. D. Deoxyribonucleic Acid homology among lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):77–83. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.77-83.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R., Sanozky R. B. Conjugal transfer from Streptococcus lactis ME2 of plasmids encoding phage resistance, nisin resistance and lactose-fermenting ability: evidence for a high-frequency conjugative plasmid responsible for abortive infection of virulent bacteriophage. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1531–1541. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-6-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotwal G. J., Moss B. Analysis of a large cluster of nonessential genes deleted from a vaccinia virus terminal transposition mutant. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):524–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oropeza-Wekerle R. L., Speth W., Imhof B., Gentschev I., Goebel W. Translocation and compartmentalization of Escherichia coli hemolysin (HlyA). J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3711–3717. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3711-3717.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N. Translation framing code and frame-monitoring mechanism as suggested by the analysis of mRNA and 16 S rRNA nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):643–652. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. J., Sandine W. E. Conjugal transfer of nisin plasmid genes from Streptococcus lactis 7962 to Leuconostoc dextranicum 181. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):352–357. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.352-357.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmanen I., Lundström K., Lehtovaara P., Sarvas M., Ruohonen M., Palva I. Transcription and translation of foreign genes in Bacillus subtilis by the aid of a secretion vector. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):176–182. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.176-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]