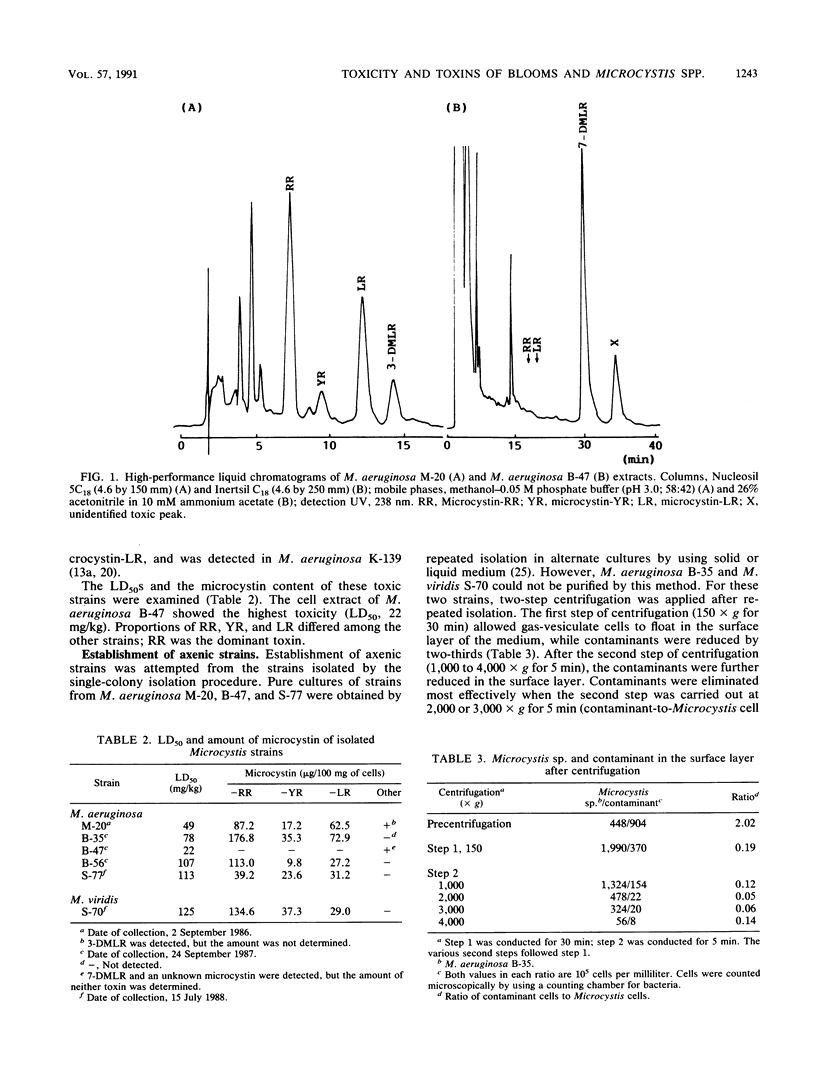
Abstract
All samples of cyanobacterial blooms collected from 1986 to 1989 from Lake Kasumigaura, Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan, were hepatotoxic. The 50% lethal doses (LD50s) of the blooms to mice ranged from 76 to 556 mg/kg of body weight. Sixty-eight Microcystis cell clones (67 Microcystis aeruginosa and 1 M. viridis) were isolated from the blooms. Twenty-three strains (including the M. viridis strain) were toxic. However, the ratio of toxic to nontoxic strains among the blooms varied (6 to 86%). Microcystins were examined in six toxic strains. Five toxic strains produced microcystin-RR, -YR, and -LR, with RR being the dominant toxin in these strains. Another strain produced 7-desmethylmicrocystin-LR and an unknown microcystin. This strain showed the highest toxicity. Establishment of axenic strains from the Microcystis cells exhibiting extracellularly mucilaginous materials was successful by using a combination of the agar plate technique and two-step centrifugation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carmichael W. W., Bent P. E. Hemagglutination method for detection of freshwater cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) toxins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1383–1388. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1383-1388.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. Algal toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Dec;42(4):725–746. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.4.725-746.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES E. O., GORHAM P. R., ZEHNDER A. Toxicity of a unialgal culture of Microcystis aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Jun;4(3):225–236. doi: 10.1139/m58-024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada K., Matsuura K., Suzuki M., Oka H., Watanabe M. F., Oishi S., Dahlem A. M., Beasley V. R., Carmichael W. W. Analysis and purification of toxic peptides from cyanobacteria by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1988 Sep 2;448(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)84589-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada K., Matsuura K., Suzuki M., Watanabe M. F., Oishi S., Dahlem A. M., Beasley V. R., Carmichael W. W. Isolation and characterization of the minor components associated with microcystins LR and RR in the cyanobacterium (blue-green algae). Toxicon. 1990;28(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(90)90006-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada K., Suzuki M., Dahlem A. M., Beasley V. R., Carmichael W. W., Rinehart K. L., Jr Improved method for purification of toxic peptides produced by cyanobacteria. Toxicon. 1988;26(5):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKintosh C., Beattie K. A., Klumpp S., Cohen P., Codd G. A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80245-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Nakano Y., Saito-Taki T., Mori N., Kojima M., Ohtake A., Shirai M. Toxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa K-139 strain. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(9):787–792. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb00964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano Y., Shirai M., Mori N., Nakano M. Neutralization of microcystin shock in mice by tumor necrosis factor alpha antiserum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):327–330. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.327-330.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtake A., Shirai M., Aida T., Mori N., Harada K., Matsuura K., Suzuki M., Nakano M. Toxicity of Microcystis species isolated from natural blooms and purification of the toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3202–3207. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3202-3207.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippka R. Isolation and purification of cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1988;167:3–27. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)67004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runnegar M. T., Falconer I. R. Effect of toxin from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa on ultrastructural morphology and actin polymerization in isolated hepatocytes. Toxicon. 1986;24(2):109–115. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90112-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai M., Matumaru K., Ohotake A., Takamura Y., Aida T., Nakano M. Development of a solid medium for growth and isolation of axenic microcystis strains (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2569–2571. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2569-2571.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai M., Takamura Y., Sakuma H., Kojima M., Nakano M. Toxicity and delayed type hypersensitivity caused by Microcystis blooms from Lake Kasumigaura. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):731–735. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M. F., Oishi S. Effects of environmental factors on toxicity of a cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa) under culture conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1342–1344. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1342-1344.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M. F., Oishi S., Harda K., Matsuura K., Kawai H., Suzuki M. Toxins contained in Microcystis species of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). Toxicon. 1988;26(11):1017–1025. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa S., Matsushima R., Watanabe M. F., Harada K., Ichihara A., Carmichael W. W., Fujiki H. Inhibition of protein phosphatases by microcystins and nodularin associated with hepatotoxicity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1990;116(6):609–614. doi: 10.1007/BF01637082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



