Abstract
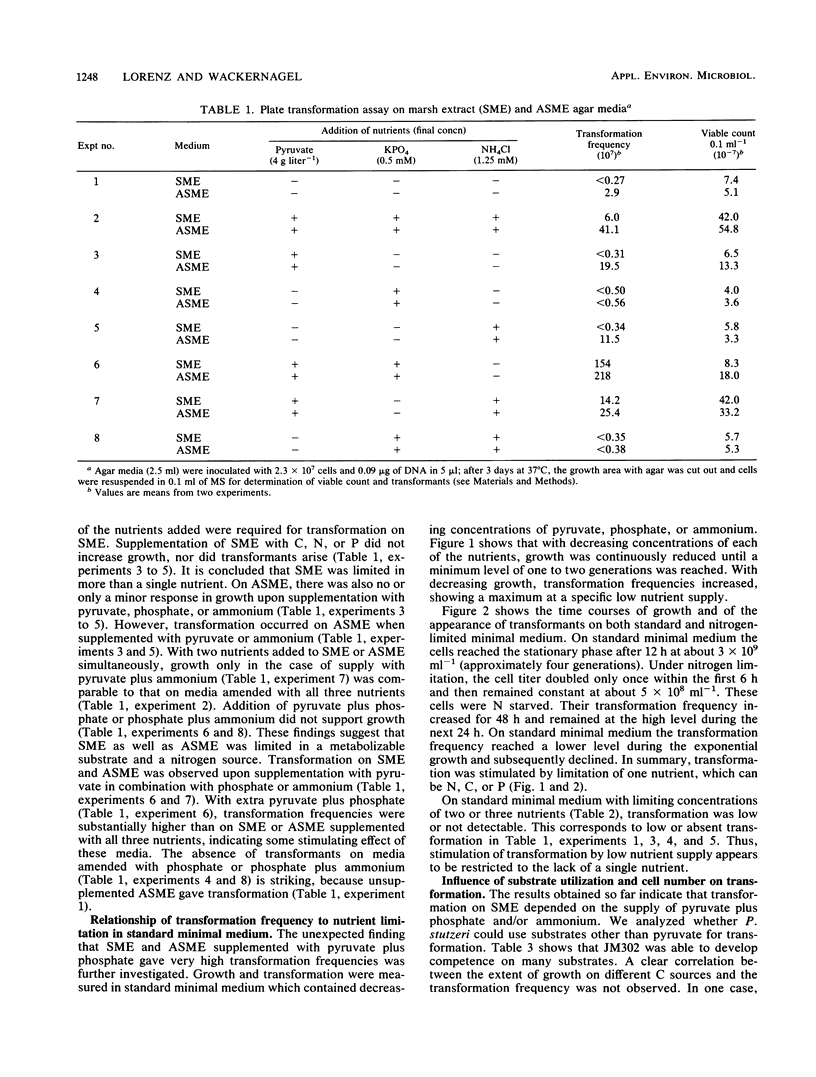
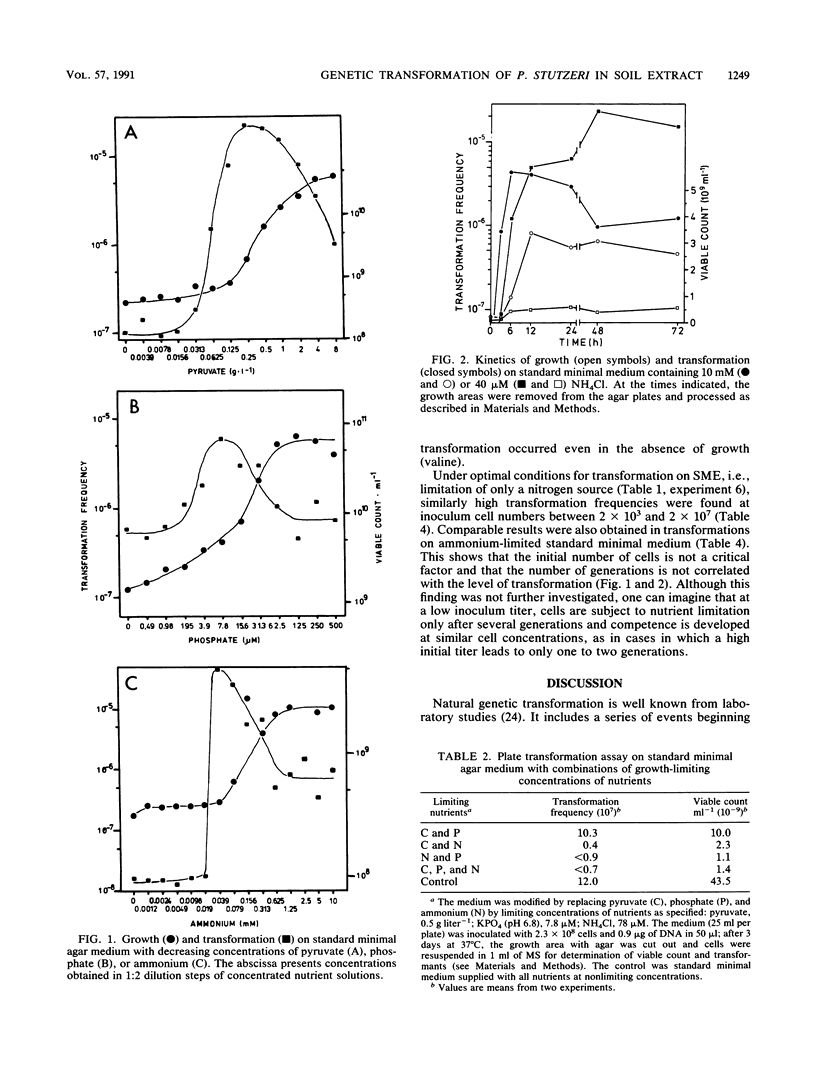
Agar medium (SME) prepared from aqueous soil extract was used to examine genetic transformation of Pseudomonas stutzeri JM302 (his-1) by homologous his+ DNA in a plate transformation assay. Growth studies indicated that SME was strongly limited in carbon and nitrogen sources. Transformation was observed on SME supplemented with pyruvate, phosphate, and ammonium. A 25-fold increase of the transformation frequency was obtained with nitrogen limitation when SME was supplemented with only pyruvate plus phosphate. Similar results were obtained with artificial soil extract medium prepared on the basis of the chemical analysis of the soil extract. On a standard minimal medium, transformation frequencies also increased (10- to 60-fold) when ammonium, phosphate, or pyruvate was growth limiting. Limitation of two or three nutrients did not stimulate transformation. The size of the inoculum (2 × 103 to 2 × 107 cells) was irrelevant to the enhanced transformation under nitrogen limitation on SME or standard minimal medium. We further show that P. stutzeri can use a variety of carbon and energy sources for competence development. It is concluded that genetic transformation of P. stutzeri is possible in the chemical environment of soil upon supply of nutrients and may be strongly stimulated by a growth-limiting concentration of single nutrients including sources of C, N, or P.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aardema B. W., Lorenz M. G., Krumbein W. E. Protection of sediment-adsorbed transforming DNA against enzymatic inactivation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):417–420. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.417-420.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATLIN B. W. Extracellular deoxyribonucleic acid of bacteria and a deoxyribonuclease inhibitor. Science. 1956 Sep 7;124(3219):441–442. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3219.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. A., Pierson L. S., Rosen J. J., Ingraham J. L. Pseudomonas stutzeri and related species undergo natural transformation. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):93–99. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.93-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb W. D., Streips U. N., Doyle R. J. Selective enrichment for genetic markers in DNA released by competent cultures of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Oct 20;155(2):179–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00393157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. B., Istock C. A. Genetic exchange in Bacillus subtilis in soil. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):287–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00267620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni E., Heym G. A. Transformation assay for identification of psychrotrophic achromobacters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Dec;40(6):1106–1114. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.6.1106-1114.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz M. G., Aardema B. W., Wackernagel W. Highly efficient genetic transformation of Bacillus subtilis attached to sand grains. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jan;134(1):107–112. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz M. G., Wackernagel W. Adsorption of DNA to sand and variable degradation rates of adsorbed DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2948–2952. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2948-2952.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz M. G., Wackernagel W. Natural genetic transformation of Pseudomonas stutzeri by sand-adsorbed DNA. Arch Microbiol. 1990;154(4):380–385. doi: 10.1007/BF00276535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page W. J., Sadoff H. L. Physiological factors affecting transformation of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1080–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1080-1087.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page W. J., von Tigerstrom M. Optimal conditions for transformation of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):1058–1061. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.1058-1061.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Cazares L., Thurmond J. Amplification of the rbcL gene from dissolved and particulate DNA from aquatic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1963–1966. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1963-1966.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., David A. W. Production of extracellular nucleic acids by genetically altered bacteria in aquatic-environment microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):1865–1869. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1865-1869.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Specka U., Spreinat A., Antranikian G., Mayer F. Immunocytochemical Identification and Localization of Active and Inactive alpha-Amylase and Pullulanase in Cells of Clostridium thermosulfurogenes EM1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1062–1069. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1062-1069.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J., Carlson C. A. The biology of natural transformation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:211–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J., Sinigalliano C. D. Detection of horizontal gene transfer by natural transformation in native and introduced species of bacteria in marine and synthetic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1818–1824. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1818-1824.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



