Abstract
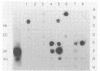
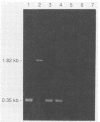
Bioluminescence is a trait observed among approximately 10% of Vibrio cholerae isolates. We have demonstrated that not only do some strains of V. cholerae produce low levels of light, undetectable by the human eye, but the luciferase gene sequence is present in strains of V. cholerae which emit no detectable light, evidenced by hybridization with a luciferase DNA probe. Comparisons of the amino acid sequences of luciferase enzymes of marine species have shown that these proteins have diverged to the point where they have only short regions of amino acid identity. The polymerase chain reaction method of DNA amplification with oligonucleotide primers based on these regions was used to isolate a region of the luxA gene from both luminescent and nonluminescent V. cholerae strains. The nucleotide sequence of this region was determined and reveals that nonluminescent V. cholerae have 99.7% nucleotide sequence similarity in this region with the luminescent biovar V. cholerae bv. albensis as well as significant similarity to other species of bioluminescent bacteria, a finding that is in accord with the hypothesis that these species have a common luminescent ancestor, most probably from the marine environment.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. O., Berends T., Bunch T. A., Holzman T. F., Rausch S. K., Shamansky L., Treat M. L., Ziegler M. M. Cloning of the luciferase structural genes from Vibrio harveyi and expression of bioluminescence in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3663–3667. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. O., Devine J. H., Heckel R. C., Lin J. W., Shadel G. S. The complete nucleotide sequence of the lux regulon of Vibrio fischeri and the luxABN region of Photobacterium leiognathi and the mechanism of control of bacterial bioluminescence. J Biolumin Chemilumin. 1989 Jul;4(1):326–341. doi: 10.1002/bio.1170040145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L. Biology of the marine enterobacteria: genera Beneckea and Photobacterium. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:39–61. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Woolkalis M. J., Bang S. S. Evolutionary relationships in vibrio and Photobacterium: a basis for a natural classification. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:369–398. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becvar J. E., Hastings J. W. Bacterial luciferase requires one reduced flavin for light emission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3374–3376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas R., Mileham A., Cohn D., Hilman M., Simon M., Silverman M. Bacterial bioluminescence: isolation and expression of the luciferase genes from Vibrio harveyi. Science. 1982 Nov 19;218(4574):791–793. doi: 10.1126/science.10636771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Functional identification of the fatty acid reductase components encoded in the luminescence operon of Vibrio fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1186–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1186-1190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M., Miyamoto C., Wall L., Graham A., Meighen E. Lux C, D and E genes of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence operon code for the reductase, transferase, and synthetase enzymes involved in aldehyde biosynthesis. Photochem Photobiol. 1989 May;49(5):681–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1989.tb08441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citarella R. V., Colwell R. R. Polyphasic taxonomy of the genus Vibrio: polynucleotide sequence relationships among selected Vibrio species. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):434–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.434-442.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. H., Mileham A. J., Simon M. I., Nealson K. H., Rausch S. K., Bonam D., Baldwin T. O. Nucleotide sequence of the luxA gene of Vibrio harveyi and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit of bacterial luciferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6139–6146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colepicolo P., Cho K. W., Poinar G. O., Hastings J. W. Growth and luminescence of the bacterium Xenorhabdus luminescens from a human wound. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2601–2606. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2601-2606.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R. Polyphasic taxonomy of the genus vibrio: numerical taxonomy of Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and related Vibrio species. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):410–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.410-433.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R., Seidler R. J., Kaper J., Joseph S. W., Garges S., Lockman H., Maneval D., Bradford H., Roberts N., Remmers E. Occurrence of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 in Maryland and Louisiana estuaries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):555–558. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.555-558.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn D. K., Michaliszyn G. A., Bogacki I. G., Meighen E. A. Conversion of aldehyde to acid in the bacterial bioluminescent reaction. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4911–4918. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard A. Inhibition and activation of bacterial luciferase synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1101–1105. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1101-1105.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Nealson K., Silverman M. Bacterial bioluminescence: isolation and genetic analysis of functions from Vibrio fischeri. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foran D. R., Brown W. M. Nucleotide sequence of the LuxA and LuxB genes of the bioluminescent marine bacterium Vibrio fischeri. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):777–777. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASTINGS J. W., GIBSON Q. H. Intermediates in the bioluminescent oxidation of reduced flavin mononucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jul;238:2537–2554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings J. W., Balny C. The oxygenated bacterial luciferase-flavin intermediate. Reaction products via the light and dark pathways. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7288–7293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings J. W., Nealson K. H. Bacterial bioluminescence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:549–595. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E., Rodrick G. E. Isolation of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 from the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):559–560. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.559-560.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illarionov B. A., Blinov V. M., Donchenko A. P., Protopopova M. V., Karginov V. A., Mertvetsov N. P., Gitelson J. I. Isolation of bioluminescent functions from Photobacterium leiognathi: analysis of luxA, luxB, luxG and neighboring genes. Gene. 1990 Jan 31;86(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90117-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illarionov B. A., Protopopova M. V., Karginov V. A., Mertvetsov N. P., Gitelson J. I. Nucleotide sequence of part of Photobacterium leiognathi lux region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9855–9855. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas R. An improved colony hybridization method with significantly increased sensitivity for detection of single genes. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):296–298. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonell M. T., Swartz D. G., Ortiz-Conde B. A., Last G. A., Colwell R. R. Ribosomal RNA phylogenies for the vibrio-enteric group of eubacteria. Microbiol Sci. 1986 Jun;3(6):172-5, 178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini J. A., Boylan M., Soly R. R., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Cloning and expression of the Photobacterium phosphoreum luminescence system demonstrates a unique lux gene organization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14308–14314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M., Showalter R., Silverman M. Identification of a locus controlling expression of luminescence genes in Vibrio harveyi. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2406–2414. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2406-2414.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A., Hastings J. W. Binding site determination from kinetic data. Reduced flavin mononucleotide binding to bacterial luciferase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7666–7674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Hastings J. W. Bacterial bioluminescence: its control and ecological significance. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):496–518. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.496-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Hastings J. W. The inhibition of bacterial luciferase by mixed function oxidase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):888–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt J. L., Baumann P., Baumann L. Study of genetic relationships among marine species of the genera Beneckea and Photobacterium by means of in vitro DNA/DNA hybridization. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Oct 11;110(1):101–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00416975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter R. E., Martin M. O., Silverman M. R. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of luxR, a regulatory gene controlling bioluminescence in Vibrio harveyi. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2946–2954. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2946-2954.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton F. L., Attwell R. W., Jangi M. S., Colwell R. R. Influence of salinity and organic nutrient concentration on survival and growth of Vibrio cholerae in aquatic microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1080–1085. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1080-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzman E., Miyamoto C., Graham A., Meighen E. Delineation of the transcriptional boundaries of the lux operon of Vibrio harveyi demonstrates the presence of two new lux genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3513–3517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzur S., Hastings J. W. Myristic acid stimulation of bacterial bioluminescence in "aldehyde" mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):266–269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West P. A., Lee J. V. Ecology of Vibrio species, including Vibrio cholerae, in natural waters in Kent, England. J Appl Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;52(3):435–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1982.tb05074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]