Abstract
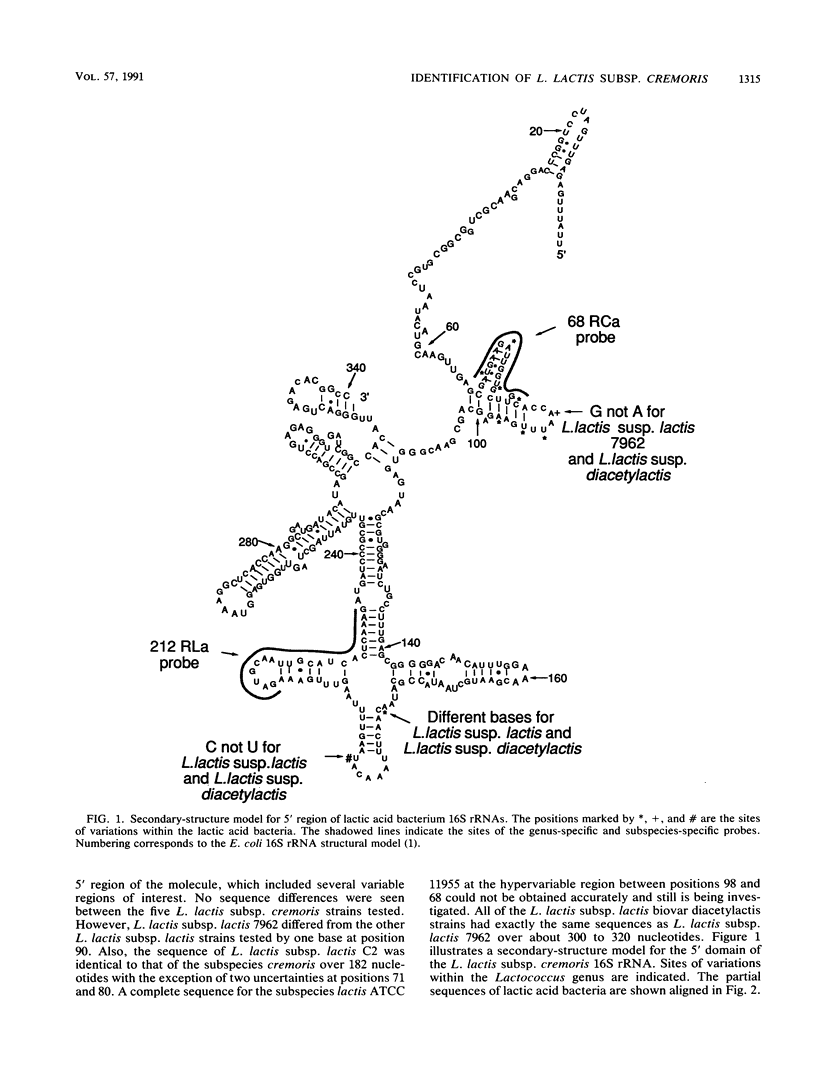
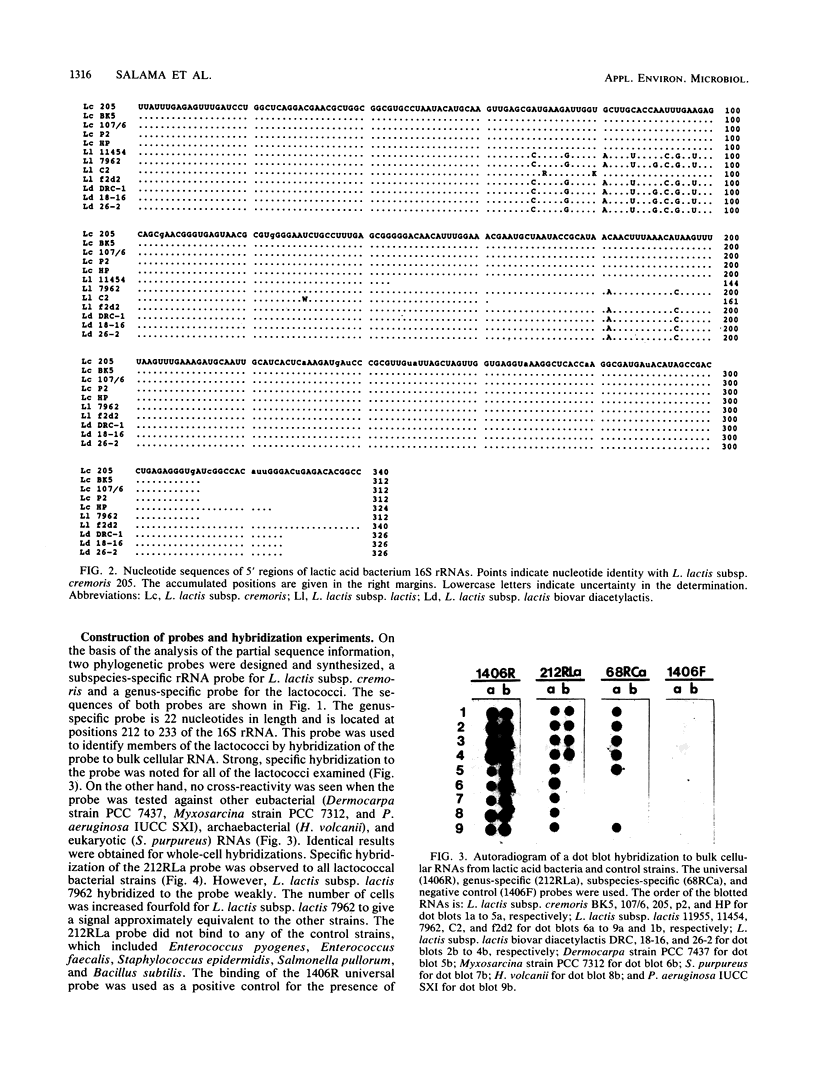
Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris is of considerable interest to the dairy industry, which relies upon the few available strains for the manufacture of cheddar cheese free of fermented and fruity flavors. The subspecies cremoris differs from related subspecies by the lack of a few phenotypic traits. Our purpose was to identify unique rRNA sequences that could be used to discriminate L. lactis subsp. cremoris from related subspecies. The 16S rRNAs from 13 Lactococcus strains were partially sequenced by using reverse transcriptase to identify domains unique to L. lactis subsp. cremoris. All five strains of the subspecies cremoris had a unique base sequence in a hypervariable region located 70 to 100 bases from the 5' terminus. In this region, all L. lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis strains examined had a sequence identical to that of L. lactis subsp. lactis 7962, which was different from other strains of the subspecies lactis by only one nucleotide at position 90 (Escherichia coli 16S rRNA structural model) (J. Brosius, J. L. Palmer, J. P. Kennedy, and H. F. Noller, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75:4801-4805, 1978). Oligonucleotide probes specific for the genus Lactococcus (212RLa) and for the subspecies cremoris (68RCa) were synthesized and evaluated by hybridization to known rRNAs as well as fixed whole cells. Efficient and specific hybridization to the genus-specific probe was observed for the 13 Lactococcus strains tested. No hybridization was seen with the control species. All five strains of the subspecies cremoris hybridized to the subspecies-specific probe.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. D., Ash C., Farrow J. A., Wallbanks S., Williams A. M. 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid sequence analyses of lactococci and related taxa. Description of Vagococcus fluvialis gen. nov., sp. nov. J Appl Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;67(4):453–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1989.tb02516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., DeLong E. F., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic group-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for identification of single microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.720-726.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Turner S., Olsen G. J., Barns S., Lane D. J., Pace N. R. Evolutionary relationships among cyanobacteria and green chloroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3584–3592. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3584-3592.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Dommarsnes K., Skurnik M., Hornes E. A synthetic oligonucleotide probe and a cloned polynucleotide probe based on the yopA gene for detection and enumeration of virulent Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):17–23. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.17-23.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Field K. G., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Reverse transcriptase sequencing of ribosomal RNA for phylogenetic analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1988;167:138–144. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)67015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A. Microbial ecology and evolution: a ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:337–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehnstam A. S., Norqvist A., Wolf-Watz H., Hagström A. Identification of Vibrio anguillarum in fish by using partial 16S rRNA sequences and a specific 16S rRNA oligonucleotide probe. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):1907–1910. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1907-1910.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgaramella V., Khorana H. G. CXII. Total synthesis of the structural gene for an alanine transfer RNA from yeast. Enzymic joining of the chemically synthesized polydeoxynucleotides to form the DNA duplex representing nucleotide sequence 1 to 20. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 28;72(2):427–444. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackebrandt E., Teuber M. Molecular taxonomy and phylogenetic position of lactic acid bacteria. Biochimie. 1988 Mar;70(3):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]