Abstract
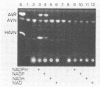
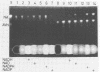
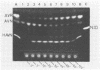
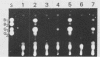
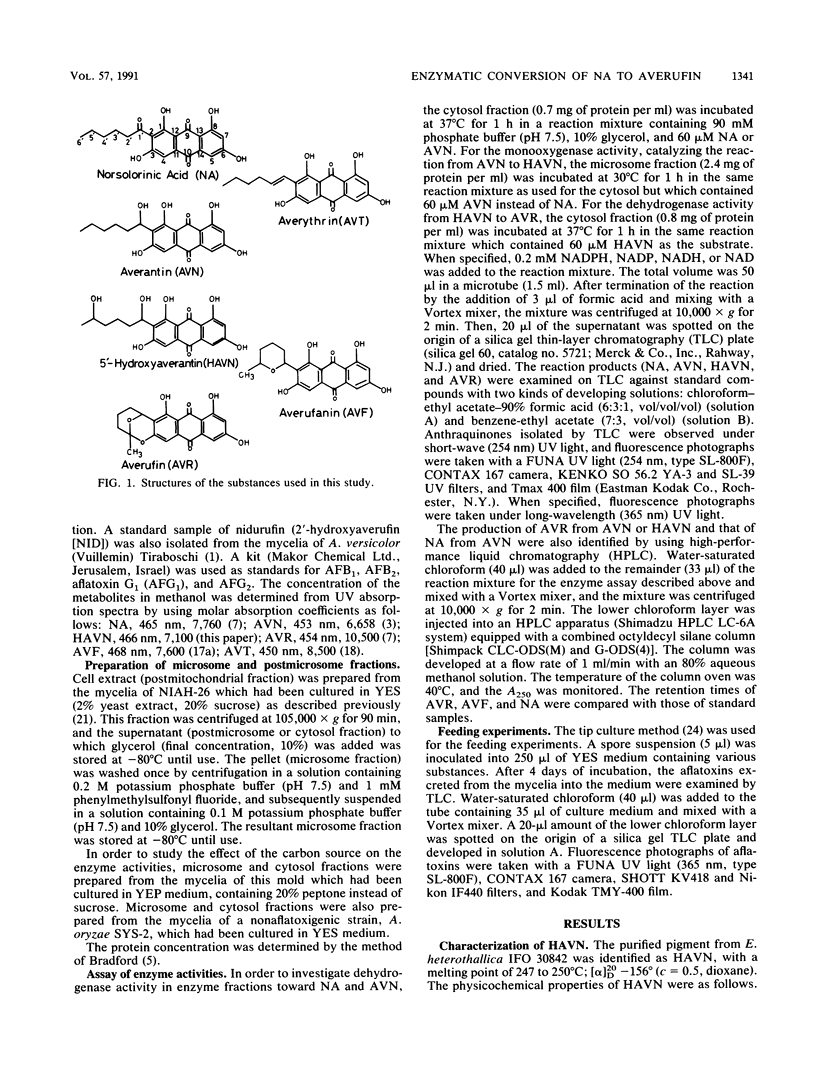
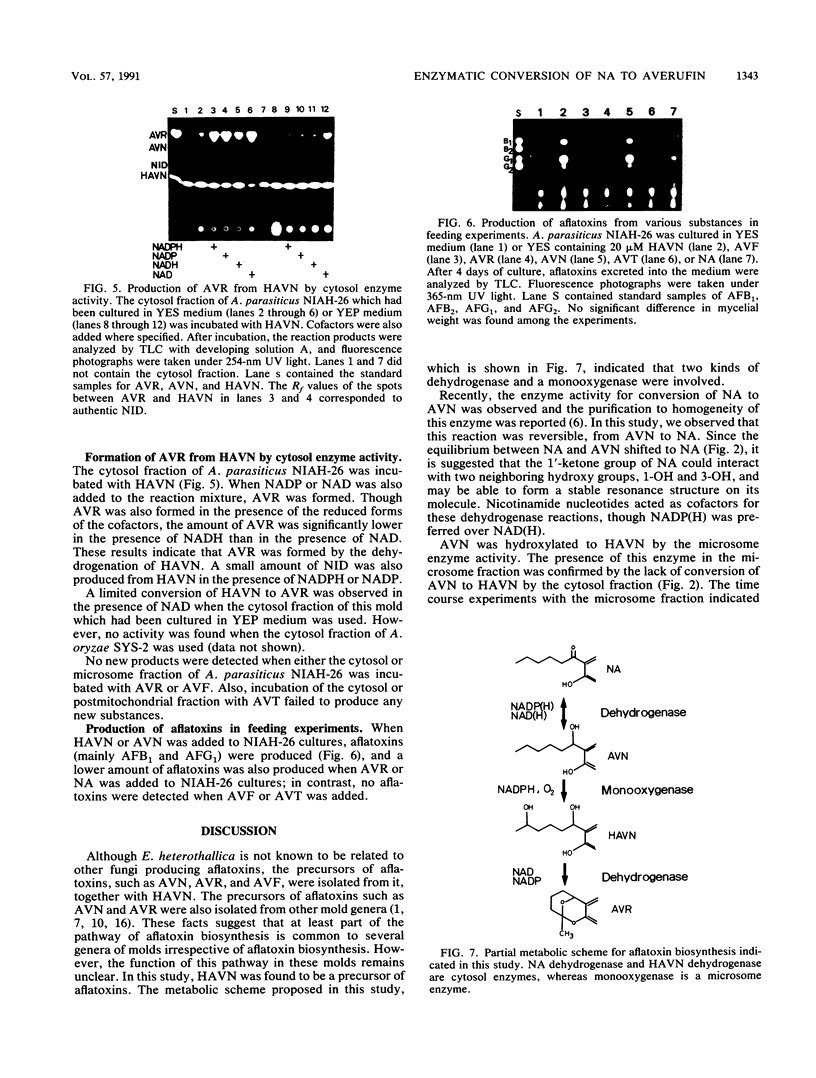
5'-Hydroxyaverantin (HAVN) was isolated from a mold, Emericella heterothallica IFO 30842. Aspergillus parasiticus NIAH-26, a UV-irradiated mutant of A. parasiticus SYS-4, produced neither aflatoxins nor precursors in yeast extract-sucrose (YES) medium. When the postmicrosome (cytosol) fraction of NIAH-26, which had been prepared from the culture in YES medium, was incubated with norsolorinic acid (NA) in the presence of NADH or NADPH, averantin (AVN) was produced. The reverse reaction from AVN to NA was promoted by the addition of NAD or NADP (dehydrogenase reaction). When the microsome fraction of NIAH-26 was incubated with AVN, HAVN was produced in the presence of NADPH (monooxygenase reaction). HAVN was, furthermore, oxidized to averufin (AVR) by the cytosol fraction of NIAH-26 in the presence of NAD or NADP (dehydrogenase reaction). In the feeding experiments with A. parasiticus NIAH-26, aflatoxins were produced from AVN, HAVN, NA, and AVR but not from averufanin or averythrin. These results indicate that the reaction sequence NA in equilibrium AVN----HAVN----AVR is involved in the biosynthetic pathway of aflatoxins. The enzyme activities described here were dependent on the culture medium, and no enzyme activities were observed in the nonaflatoxigenic strain A. oryzae SYS-2 (IFO 4251).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. W., Christensen S. B. New perspectives on aflatoxin biosynthesis. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1983;29:53–92. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. W., Lee L. S., Shoss S. M., Boudreaux G. H. Identification of averantin as an aflatoxin B1 precursor: placement in the biosynthetic pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):835–839. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.835-839.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkinshaw J. H., Roberts J. C., Roffey P. Studies in mycological chemistry. XIX. "Product B" (averantin) [1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxy-2-(1-hydroxyhexyl)anthraquinone], a pigment from Aspergillus versicolor (Vuillemin) Tiraboschi. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1966;9:855–857. doi: 10.1039/j39660000855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuturgoon A. A., Dutton M. F., Berry R. K. The preparation of an enzyme associated with aflatoxin biosynthesis by affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):38–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91908-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donkersloot J. A., Mateles R. I., Yang S. S. Isolation of averufin from a mutant of Aspergillus parasiticus impaired in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 9;47(5):1051–1055. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90939-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton M. F. Enzymes and aflatoxin biosynthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):274–295. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.274-295.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Lin M. T., Yao R. C., Singh R. Biosynthesis of aflatoxin. Conversion of norsolorinic acid and other hypothetical intermediates into aflatoxin B1. J Agric Food Chem. 1976 Nov-Dec;24(6):1170–1174. doi: 10.1021/jf60208a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L., Bennett J. W., Goldblatt L. A., Lundin R. E. Norsolorinic acid from a mutant strain of Aspergillus parasiticus. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1971 Feb;48(2):93–94. doi: 10.1007/BF02635696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. T., Hsieh D. P., Yao R. C., Donkersloot J. A. Conversion of averufin into aflatoxins by Aspergillus parasiticus. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5167–5171. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick S. P., Bhatnagar D., Lee L. S. Averufanin is an aflatoxin B1 precursor between averantin and averufin in the biosynthetic pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):14–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.14-16.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS J. C., ROFFEY P. STUDIES IN MYCOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY. XVII. AVERYTHRIN, AN ANTHRAQUINONOID PIGMENT FROM ASPERGILLUS VERSICOLOR (VUILLEMIN) TIRABOSCHI. J Chem Soc. 1965 Jun;33:3666–3672. doi: 10.1039/jr9650003666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Hamasaki T. Biosynthetic relationship among aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, and G2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):2101–2106. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.2101-2106.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Hashimoto J., Hamasaki T. Two distinct O-methyltransferases in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2172–2177. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2172-2177.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Ito M., Terakado N. Simple method for screening aflatoxin-producing molds by UV photography. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):230–234. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.230-234.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Nakamura H., Ando Y., Terakado N., Nakajima H., Hamasaki T. Isolation and characterization of Aspergillus parasiticus mutants with impaired aflatoxin production by a novel tip culture method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):2096–2100. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.2096-2100.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]