Abstract
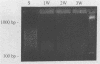
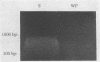
In order to develop a rapid and specific detection test for bacteria in soil, we improved a method based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Each step of the protocol, including direct lysis of cells, DNA purification, and PCR amplification, was optimized. To increase the efficiency of lysis, a step particularly critical for some microorganisms which resist classical techniques, we used small soil samples (100 mg) and various lytic treatments, including sonication, microwave heating, and thermal shocks. Purification of nucleic acids was achieved by passage through up to three Elutip d columns. Finally, PCR amplifications were optimized via biphasic protocols using booster conditions, lower denaturation temperatures, and addition of formamide. Two microorganisms were used as models: Agrobacterium tumefaciens, which is naturally absent from the soil used and was inoculated to calibrate the validity of the protocol, and Frankia spp., an actinomycete indigenous to the soil used. Specific primers were characterized either in the plasmid-borne vir genes for A. tumefaciens or in the variable regions of the 16S ribosomal gene for Frankia spp. Specific detection of the inoculated A. tumefaciens strain was routinely obtained when inocula ranged from 10(7) to 10(3) cells. Moreover, the strong correlation we observed between the size of the inocula and the results of the PCR reactions permitted assessment of the validity of the protocol in enumerating the number of microbial cells present in a soil sample. This allowed us to estimate the indigenous population of Frankia spp. at 0.2 x 10(5) genomes (i.e., amplifiable target sequences) per g of soil.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aardema B. W., Lorenz M. G., Krumbein W. E. Protection of sediment-adsorbed transforming DNA against enzymatic inactivation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):417–420. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.417-420.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bej A. K., Steffan R. J., DiCesare J., Haff L., Atlas R. M. Detection of coliform bacteria in water by polymerase chain reaction and gene probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):307–314. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.307-314.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollet C., Gevaudan M. J., de Lamballerie X., Zandotti C., de Micco P. A simple method for the isolation of chromosomal DNA from gram positive or acid-fast bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1955–1955. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouzar H., Moore L. W. Isolation of different agrobacterium biovars from a natural oak savanna and tallgrass prairie. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):717–721. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.717-721.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. French Mathematicians Push the Panic Button: A lack of university teaching posts is fueling a new brain drain to the United States which, some claim, threatens to erode one of the country's most prized intellectual achievements. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):251–252. doi: 10.1126/science.239.4837.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartskeerl R. A., de Wit M. Y., Klatser P. R. Polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Mycobacterium leprae. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Sep;135(9):2357–2364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-9-2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Kieser T., Wright H. M., Bibb M. J. Plasmids, recombination and chromosome mapping in Streptomyces lividans 66. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2257–2269. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz M. G., Wackernagel W. Adsorption of DNA to sand and variable degradation rates of adsorbed DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2948–2952. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2948-2952.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa T., Yamaguchi M. Fractionation and Estimation of Particle-Attached and Unattached Bradyrhizobium japonicum Strains in Soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):911–914. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.911-914.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruano G., Fenton W., Kidd K. K. Biphasic amplification of very dilute DNA samples via 'booster' PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5407–5407. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Kapelner S., Sommer S. S. Formamide can dramatically improve the specificity of PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7465–7465. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selenska S., Klingmüller W. DNA recovery and direct detection of Tn5 sequences from soil. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1991 Jul;13(1):21–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1991.tb00559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet P., Grosjean M. C., Misra A. K., Nazaret S., Cournoyer B., Normand P. Frankia genus-specific characterization by polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3278–3286. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3278-3286.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffan R. J., Atlas R. M. DNA amplification to enhance detection of genetically engineered bacteria in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Sep;54(9):2185–2191. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.9.2185-2191.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffan R. J., Goksøyr J., Bej A. K., Atlas R. M. Recovery of DNA from soils and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2908–2915. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2908-2915.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. J., King R. K., Burchak J., Gannon V. P. Sensitive and specific detection of Listeria monocytogenes in milk and ground beef with the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2576–2580. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2576-2580.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torsvik V., Goksøyr J., Daae F. L. High diversity in DNA of soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Mar;56(3):782–787. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.3.782-787.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. L., Olson B. H. Rapid method for direct extraction of DNA from soil and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1070-1074.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Weller R., Bateson M. M. 16S rRNA sequences reveal numerous uncultured microorganisms in a natural community. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):63–65. doi: 10.1038/345063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyant R. S., Edmonds P., Swaminathan B. Effect of ionic and nonionic detergents on the Taq polymerase. Biotechniques. 1990 Sep;9(3):308–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap E. P., McGee J. O. Short PCR product yields improved by lower denaturation temperatures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1713–1713. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]