Abstract
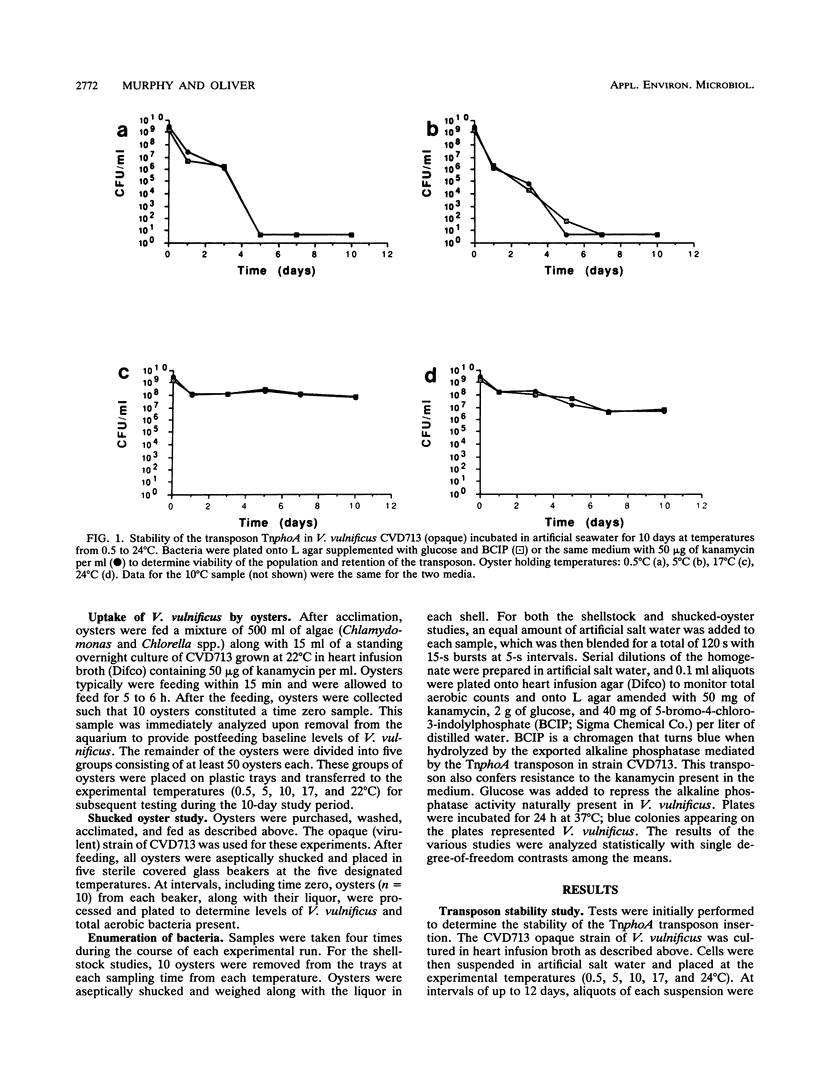
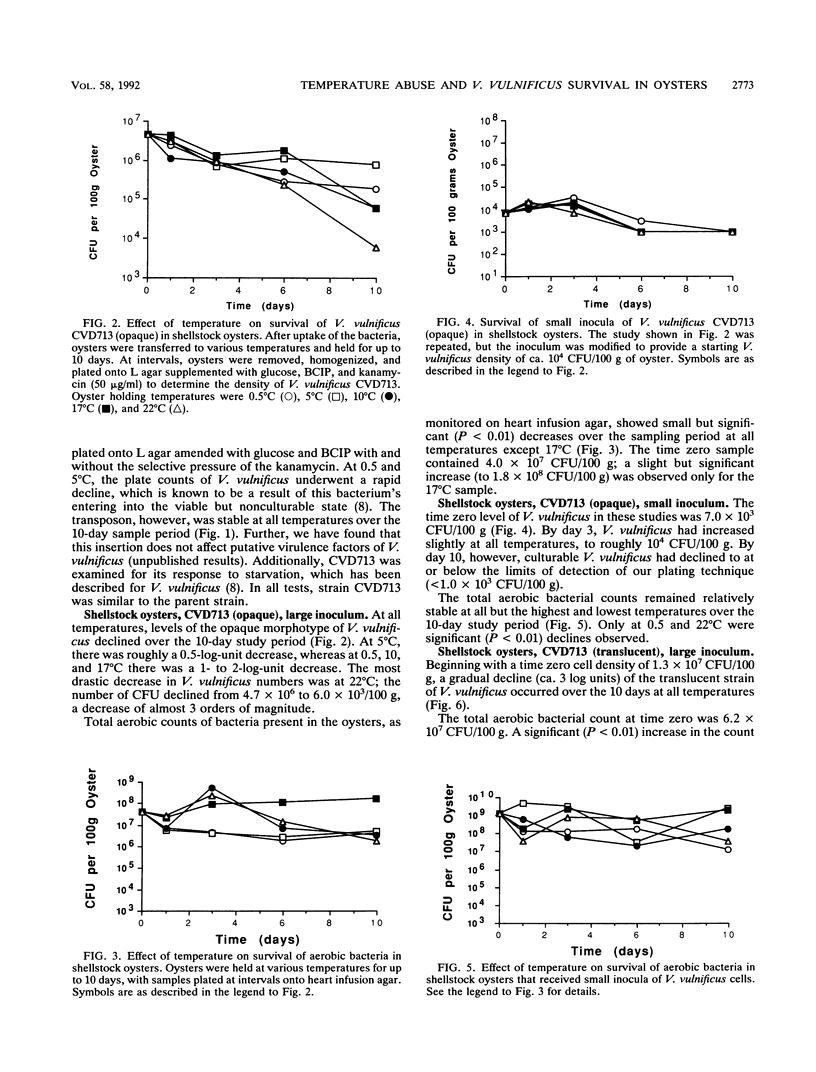
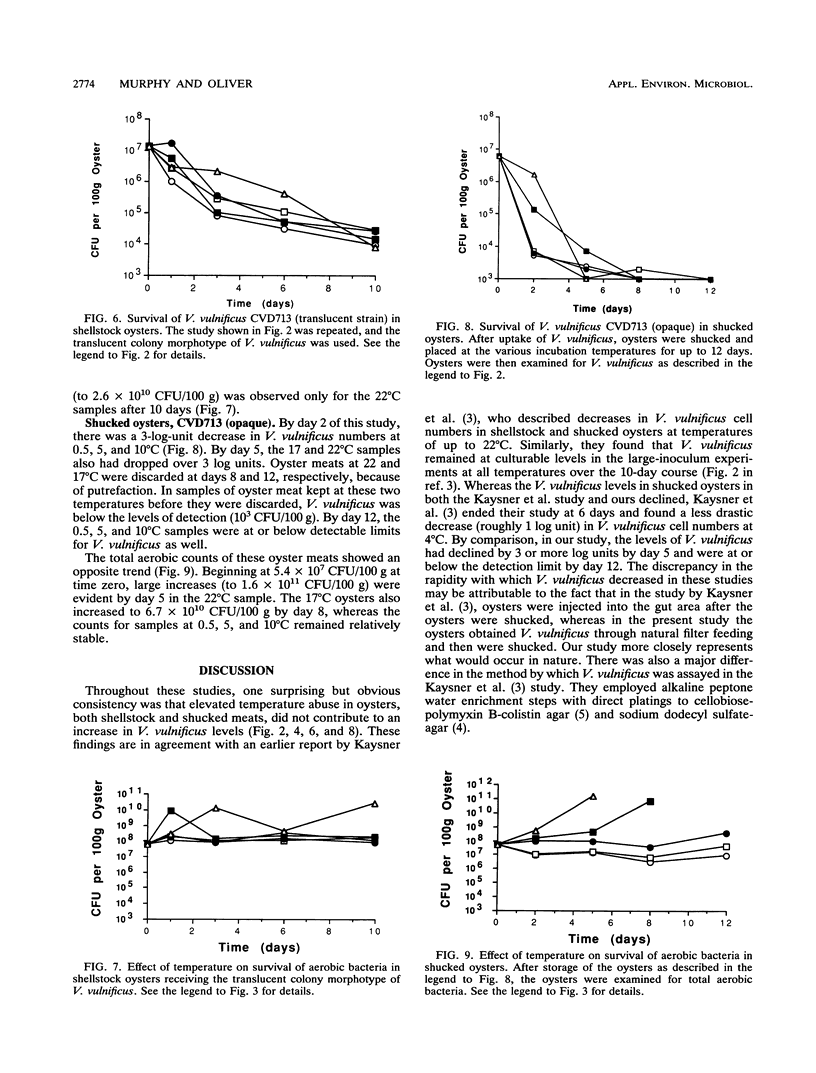
Opaque and translucent morphotypes of a TnphoA-containing strain of Vibrio vulnificus were fed to oysters, which were subsequently stored at temperatures ranging from 0.5 to 22 degrees C for 10 days. Samples of oysters were homogenized and plated at intervals to determine the cell density of V. vulnificus and total aerobic population of bacteria present. At all temperatures, the numbers of V. vulnificus (both morphotypes) declined over the 10-day study period. The same observation was made with a lower inoculum of V. vulnificus. Identical experiments with shucked oysters showed a more rapid decrease in V. vulnificus. Identical experiments with shucked oysters showed a more rapid decrease in V. vulnificus to levels below limits of detection. Little change in the total bacterial counts was observed in shellstock oysters at any of the test temperatures, whereas incubation at the higher temperatures (17 and 22 degrees C) resulted in large increases in total counts in shucked oysters. These data suggest that temperature abuse of oysters may not be a factor in increasing the public health risk of V. vulnificus through raw oyster consumption. However, the data also suggest that even with proper storage, indigenous levels of V. vulnificus may remain sufficiently higher in shellstock oysters to produce infection in compromised hosts.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E., Rodrick G. E., Blake N. J. Effects of storage on microbial loads of two commercially important shellfish species, Crassostrea virginica and Mercenaria campechiensis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1221–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1221-1228.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaysner C. A., Tamplin M. L., Wekell M. M., Stott R. F., Colburn K. G. Survival of Vibrio vulnificus in shellstock and shucked oysters (Crassostrea gigas and Crassostrea virginica) and effects of isolation medium on recovery. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3072–3079. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3072-3079.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massad G., Oliver J. D. New selective and differential medium for Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio vulnificus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2262–2264. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2262-2264.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. D., Guthrie K., Preyer J., Wright A., Simpson L. M., Siebeling R., Morris J. G., Jr Use of colistin-polymyxin B-cellobiose agar for isolation of Vibrio vulnificus from the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):737–739. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.737-739.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. D., Nilsson L., Kjelleberg S. Formation of nonculturable Vibrio vulnificus cells and its relationship to the starvation state. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2640–2644. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2640-2644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. M., White V. K., Zane S. F., Oliver J. D. Correlation between virulence and colony morphology in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):269–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.269-272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. C., Simpson L. M., Oliver J. D., Morris J. G., Jr Phenotypic evaluation of acapsular transposon mutants of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1769–1773. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1769-1773.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Ogawa M., Mizuguchi Y. Relation of capsular materials and colony opacity to virulence of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.446-451.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


