Abstract
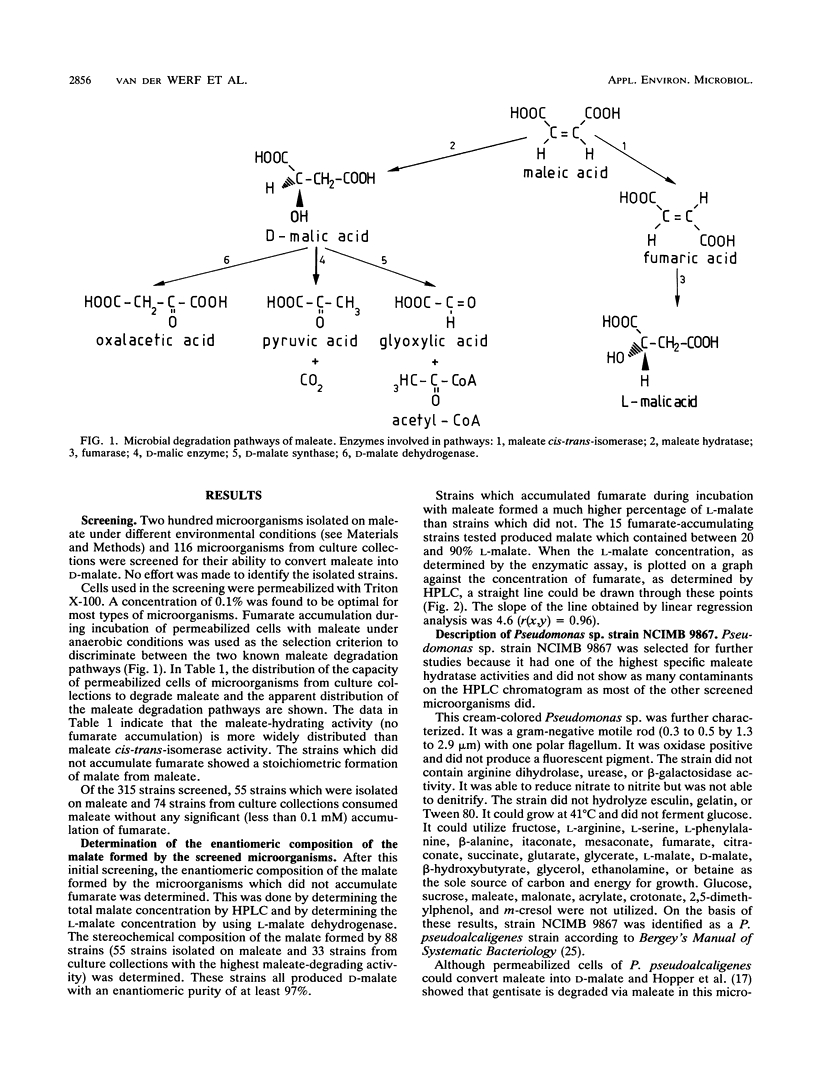
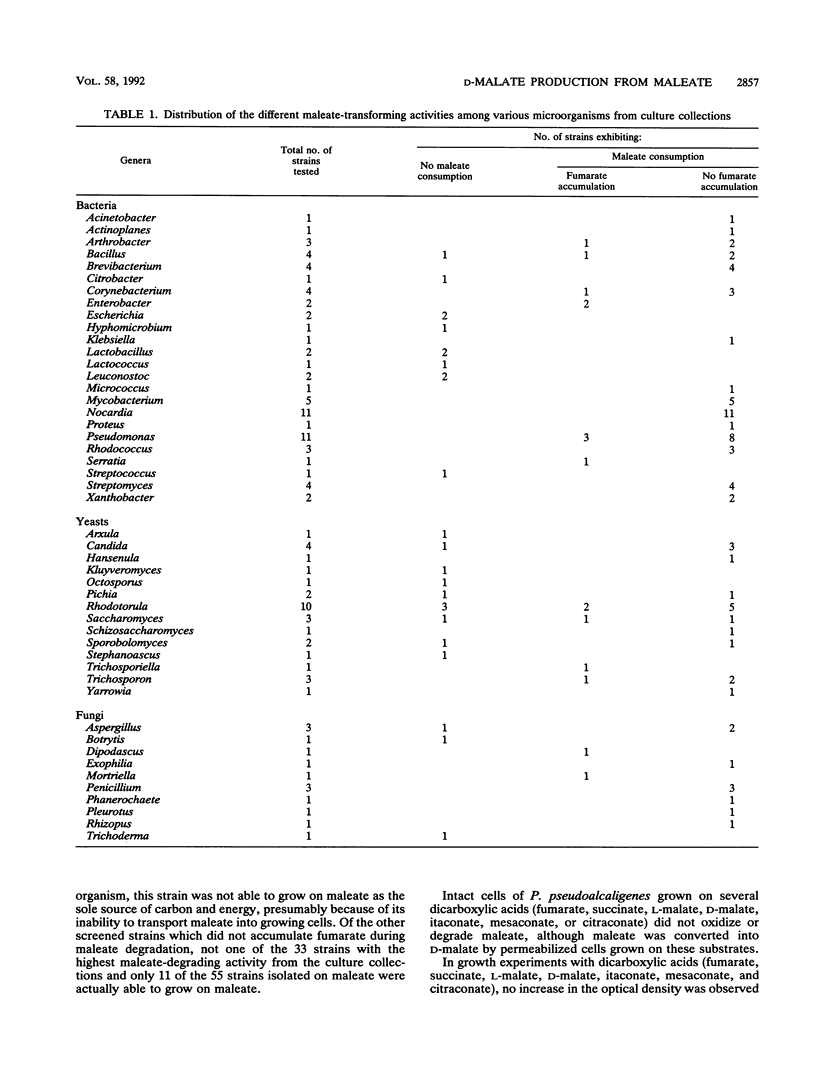
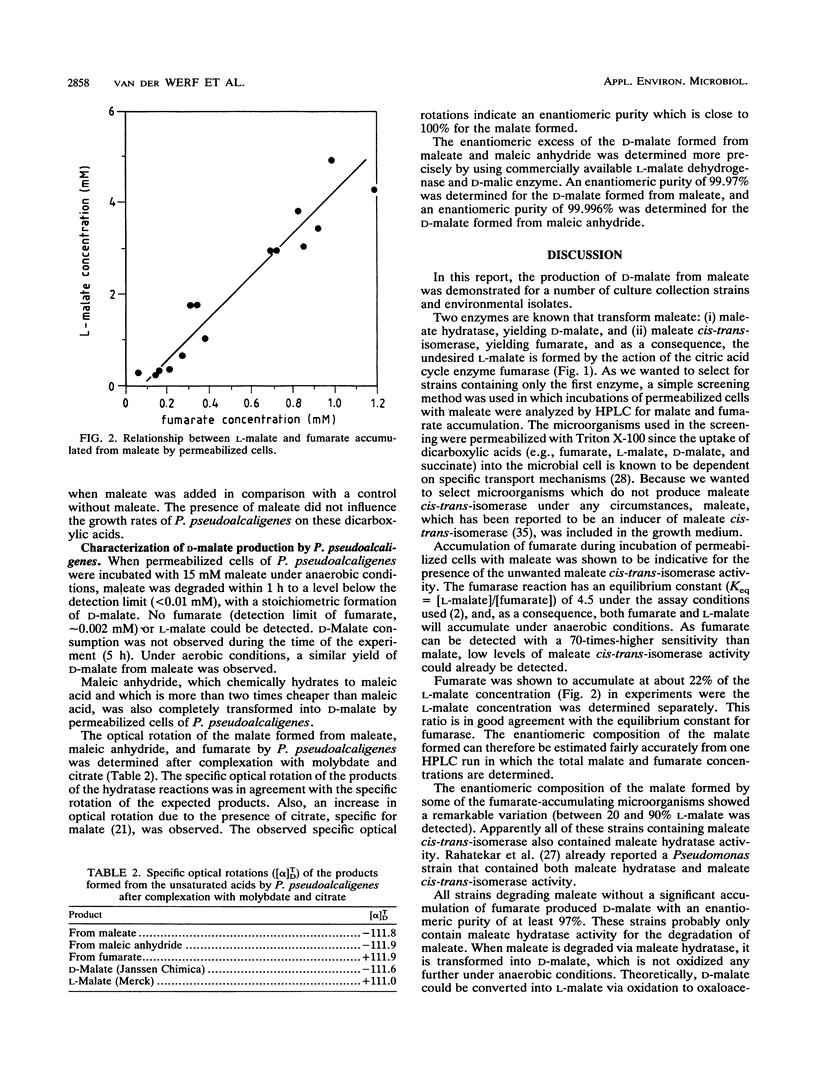
More than 300 microorganisms were screened for their ability to convert maleate into D-malate as a result of the action of maleate hydratase. Accumulation of fumarate during incubation of permeabilized cells with maleate was shown to be indicative of one of the two enzymes known to transform maleate. The ratio in which fumarate and malate accumulated could be used to estimate the enantiomeric composition of the malate formed. Many strains (n = 128) were found to be capable of converting maleate to D-malate with an enantiomeric purity of more than 97%. Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes NCIMB 9867 was selected for more detailed studies. Although this strain was not able to grow on maleate, permeabilized cells were able to degrade maleate to undetectable levels, with a concomitant formation of D-malate. The D-malate was formed with an enantiomeric purity of more than 99.97%.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEHRMAN E. J., STANIER R. Y. The bacterial oxidation of nicotinic acid. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):923–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckel W., Miller S. L. Equilibrium constants of several reactions involved in the fermentation of glutamate. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 4;164(3):565–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMONA T. THE LACTIC DEHYDROGENASES OF YEAST. IV. D-ALPHA-HYDROXY ACID DEHYDROGENASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1457–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain R. B., Houghton C., Wright K. A. Microbial metabolism of the pyridine ring. Metabolism of 2- and 3-hydroxypyridines by the maleamate pathway in Achromobacter sp. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):293–300. doi: 10.1042/bj1400293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L. Degradation of 3-hydroxybenzoate by bacteria of the genus Bacillus. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):439–444. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.439-444.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dervartanian D. V., Veeger C. Studies on succinate dehydrogenase. II. On the nature of the reaction of competitive inhibitors and substrates with succinate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 20;105(3):424–436. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer J. L. Isolation and biochemical characterization of maleic-acid hydratase, an iron-requiring hydro-lyase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jul 1;150(1):145–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giffhorn F., Kuhn A. Purification and characterization of a bifunctional L-(+)-tartrate dehydrogenase-D-(+)-malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides Y. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.281-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmans S., Smits J. P., van der Werf M. J., Volkering F., de Bont J. A. Metabolism of Styrene Oxide and 2-Phenylethanol in the Styrene-Degrading Xanthobacter Strain 124X. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2850–2855. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2850-2855.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Unemoto T. The presence of D-malate dehydrogenase (D-malate:NAD oxidoreductase) in Serratia marcescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 10;122(2):374–376. doi: 10.1016/0926-6593(66)90082-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Enzymic formation of D-malate. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):798–800. doi: 10.1042/bj1100798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Metabolism of l-Malate and d-Malate by a Species of Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1197–1202. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1197-1202.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakura M., Tokushige M., Katsuki H., Muramatsu S. Studies on regulatory functions of malic enzymes. V. Comparative studies of malic enzymes in bacteria. J Biochem. 1978 May;83(5):1387–1394. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knichel W., Radler F. D-Malic enzyme of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):547–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., Eggleston L. V. The effect of citrate on the rotation of the molybdate complexes of malate, citramalate and isocitrate. Biochem J. 1943 Sep;37(3):334–338. doi: 10.1042/bj0370334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miozzari G. F., Niederberger P., Hütter R. Permeabilization of microorganisms by Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):220–233. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misawa T., Aikawa H., Shigeta S. [Effects of alcohol drinking on mental task performance]. Sangyo Igaku. 1983 Sep;25(5):406–414. doi: 10.1539/joh1959.25.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poh C. L., Bayly R. C. Evidence for isofunctional enzymes used in m-cresol and 2,5-xylenol degradation via the gentisate pathway in Pseudomonas alcaligenes. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):59–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.59-69.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN J. R. Enzymic activation and cleavage of D- and L-malate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 5;69:435–438. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl C. L., Sojka G. A. Growth of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata on L- and D-malic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 28;297(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian S. S., Rao M. R. Purification and properties of citraconase. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2367–2372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUBBS P. K., GREVILLE G. D. The oxidation of D-alpha-hydroxy acids in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81:104–114. doi: 10.1042/bj0810104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


