Abstract
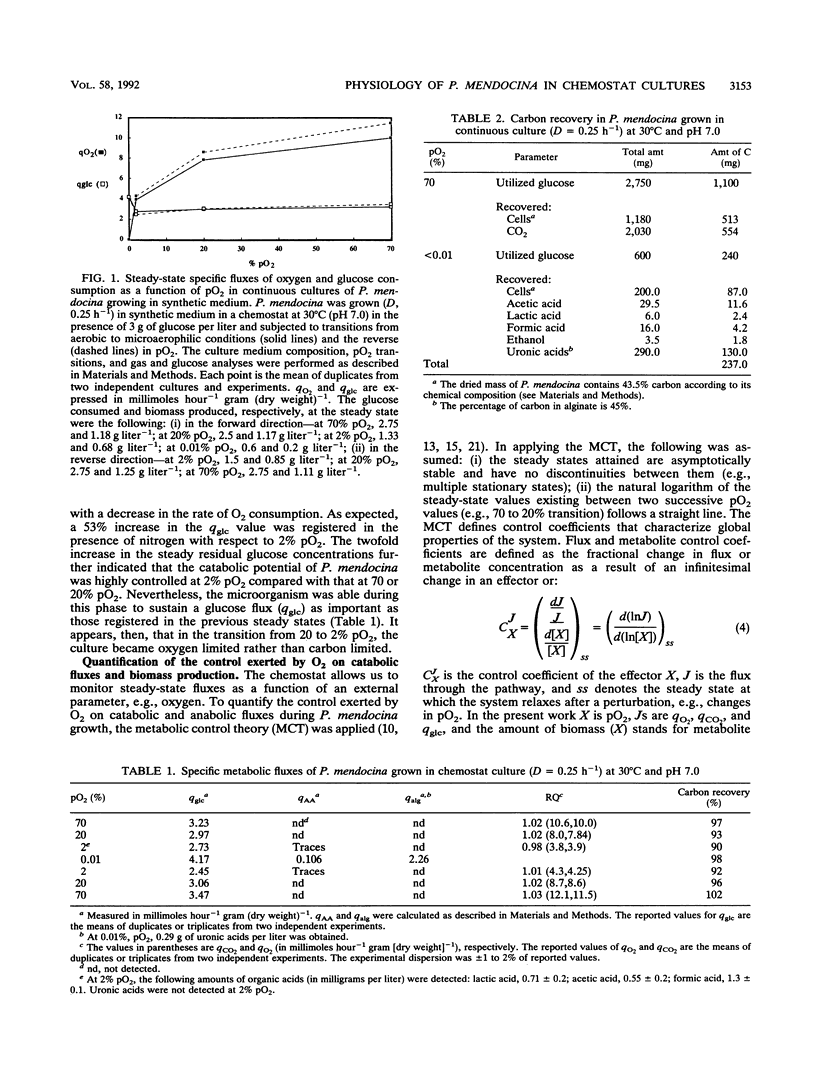
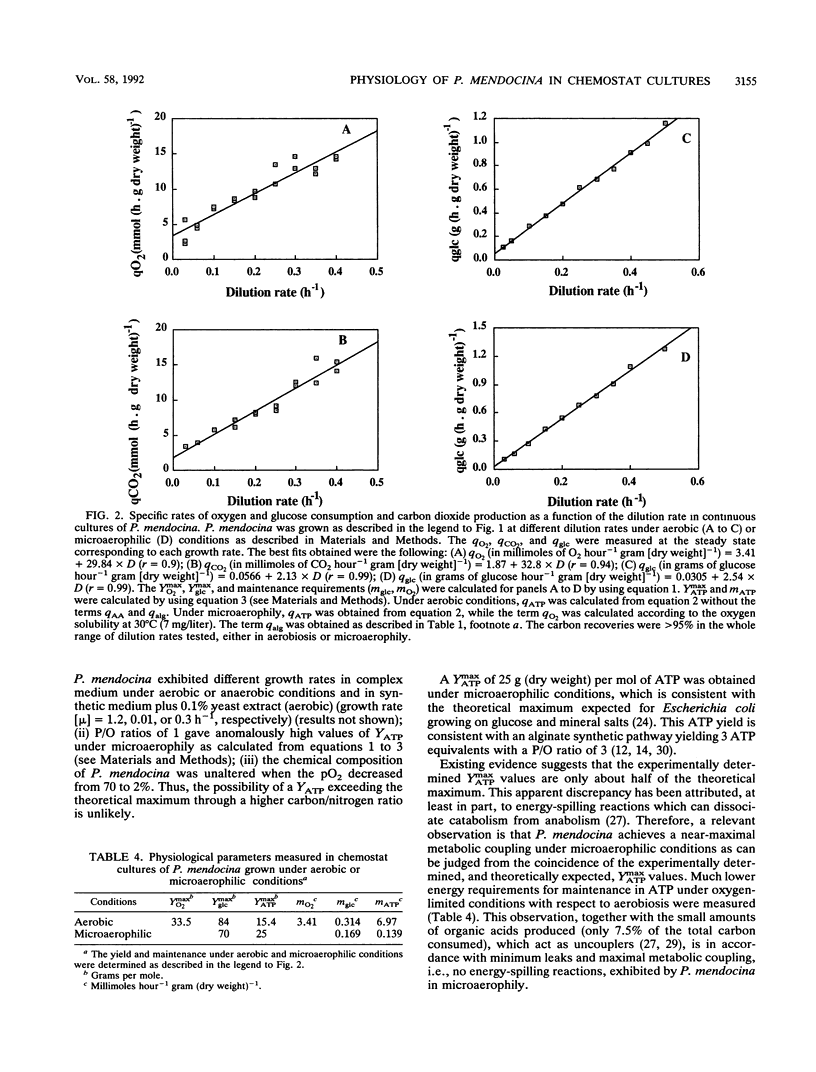
Several metabolic fluxes were analyzed during gradual transitions from aerobic to oxygen-limited conditions in chemostat cultures of Pseudomonas mendocina growing in synthetic medium at a dilution rate of 0.25 h-1. P. mendocina growth was glucose limited at high oxygen partial pressures (70 and 20% pO2) and exhibited an oxidative type of metabolism characterized by respiratory quotient (RQ) values of 1.0. A similar RQ value was obtained at low pO2 (2%), and detectable levels of acetic, formic, and lactic acids were determined in the extracellular medium. RQs of 0.9 +/- 0.12 were found at 70% pO2 for growth rates ranging from 0.025 to 0.5 h-1. At high pO2, the control coefficients of oxygen on catabolic fluxes were 0.19 and 0.22 for O2 uptake and CO2 production, respectively. At low pO2 (2%), the catabolic and anabolic fluxes were highly controlled by oxygen. P. mendocina showed a mixed-type fermentative metabolism when nitrogen was flushed into chemostat cultures. Ethanol and acetic, lactic, and formic acids were excreted and represented 7.5% of the total carbon recovered. Approximately 50% of the carbon was found as uronic acids in the extracellular medium. Physiological studies were performed under microaerophilic conditions (nitrogen flushing) in continuous cultures for a wide range of growth rates (0.03 to 0.5 h-1). A cell population, able to exhibit a near-maximum theoretical yield of ATP (YmaxATP = 25 g/mol) with a number of ATP molecules formed during the transfer of an electron towards oxygen along the respiration chain (P/O ratio) of 3, appears to have adapted to microaerophilic conditions.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson A. J., Dawes E. A. Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):450–472. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.450-472.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aon M. A., Cortassa S., Westerhoff H. V., Berden J. A., Van Spronsen E., Van Dam K. Dynamic regulation of yeast glycolytic oscillations by mitochondrial functions. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jun;99(Pt 2):325–334. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee P. C., Vanags R. I., Chakrabarty A. M., Maitra P. K. Alginic acid synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants defective in carbohydrate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):238–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.238-245.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. P. The fermentation pathways of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;5(3):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiechter A., Fuhrmann G. F., Käppeli O. Regulation of glucose metabolism in growing yeast cells. Adv Microb Physiol. 1981;22:123–183. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich R., Rapoport T. A. A linear steady-state treatment of enzymatic chains. General properties, control and effector strength. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 15;42(1):89–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacser H., Burns J. A. The control of flux. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1973;27:65–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Stoichiometry of the H+-ATPase of growing and resting, aerobic Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5534–5538. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T. G., Phibbs P. V., Jr Alternative pathways of carbohydrate utilization in pseudomonads. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:359–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton J. D. The relationship between metabolite production and the growth efficiency of the producing organism. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Mar;6(1):1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian F. A., Jarman T. R., Righelato R. C. Biosynthesis of exopolysaccharide by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):418–422. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.418-422.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neijssel O. M., Tempest D. W. Bioenergetic aspects of aerobic growth of Klebsiella aerogenes NCTC 418 in carbon-limited and carbon-sufficient chemostat culture. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Mar 19;107(2):215–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00446843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgers M., Balk P. A., van Dam K. Quantification of multiple-substrate controlled growth--simultaneous ammonium and glucose limitation in chemostat cultures of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(5):478–484. doi: 10.1007/BF00248430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior P. J., Beech G. A., Ritchie G. A., Dawes E. A. The role of oxygen limitation in the formation of poly- -hydroxybutyrate during batch and continuous culture of Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1193–1201. doi: 10.1042/bj1281193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H., Bettenhaussen C. Utilization of energy for growth and maintenance in continuous and batch cultures of microorganisms. A reevaluation of the method for the determination of ATP production by measuring molar growth yields. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 12;301(1):53–70. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(73)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W. Biosynthesis of microbial exopolysaccharides. Adv Microb Physiol. 1982;23:79–150. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60336-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Neijssel O. M. The status of YATP and maintenance energy as biologically interpretable phenomena. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:459–486. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoni N., Aon M. A., Lebeault J. M., Thomas D. Proton motive force, energy recycling by end product excretion, and metabolic uncoupling during anaerobic growth of Pseudomonas mendocina. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6673–6681. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6673-6681.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannoni D. The respiratory chains of pathogenic pseudomonads. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 3;975(3):299–316. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(89)80337-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


