Abstract
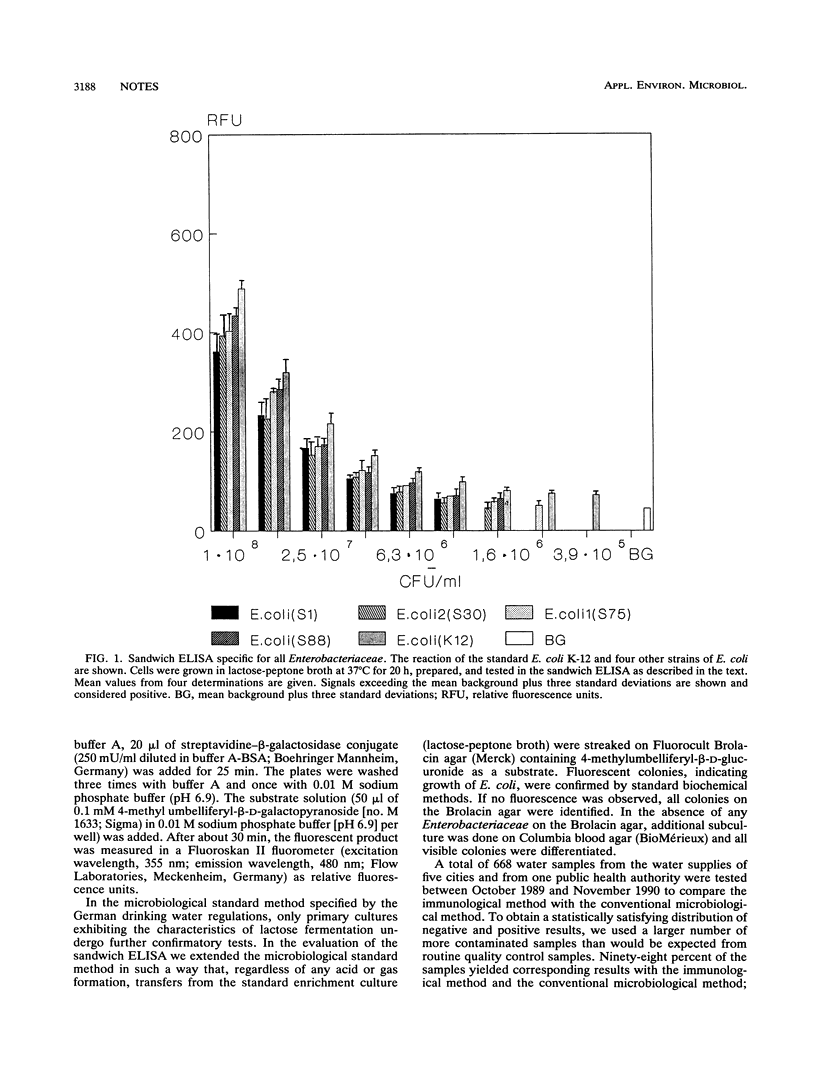
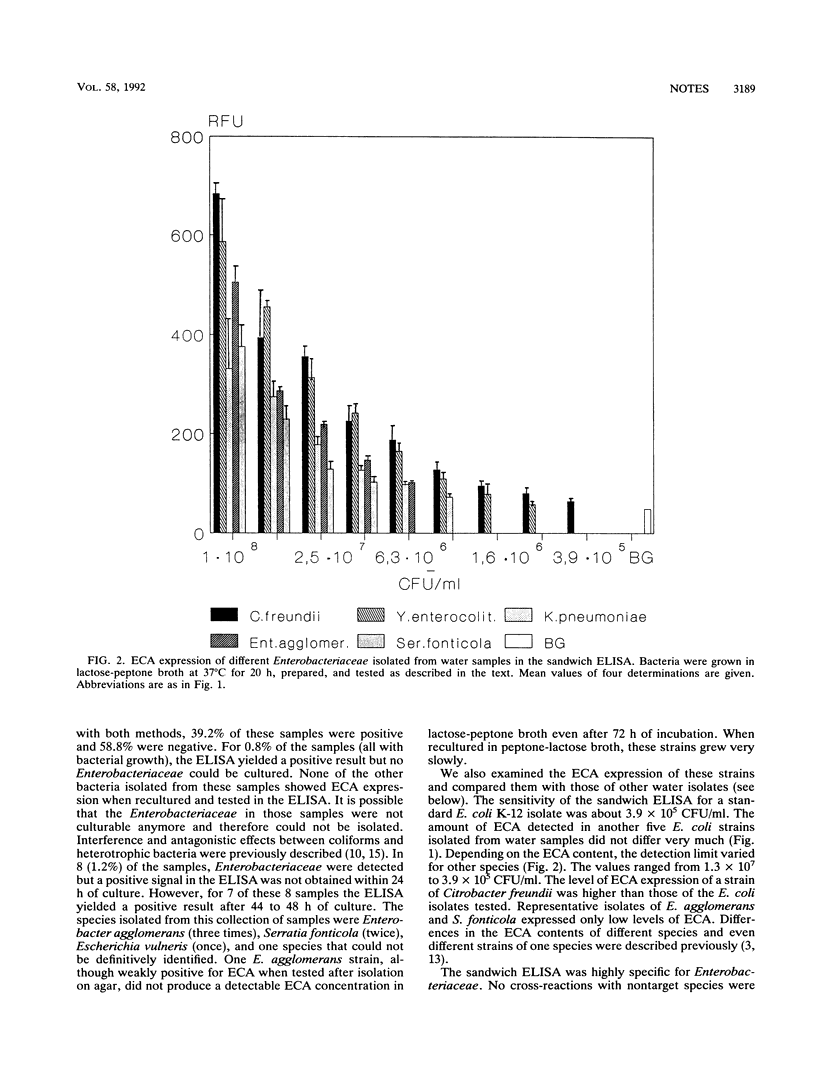
An immunological method for the detection of members of the family Enterobacteriaceae in drinking water was developed. The method was based on a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with monoclonal antibody immunoglobulin G2a 898 against enterobacterial common antigen. The enterobacterial common antigen sandwich ELISA combined with selective preenrichment culture could be performed in only 24 h. Six hundred sixty-eight water samples from a variety of German public water supplies were screened to verify the effectiveness of the new method. Ninety-eight percent of the results obtained by the immunological method could be confirmed by conventional microbiological methods. The immunological method proved to be considerably faster and more specific and sensitive than the standard method specified by the German drinking water regulations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acker G., Bitter-Suermann D., Meier-Dieter U., Peters H., Mayer H. Immunocytochemical localization of enterobacterial common antigen in Escherichia coli and Yersinia enterocolitica cells. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):348–356. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.348-356.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger E. C., Jürs M., Barrett T., Wachsmuth K., Metzger S., Bitter-Suermann D. Qualitative and quantitative determination of enterobacterial common antigen (ECA) with monoclonal antibodies: expression of ECA by two Actinobacillus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):377–382. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.377-382.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübner I., Knoll C., Obst U. Erfahrungen mit dem Nachweis von E. coli und coliformen Bakterien unter Berücksichtigung der Trinkwasserverordnung von 1986. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1989 Feb;187(3):209–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn H. M., Meier-Dieter U., Mayer H. ECA, the enterobacterial common antigen. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1988 Sep;4(3):195–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1988.tb02743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., McFeters G. A. Interactions between heterotrophic plate count bacteria and coliform organisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1338–1341. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1338-1341.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkamäki M. Antibodies to the enterobacterial common antigen: standardization of the passive hemagglutination test and levels in normal human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1074–1079. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1074-1079.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D., Mayer H. Isolation and chemical characterization of the enterobacterial common antigen. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May 16;86(2):361–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H., Jürs M., Jann B., Jann K., Timmis K. N., Bitter-Suermann D. Monoclonal antibodies to enterobacterial common antigen and to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide outer core: demonstration of an antigenic determinant shared by enterobacterial common antigen and E. coli K5 capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):459–466. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.459-466.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernicke F., Dott W. Vorkommen und Häufigkeit von Bakterien im Trinkwasserbereich mit antagonistischen Eigenschaften gegenüber Indikatorbakterien. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1987 Aug;184(6):515–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang H. Y., Heller M. E., Neter E. Production by Aeromonas of common enterobacterial antigen and its possible taxonomic significance. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):161–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.161-164.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann A., Langhammer W., Botzenhart K. Enterobakterien als Qualitätskriterium bei Roh-, Trink- und Badewasser. Vergleichende Untersuchung über das Vorkommen von Enterobakterien, Escherichia coli, coliformen Keimen, Koloniezahl, Fäkalstreptokokken und Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1988 Dec;187(2):91–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Leister F. J., Whitcomb L. S., Santosham M. Enzyme immunoassays for the detection of bacterial antigens utilizing biotin-labeled antibody and peroxidase biotin--avidin complex. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 11;56(3):319–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



