Abstract
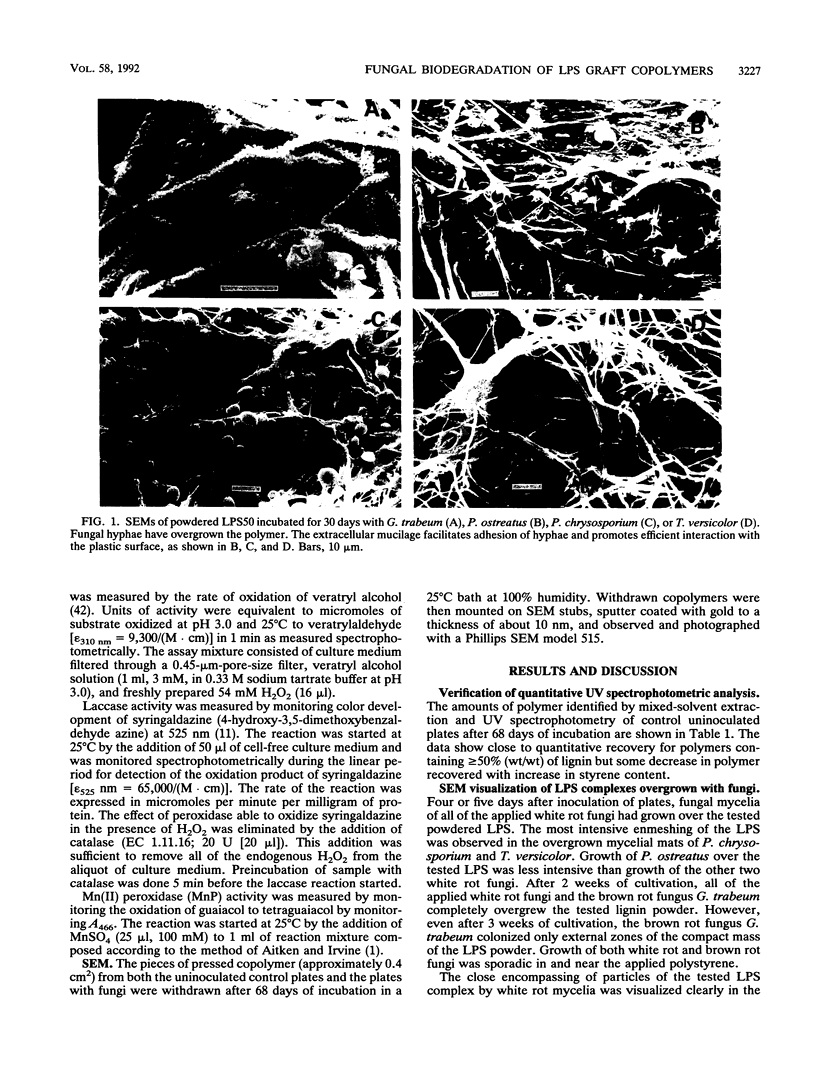
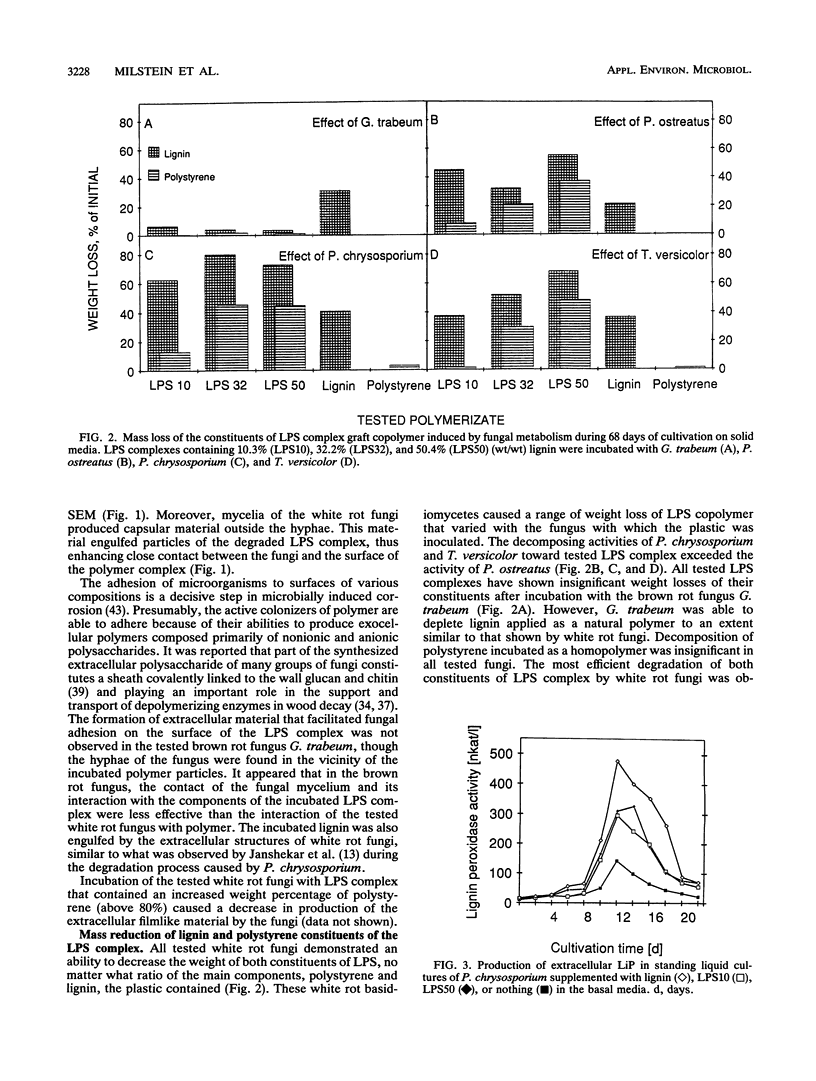
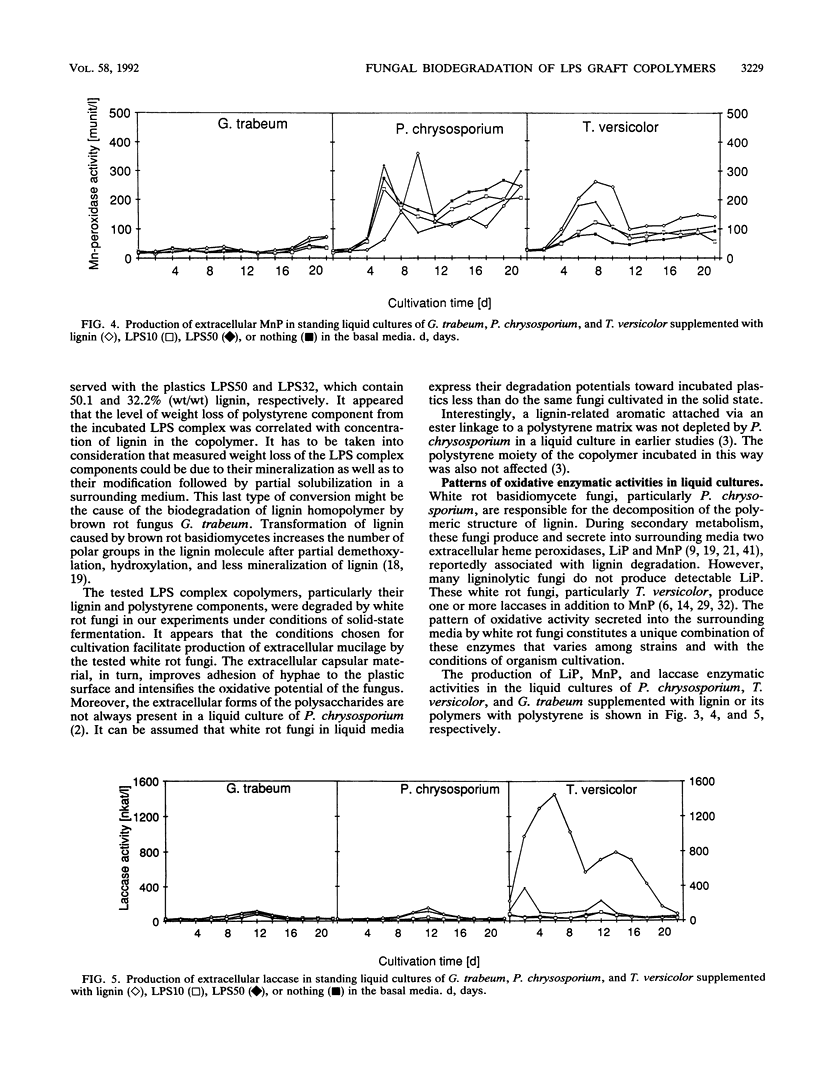
White rot basidiomycetes were able to biodegrade styrene (1-phenylethene) graft copolymers of lignin containing different proportions of lignin and polystyrene [poly(1-phenylethylene)]. The biodegradation tests were run on lignin-styrene copolymerization products which contained 10.3, 32.2, and 50.4% (wt/wt) lignin. The polymer samples were incubated with the white rot fungi Pleurotus ostreatus, Phanerochaete chrysosporium, and Trametes versicolor and the brown rot fungus Gloeophyllum trabeum. White rot fungi degraded the plastic samples at a rate which increased with increasing lignin content in the copolymer sample. Both polystyrene and lignin components of the copolymer were readily degraded. Polystyrene pellets were not degradable in these tests. Degradation was verified for both incubated and control samples by weight loss, quantitative UV spectrophotometric analysis of both lignin and styrene residues, scanning electron microscopy of the plastic surface, and the presence of enzymes active in degradation during incubation. Brown rot fungus did not affect any of the plastics. White rot fungi produced and secreted oxidative enzymes associated with lignin degradation in liquid media during incubation with lignin-polystyrene copolymer.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fåhraeus G., Reinhammar B. Large scale production and purification of laccase from cultures of the fungus Polyporus versicolor and some properties of laccase A. Acta Chem Scand. 1967;21(9):2367–2378. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.21-2367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. K., Morgan M. A., Mayfield M. B., Kuwahara M., Gold M. H. An extracellular H2O2-requiring enzyme preparation involved in lignin biodegradation by the white rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 12;114(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90672-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz A., Teschemacher H. Development of tolerance to the antinociceptive effect of morphine after intraventricular injection. Experientia. 1973 May 1;29(1):64–65. doi: 10.1007/BF01913254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersten P. J., Kalyanaraman B., Hammel K. E., Reinhammar B., Kirk T. K. Comparison of lignin peroxidase, horseradish peroxidase and laccase in the oxidation of methoxybenzenes. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):475–480. doi: 10.1042/bj2680475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk T. K., Farrell R. L. Enzymatic "combustion": the microbial degradation of lignin. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:465–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Pometto A. L., Fratzke A., Bailey T. B. Biodegradation of degradable plastic polyethylene by phanerochaete and streptomyces species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):678–685. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.678-685.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis N. G., Yamamoto E. Lignin: occurrence, biogenesis and biodegradation. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1990;41:455–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pp.41.060190.002323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruel K., Joseleau J. P. Involvement of an Extracellular Glucan Sheath during Degradation of Populus Wood by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):374–384. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.374-384.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkanen S., Razal R. A., Piccariello T., Yamamoto E., Lewis N. G. Lignin peroxidase: toward a clarification of its role in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3636–3643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sietsma J. H., Wessels J. G. Solubility of (1 leads to 3)-beta-D/(1 leads to 6)-beta-D-glucan in fungal walls: importance of presumed linkage between glucan and chitin. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jul;125(1):209–212. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-1-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-Degrading Enzyme from the Hymenomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium Burds. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):661–663. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4611.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of a unique H(2)O(2)-requiring oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2280–2284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]