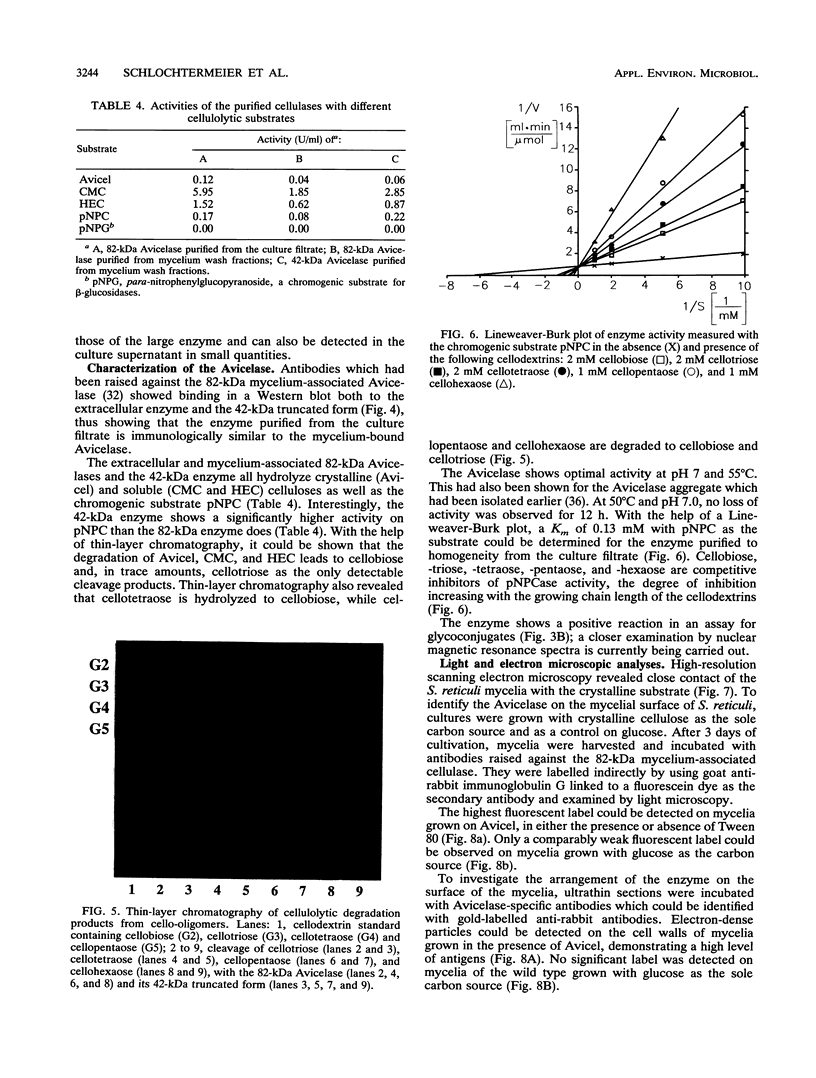
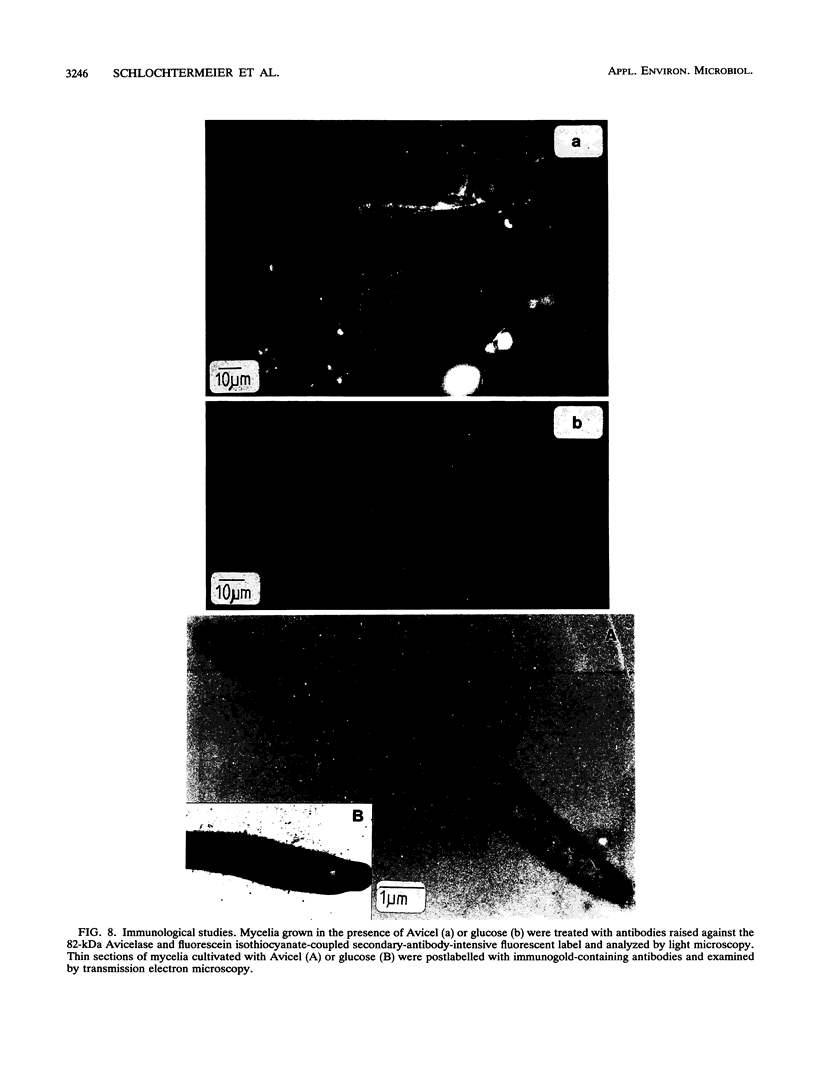
Abstract
Streptomyces reticuli is able to grow efficiently with crystalline cellulose (Avicel) as the sole carbon source. Cultivation in the presence of the nonionic detergent Tween 80 at a concentration of 0.1% led to a 10-fold increase in extracellular cellulolytic activity. Under these conditions, one single 82-kDa cellulase (Avicelase) capable of degrading crystalline and soluble cellulose as well as cellodextrins and p-nitrophenylcellobioside was purified to apparent homogeneity by a procedure which consisted of two consecutive anion-exchange chromatographies followed by chromatofocusing. Aggregation, which was a major problem during protein purification, could be avoided by including Triton X-100 at a concentration of 0.1% in every chromatographic step. The Avicelase was identified in extracellular and mycelium-associated forms, the latter of which could be released efficiently by nonionic detergents. In addition, a 42-kDa truncated form retaining cellulolytic activity was identified which had been generated from the 82-kDa enzyme by a protease. Antibodies raised against the mycelium-associated Avicelase reacted with the 42-kDa derivative and the extracellular form. The mycelial association of the enzyme was confirmed by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopies.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer E. A., Lamed R. Ultrastructure of the cell surface cellulosome of Clostridium thermocellum and its interaction with cellulose. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):828–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.828-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronnenmeier K., Rücknagel K. P., Staudenbauer W. L. Purification and properties of a novel type of exo-1,4-beta-glucanase (avicelase II) from the cellulolytic thermophile Clostridium stercorarium. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):379–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. L., McCoy E. Cellulases of Thermomonospora fusca and Streptomyces thermodiastaticus. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jul;24(1):150–152. doi: 10.1128/am.24.1.150-152.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande M. V., Eriksson K. E., Pettersson L. G. An assay for selective determination of exo-1,4,-beta-glucanases in a mixture of cellulolytic enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):481–487. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90843-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGER M. D., SLEEPER B. P. MULTIPLE CELLULASE SYSTEM FROM STREPTOMYCES ANTIBIOTICUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:23–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.23-27.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Langsford M. L., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren R. A. Mode of action and substrate specificities of cellulases from cloned bacterial genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10455–10459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrissat B., Claeyssens M., Tomme P., Lemesle L., Mornon J. P. Cellulase families revealed by hydrophobic cluster analysis. Gene. 1989 Sep 1;81(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Sakajoh M., Halliwell G., Madia A., Demain A. L. Saccharification of Complex Cellulosic Substrates by the Cellulase System from Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1125-1132.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie C. R., Bilous D., Johnson K. G. Purification and characterization of an exoglucanase from Streptomyces flavogriseus. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Sep;30(9):1171–1178. doi: 10.1139/m84-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer F., Coughlan M. P., Mori Y., Ljungdahl L. G. Macromolecular Organization of the Cellulolytic Enzyme Complex of Clostridium thermocellum as Revealed by Electron Microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2785–2792. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2785-2792.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai R., Horinouchi S., Beppu T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a cellulase gene, casA, from an alkalophilic Streptomyces strain. Gene. 1988 May 30;65(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90459-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman G. R., Hobot J. A. Modern acrylics for post-embedding immunostaining techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Sep;35(9):971–981. doi: 10.1177/35.9.3302021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. B., Lampen J. O. Membrane-bound penicillinases in Gram-positive bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4490–4495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz W. H., Bronnenmeier K., Gräbnitz F., Staudenbauer W. L. Activity staining of cellulases in polyacrylamide gels containing mixed linkage beta-glucans. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jul;164(1):72–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90369-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomme P., Van Tilbeurgh H., Pettersson G., Van Damme J., Vandekerckhove J., Knowles J., Teeri T., Claeyssens M. Studies of the cellulolytic system of Trichoderma reesei QM 9414. Analysis of domain function in two cellobiohydrolases by limited proteolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 4;170(3):575–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachinger G., Bronnenmeier K., Staudenbauer W. L., Schrempf H. Identification of Mycelium-Associated Cellulase from Streptomyces reticuli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2653–2657. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2653-2657.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]