Abstract
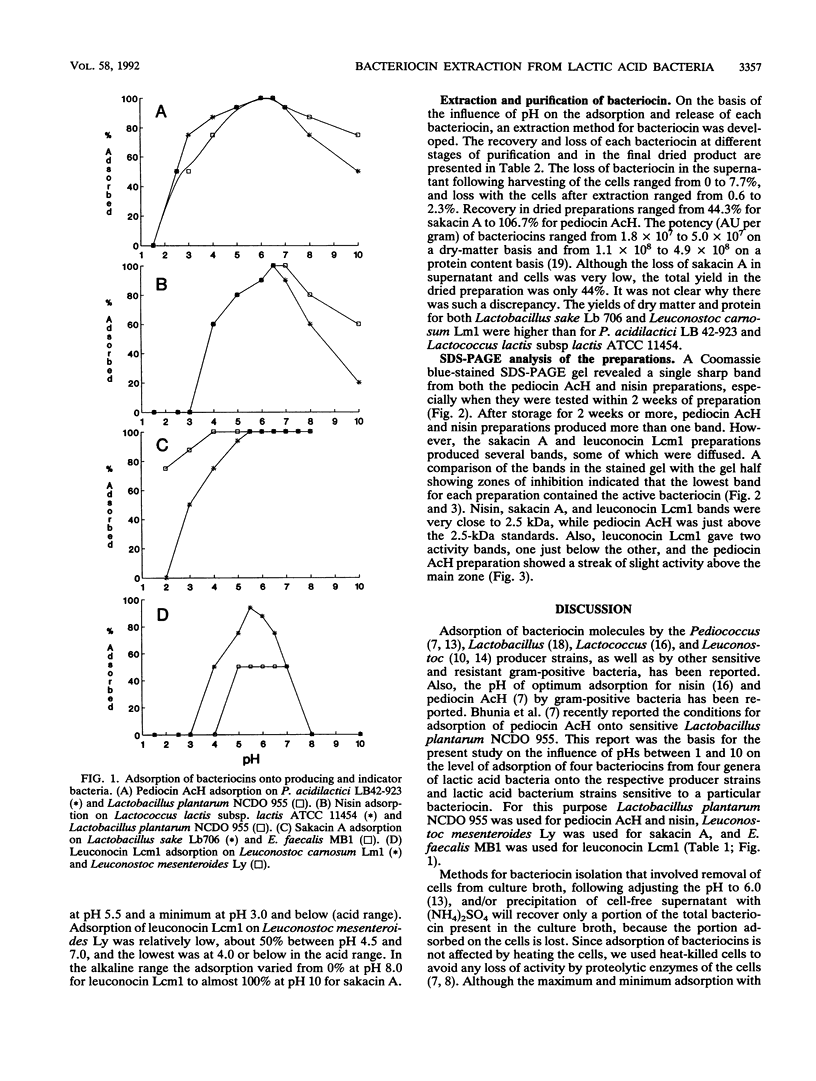
Antimicrobial peptides, bacteriocins, produced by lactic acid bacteria were adsorbed on the cells of producing strains and other gram-positive bacteria. pH was a crucial factor in determining the degree of adsorption of these peptides onto cell surfaces. In general, between 93 and 100% of the bacteriocin molecules were adsorbed at pHs near 6.0, and the lowest (< or = 5%) adsorption took place at pH 1.5 to 2.0. On the basis of this property, a novel isolation method was developed for bacteriocins from four genera of lactic acid bacteria. By using this method we made preparations of pediocin AcH, nisin, sakacin A, and leuconocin Lcm1 that were potent and concentrated. This method produced a higher yield than isolation procedures, which rely on precipitation of the bacteriocins from the cell-free culture liquor. It is simple and can be used to produce large quantities of bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria to be used as food biopreservatives.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERRIDGE N. J. Preparation of the antibiotic nisin. Biochem J. 1949;45(4):486–493. doi: 10.1042/bj0450486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey F. J., Hurst A. Preparation of a highly active form of nisin from Streptococcus lactis. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jan;17(1):61–67. doi: 10.1139/m71-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia A. K., Johnson M. C., Ray B., Belden E. L. Antigenic property of pediocin AcH produced by Pediococcus acidilactici H. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;69(2):211–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb01511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia A. K., Johnson M. C., Ray B. Purification, characterization and antimicrobial spectrum of a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici. J Appl Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;65(4):261–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb01893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas S. R., Ray P., Johnson M. C., Ray B. Influence of Growth Conditions on the Production of a Bacteriocin, Pediocin AcH, by Pediococcus acidilactici H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1265–1267. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1265-1267.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEESEMAN G. C., BERRIDGE N. J. Observations on the molecular weight and chemical composition of nisin A. Biochem J. 1959 Jan;71(1):185–194. doi: 10.1042/bj0710185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daba H., Pandian S., Gosselin J. F., Simard R. E., Huang J., Lacroix C. Detection and activity of a bacteriocin produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3450–3455. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3450-3455.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey G. P., Richardson B. C. Purification and Some Properties of Diplococcin from Streptococcus cremoris 346. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.84-89.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S. Plasmid-Associated Bacteriocin Production and Sucrose Fermentation in Pediococcus acidilactici. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2534–2538. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2534-2538.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings J. W., Sailer M., Johnson K., Roy K. L., Vederas J. C., Stiles M. E. Characterization of leucocin A-UAL 187 and cloning of the bacteriocin gene from Leuconostoc gelidum. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7491–7500. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7491-7500.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holo H., Nilssen O., Nes I. F. Lactococcin A, a new bacteriocin from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris: isolation and characterization of the protein and its gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3879–3887. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3879-3887.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joerger M. C., Klaenhammer T. R. Characterization and purification of helveticin J and evidence for a chromosomally determined bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus helveticus 481. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):439–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.439-446.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R. Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Biochimie. 1988 Mar;70(3):337–349. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muriana P. M., Klaenhammer T. R. Purification and partial characterization of lactacin F, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus acidophilus 11088. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):114–121. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.114-121.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mørtvedt C. I., Nissen-Meyer J., Sletten K., Nes I. F. Purification and amino acid sequence of lactocin S, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus sake L45. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1829–1834. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1829-1834.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piard J. C., Muriana P. M., Desmazeaud M. J., Klaenhammer T. R. Purification and Partial Characterization of Lacticin 481, a Lanthionine-Containing Bacteriocin Produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis CNRZ 481. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):279–284. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.279-284.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schillinger U., Lücke F. K. Antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus sake isolated from meat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):1901–1906. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1901-1906.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Hurst A. The location of nisin in the producer organism, Streptococcus lactis. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Sep;53(2):171–179. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




