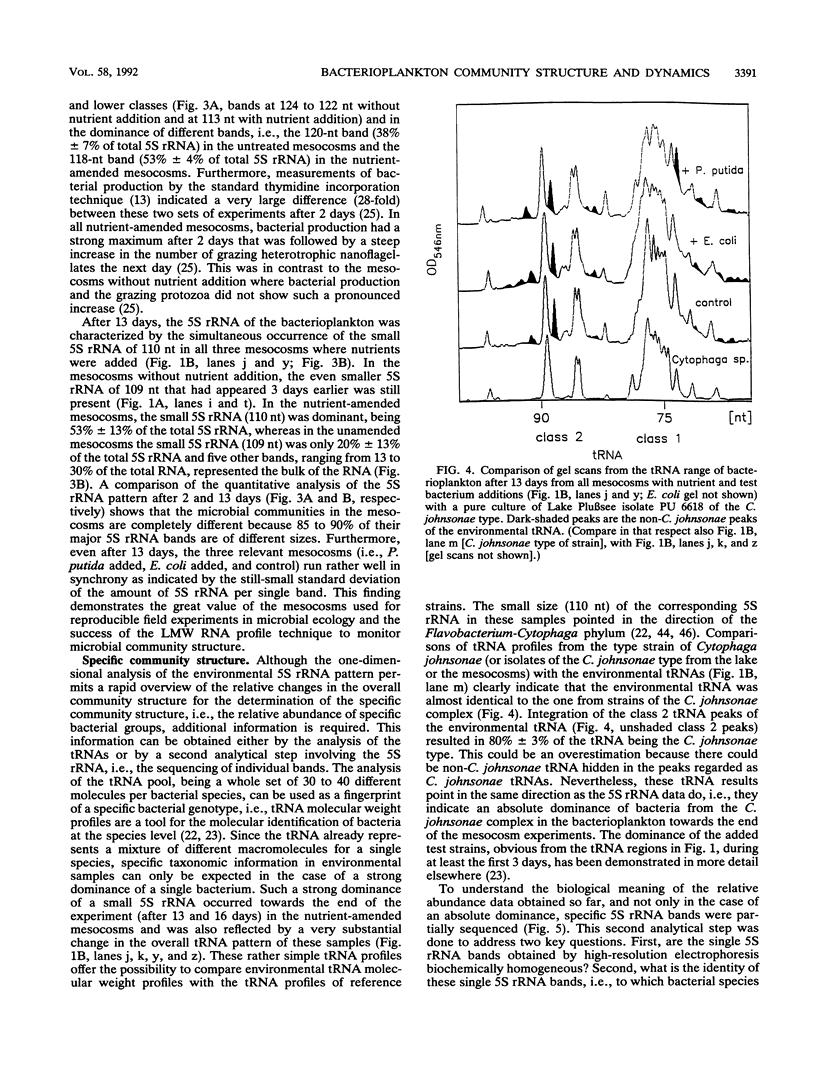
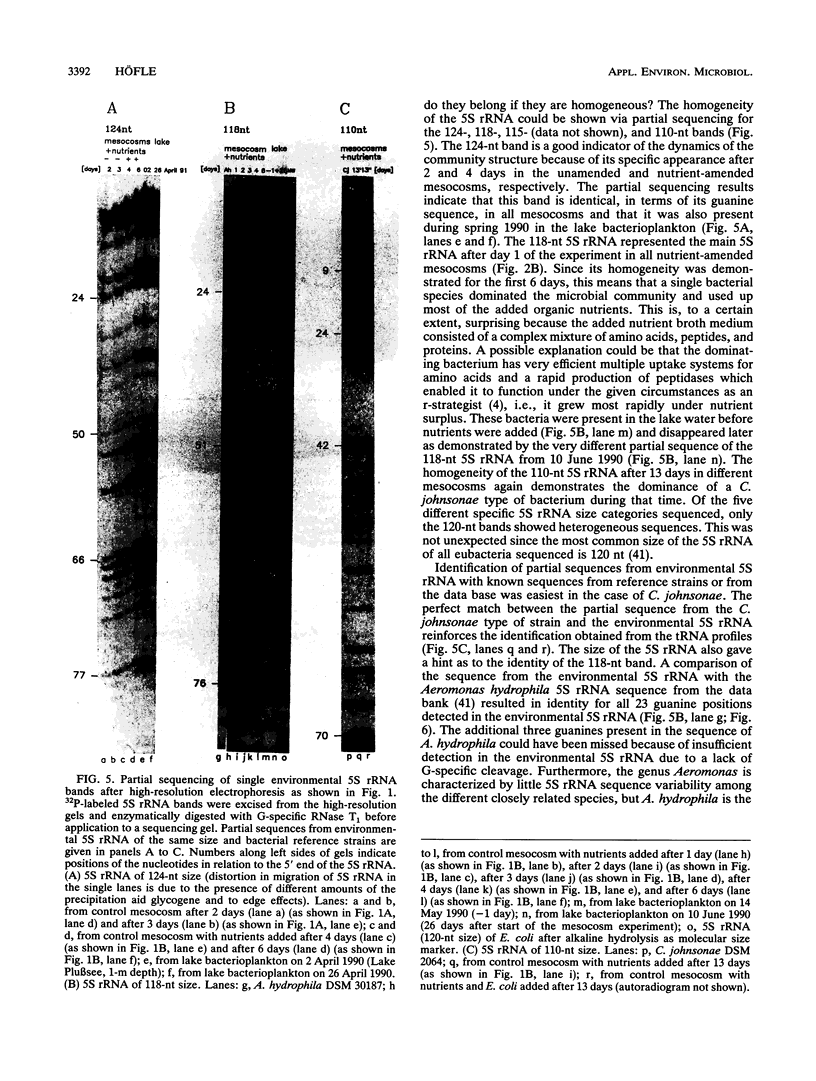
Abstract
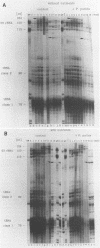
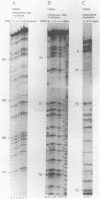
A set of freshwater mesocosms (1.7 m3 each) was inoculated with large amounts of Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida, and their culture medium to substantially disturb the natural microbial community. To monitor microbial community dynamics, low-molecular-weight RNA (5S rRNA and tRNA) obtained directly from bacterioplankton was analyzed by using high-resolution electrophoresis. The introduced bacteria showed no significant effect on the community structure of the natural bacterial assemblage and its dynamics for 16 days. In contrast, the addition of culture medium resulted within 2 days in a reduction of community diversity due to dominance of a single 5S rRNA band from an indigenous bacterium. Partial sequencing of several 5S rRNAs demonstrated the molecular homogeneity of most of the abundant bands and enabled the identification of corresponding bacterial isolates and/or species. The dominating bacterium (around 54% of the total 5S rRNA) in the nutrient-amended mesocosms could be identified by partial sequencing as a member of the Aeromonas hydrophila complex. Another bloom of heterotrophic bacteria belonging to the Cytophaga johnsonae complex was detected in the nutrient-amended mesocosms after 13 days. The dominance of this C. johnsonae-like bacterium could even be seen in the environmental tRNAs of the bacterioplankton, where its specific tRNAs prevailed from day 13 onward. This event was also independent of the introduced nonindigenous bacteria because it occurred at the same time in all nutrient-amended mesocosms. By contrast, in the unamended experiments, a different small 5S rRNA could by observed from day 10 onward with less pronounced dominance.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON R. L., ORDAL E. J. Cytophaga succinicans sp. n., a factaltatively anaerobic, aquatic myxobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81:130–138. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.1.130-138.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altwegg M., Steigerwalt A. G., Altwegg-Bissig R., Lüthy-Hottenstein J., Brenner D. J. Biochemical identification of Aeromonas genospecies isolated from humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):258–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.258-264.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann R., Springer N., Ludwig W., Görtz H. D., Schleifer K. H. Identification in situ and phylogeny of uncultured bacterial endosymbionts. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):161–164. doi: 10.1038/351161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo R. M., Arribas R. M., Pares R. Distribution of Aeromonas species in waters with different levels of pollution. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;71(2):182–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb02976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brettar I., Höfle M. G. Influence of ecosystematic factors on survival of Escherichia coli after large-scale release into lake water mesocosms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2201–2210. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2201-2210.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnahan A., Fanning G. R., Joseph S. W. Aeromonas jandaei (formerly genospecies DNA group 9 A. sobria), a new sucrose-negative species isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):560–564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.560-564.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific labeling of 3' termini of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., Azam F. Bacterioplankton secondary production estimates for coastal waters of british columbia, antarctica, and california. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1085-1095.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Britschgi T. B., Moyer C. L., Field K. G. Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):60–63. doi: 10.1038/345060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Steigerwalt A. G., Schoenmakers B. S., Peeters M. F., Zanen H. C., Brenner D. J. Phenotypic characterization and DNA relatedness in human fecal isolates of Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):132–138. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.132-138.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Lane D. J., Giovannoni S. J., Pace N. R., Stahl D. A. Microbial ecology and evolution: a ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:337–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichenbach H. Taxonomy of the gliding bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:339–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Colwell R. R. Survival strategies of bacteria in the natural environment. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):365–379. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.365-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. M., DeLong E. F., Pace N. R. Analysis of a marine picoplankton community by 16S rRNA gene cloning and sequencing. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4371–4378. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4371-4378.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Lane D. J., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Characterization of a Yellowstone hot spring microbial community by 5S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1379–1384. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1379-1384.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Eynde H., Van de Peer Y., Perry J., De Wachter R. 5S rRNA sequences of representatives of the genera Chlorobium, Prosthecochloris, Thermomicrobium, Cytophaga, Flavobacterium, Flexibacter and Saprospira and a discussion of the evolution of eubacteria in general. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jan;136(1):11–18. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]