Abstract
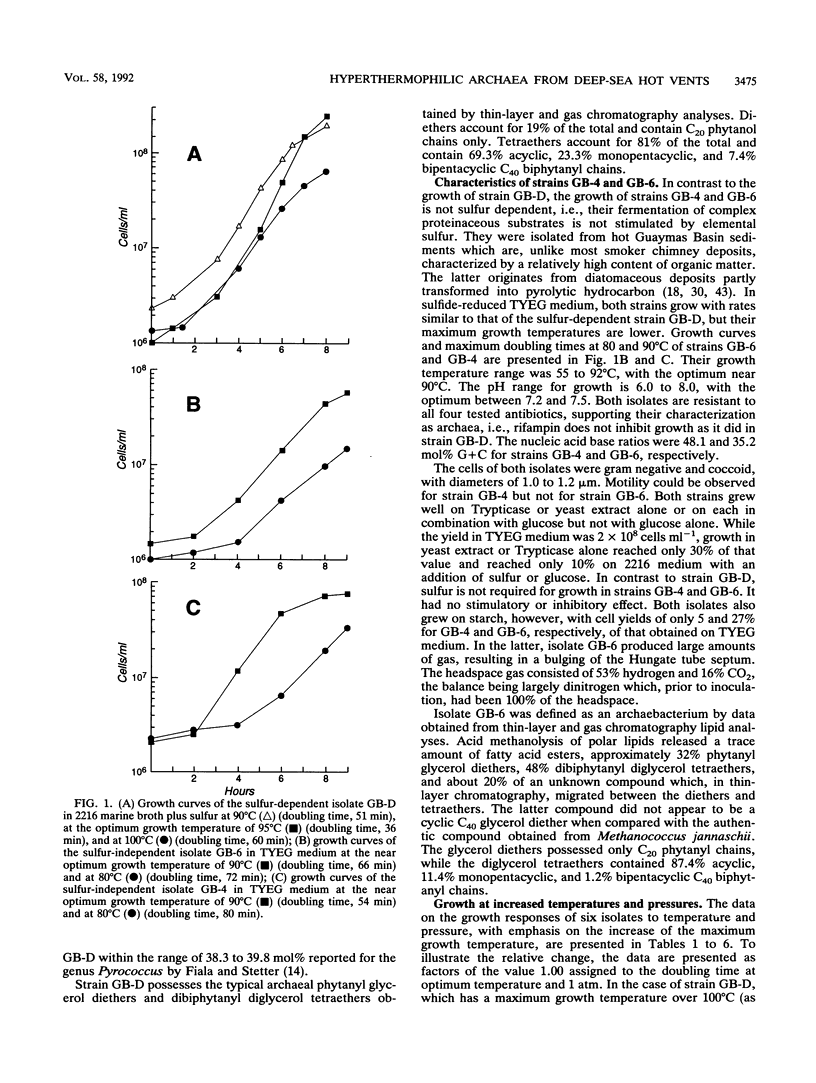
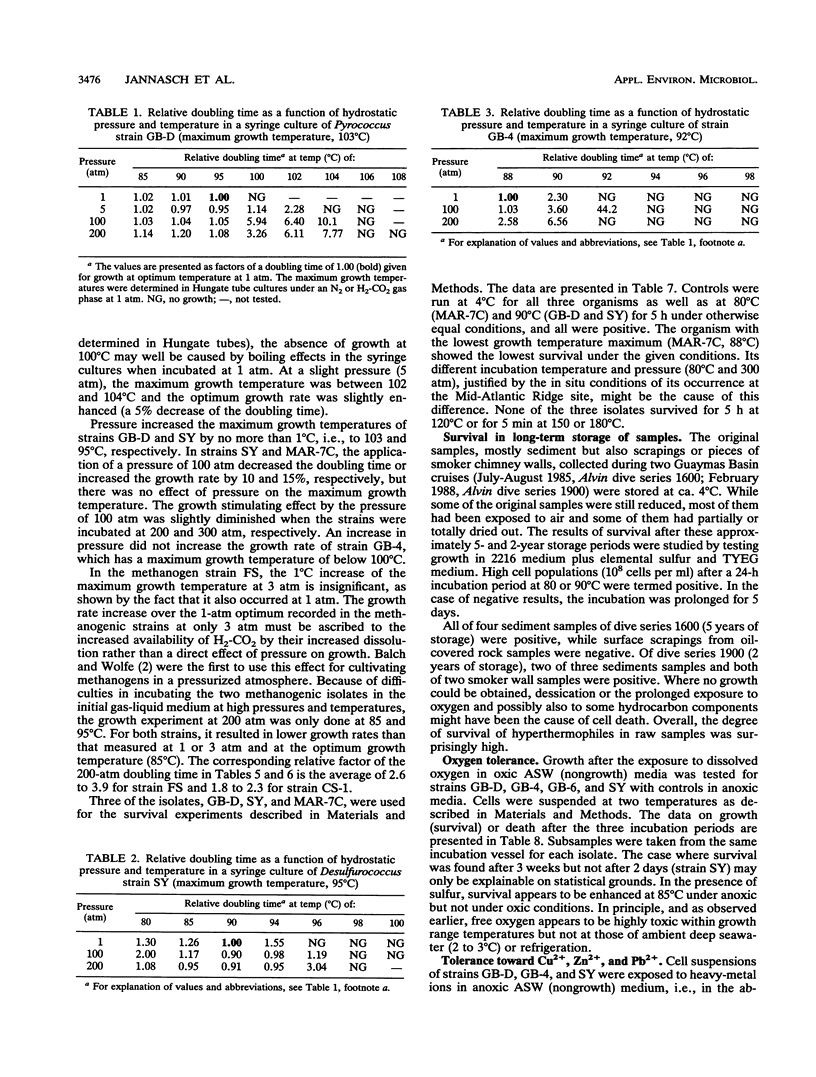
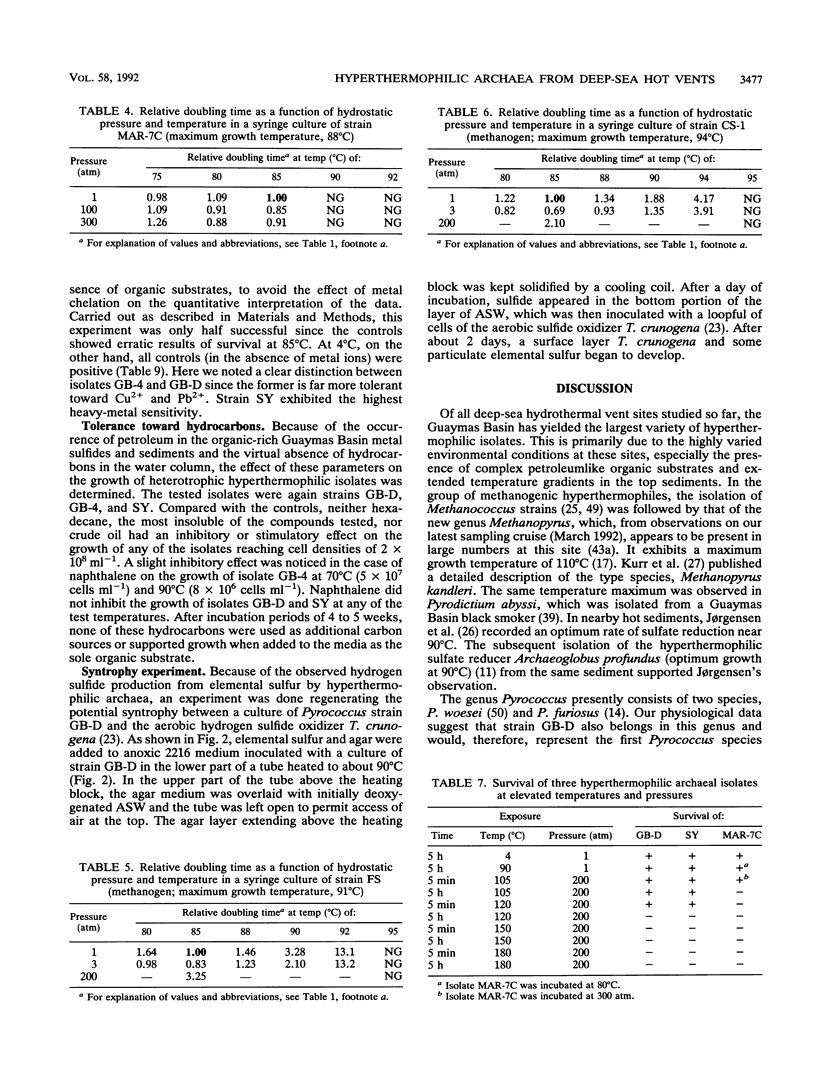
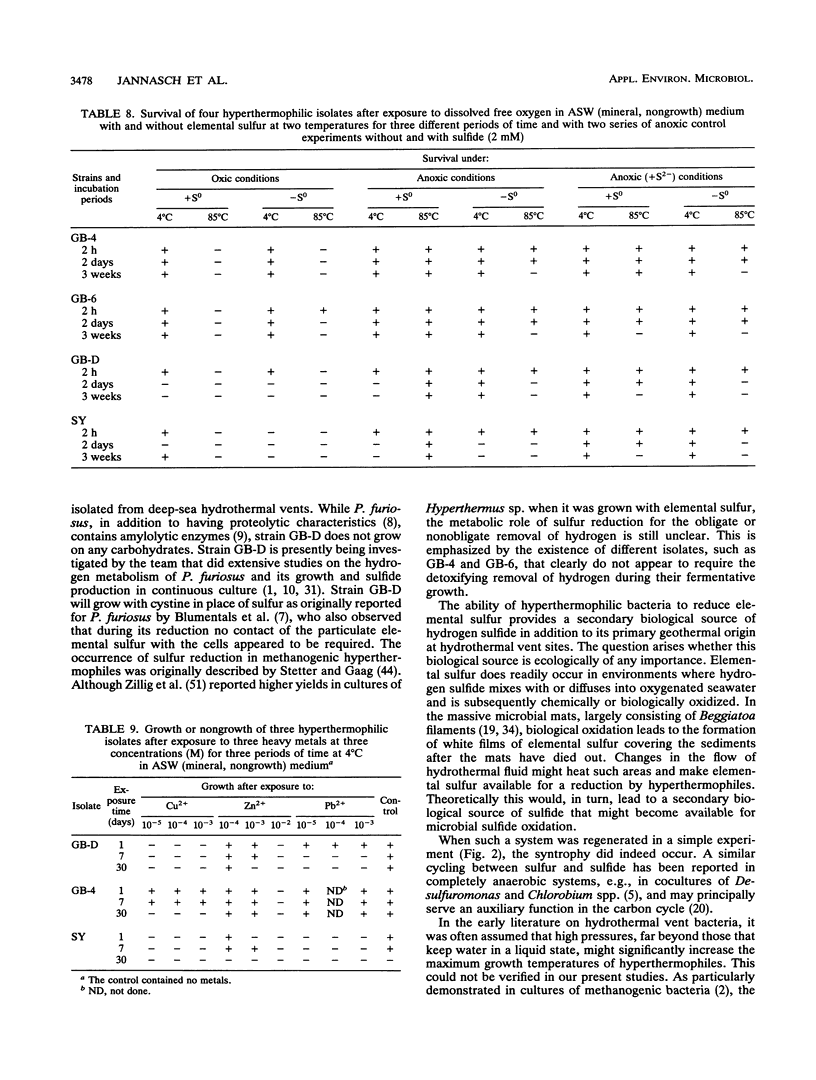
Three new sulfur- or non-sulfur-dependent archaeal isolates, including a Pyrococcus strain, from Guaymas Basin hydrothermal vents (Gulf of California; depth, 2,010 m) were characterized and physiologically compared with four known hyperthermophiles, previously isolated from other vent sites, with an emphasis on growth and survival under the conditions particular to the natural habitat. Incubation under in situ pressure (200 atm [1 atm = 101.29 kPa]) did not increase the maximum growth temperature by more than 1°C for any of the organisms but did result in increases in growth rates of up to 15% at optimum growth temperatures. At in situ pressure, temperatures considerably higher than those limiting growth (i.e., > 105°C) were survived best by isolates with the highest maximum growth temperatures, but none of the organisms survived at temperatures of 150°C or higher for 5 min. Free oxygen was toxic to all isolates at growth range temperatures, but at ambient deep-sea temperature (3 to 4°C), the effect varied in different isolates, the non-sulfur-dependent isolate being the most oxygen tolerant. Hyperthermophiles could be isolated from refrigerated and oxygenated samples after 5 years of storage. Cu, Zn, and Pb ions were found to be toxic under nongrowth conditions (absence of organic substrate), with the non-sulfur-dependent isolate again being the most tolerant.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressureized atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):781–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.781-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazylinski D. A., Wirsen C. O., Jannasch H. W. Microbial utilization of naturally occurring hydrocarbons at the guaymas basin hydrothermal vent site. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2832–2836. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2832-2836.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumentals I. I., Itoh M., Olson G. J., Kelly R. M. Role of Polysulfides in Reduction of Elemental Sulfur by the Hyperthermophilic Archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1255–1262. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1255-1262.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumentals I. I., Robinson A. S., Kelly R. M. Characterization of sodium dodecyl sulfate-resistant proteolytic activity in the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):1992–1998. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.1992-1998.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. H., Costantino H. R., Kelly R. M. Characterization of Amylolytic Enzyme Activities Associated with the Hyperthermophilic Archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):1985–1991. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.1985-1991.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. H., Kelly R. M. Cultivation Techniques for Hyperthermophilic Archaebacteria: Continuous Culture of Pyrococcus furiosus at Temperatures near 100 degrees C. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):2086–2088. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.2086-2088.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannasch H. W., Wirsen C. O., Molyneaux S. J., Langworthy T. A. Extremely thermophilic fermentative archaebacteria of the genus desulfurococcus from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1203–1209. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1203-1209.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannasch H. W., Wirsen C. O. Morphological survey of microbial mats near deep-sea thermal vents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):528–538. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.528-538.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Shah N. N., Nelson C. M., Ludlow J. M., Clark D. S. Pressure and Temperature Effects on Growth and Methane Production of the Extreme Thermophile Methanococcus jannaschii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3039–3042. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3039-3042.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. M., Schuppenhauer M. R., Clark D. S. Effects of hyperbaric pressure on a deep-sea archaebacterium in stainless steel and glass-lined vessels. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3576–3580. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3576-3580.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. C., Wirsen C. O., Jannasch H. W. Characterization of Large, Autotrophic Beggiatoa spp. Abundant at Hydrothermal Vents of the Guaymas Basin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2909–2917. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2909-2917.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reysenbach A. L., Deming J. W. Effects of hydrostatic pressure on growth of hyperthermophilic archaebacteria from the juan de fuca ridge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1271–1274. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1271-1274.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN E. A., WOLIN M. J., WOLFE R. S. FORMATION OF METHANE BY BACTERIAL EXTRACTS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2882–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Kandler O., Wheelis M. L. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Holz I., Janekovic D., Klenk H. P., Imsel E., Trent J., Wunderl S., Forjaz V. H., Coutinho R., Ferreira T. Hyperthermus butylicus, a hyperthermophilic sulfur-reducing archaebacterium that ferments peptides. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3959–3965. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3959-3965.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



