Abstract
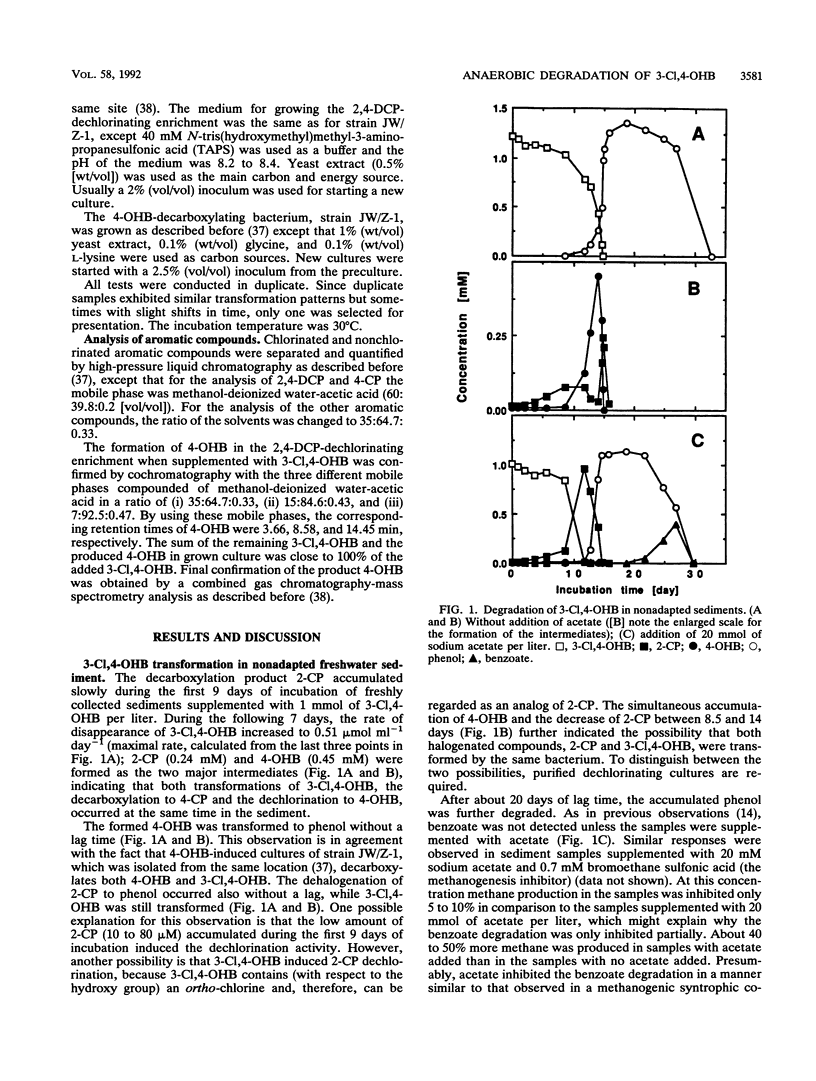
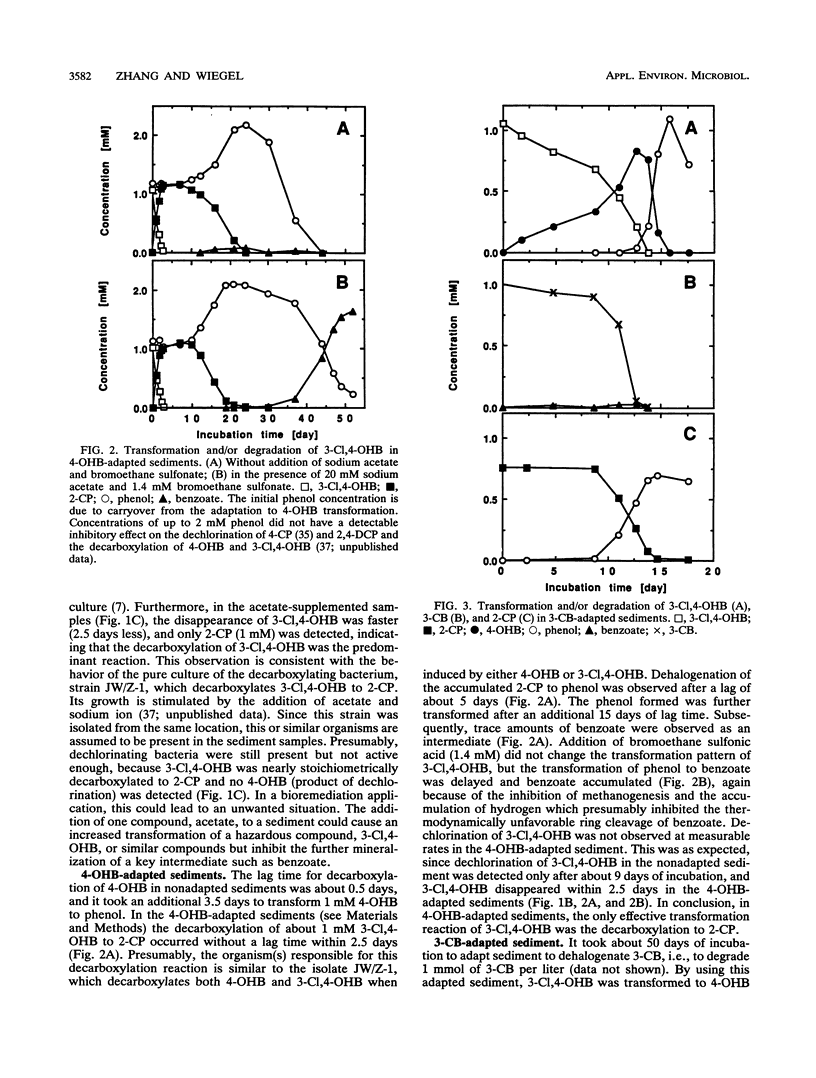
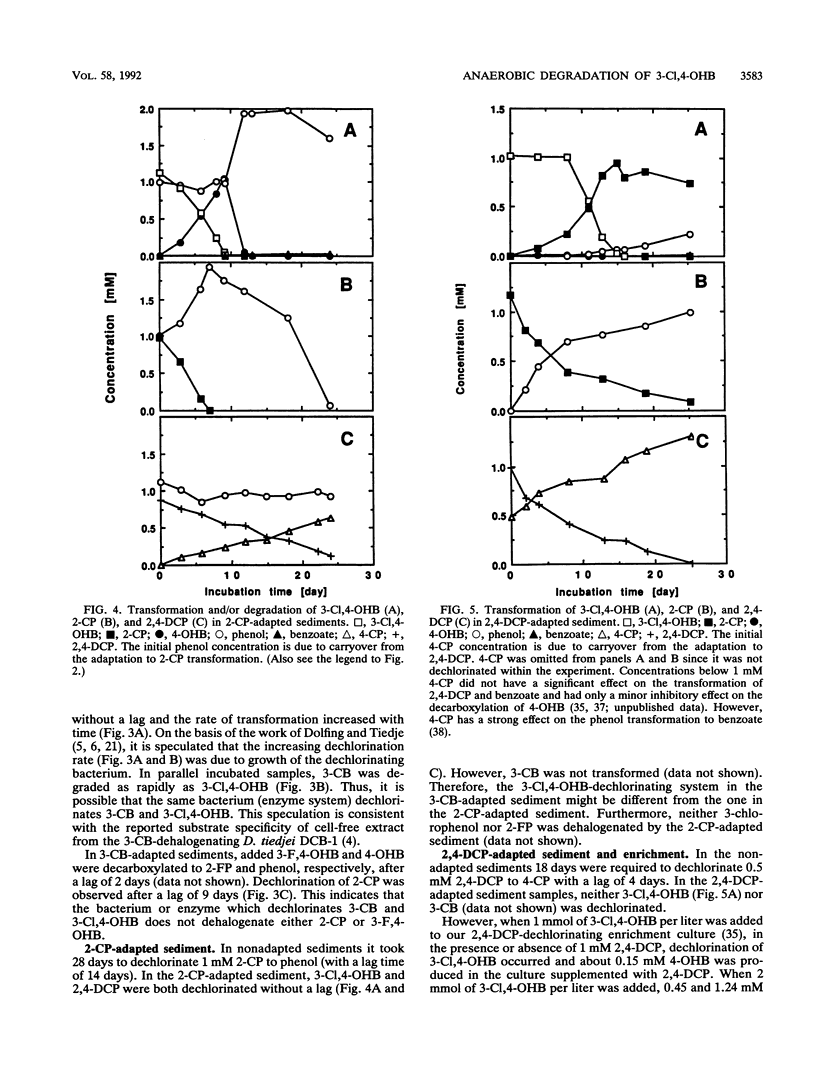
To study the anaerobic degradation of the chimera 3-chloro-4-hydroxybenzoate (3-Cl,4-OHB), anaerobic freshwater sediment samples from the vicinity of Athens, Ga., were adapted for the transformation of 4-hydroxybenzoate (4-OHB), 3-chlorobenzoate (3-CB), 2-chlorophenol (2-CP), and 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP). In nonadapted samples, both 4-OHB (product of aryl dechlorination) and 2-CP (product of aryl decarboxylation) were observed as intermediates in the transformation of 3-Cl,4-OHB to phenol. The accumulated phenol was subsequently transformed to benzoate, an intermediate in the conversion to methane and CO2. In 4-OHB-adapted samples (i.e., samples adapted for aryl decarboxylation), 2-CP was the first intermediate which was subsequently dechlorinated to phenol. In 3-CB-adapted samples (i.e., samples adapted for meta-chlorobenzoate dehalogenation), 3-Cl,4-OHB was stoichiometrically dechlorinated to 4-OHB. In 2-CP-adapted samples (i.e., samples adapted for ortho-chlorophenol dehalogenation), 4-OHB was the first major intermediate. Furthermore, 3-CB was not dechlorinated in 2-CP-adapted sediment samples, suggesting the possibility that different 3-Cl,4-OHB dechlorinating systems were induced in the 2-CP- and 3-CB-adapted sediments. Adaptation of sediment samples for dechlorination of 2,4-DCP did not lead to adaptation for dechlorination of 3-Cl,4-OHB. However, 3-Cl,4-OHB was dechlorinated to 4-OHB in our stable, sediment-free 2,4-DCP-dechlorinating enrichment, isolated previously from the same environment.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd S. A., Shelton D. R. Anaerobic biodegradation of chlorophenols in fresh and acclimated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.272-277.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deweerd K. A., Suflita J. M. Anaerobic Aryl Reductive Dehalogenation of Halobenzoates by Cell Extracts of "Desulfomonile tiedjei". Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Oct;56(10):2999–3005. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.10.2999-3005.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J. Reductive dechlorination of 3-chlorobenzoate is coupled to ATP production and growth in an anaerobic bacterium, strain DCB-1. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(3):264–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00249079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J., Tiedje J. M. Acetate inhibition of methanogenic, syntrophic benzoate degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1871–1873. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1871-1873.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J., Tiedje J. M. Growth yield increase linked to reductive dechlorination in a defined 3-chlorobenzoate degrading methanogenic coculture. Arch Microbiol. 1987;149(2):102–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00425073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Price W. A., Pritchard P. H. Anaerobic Degradation of Chloroaromatic Compounds in Aquatic Sediments under a Variety of Enrichment Conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1466–1471. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1466-1471.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Price W. A., Pritchard P. H. Characterization of anaerobic dechlorinating consortia derived from aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1472-1476.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Townsend G. T., Chapman P. J. Anaerobic transformation of phenol to benzoate via para-carboxylation: use of fluorinated analogues to elucidate the mechanism of transformation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):945–951. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90764-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. A., Suflita J. M. Anaerobic biodegradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic Acid in samples from a methanogenic aquifer: stimulation by short-chain organic acids and alcohols. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1825–1832. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1825-1832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A., Suflita J. M., Tiedje J. M. Reductive dehalogenations of halobenzoates by anaerobic lake sediment microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1459-1465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu T. D., Lux M. F., Drake H. L. Expression of an aromatic-dependent decarboxylase which provides growth-essential CO2 equivalents for the acetogenic (Wood) pathway of Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5901–5907. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5901-5907.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu T., Daniel S. L., Lux M. F., Drake H. L. Biotransformations of carboxylated aromatic compounds by the acetogen Clostridium thermoaceticum: generation of growth-supportive CO2 equivalents under CO2-limited conditions. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):212–217. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.212-217.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggblom M. M., Young L. Y. Chlorophenol degradation coupled to sulfate reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3255–3260. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3255-3260.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohring G. W., Rogers J. E., Wiegel J. Anaerobic biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in freshwater lake sediments at different temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):348–353. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.348-353.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohring G. W., Zhang X. M., Wiegel J. Anaerobic dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol in freshwater sediments in the presence of sulfate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2735–2737. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2735-2737.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linkfield T. G., Suflita J. M., Tiedje J. M. Characterization of the acclimation period before anaerobic dehalogenation of halobenzoates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2773–2778. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2773-2778.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikesell M. D., Boyd S. A. Complete reductive dechlorination and mineralization of pentachlorophenol by anaerobic microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):861–865. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.861-865.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharak Genthner B. R., Townsend G. T., Chapman P. J. Effect of fluorinated analogues of phenol and hydroxybenzoates on the anaerobic transformation of phenol to benzoate. Biodegradation. 1990;1(1):65–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00117052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Isolation and partial characterization of bacteria in an anaerobic consortium that mineralizes 3-chlorobenzoic Acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):840–848. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.840-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suflita J. M., Horowitz A., Shelton D. R., Tiedje J. M. Dehalogenation: a novel pathway for the anaerobic biodegradation of haloaromatic compounds. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1115–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4577.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suflita J. M., Robinson J. A., Tiedje J. M. Kinetics of microbial dehalogenation of haloaromatic substrates in methanogenic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1466–1473. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1466-1473.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Wiegel J. Sequential anaerobic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1119–1127. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1119-1127.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



