Abstract
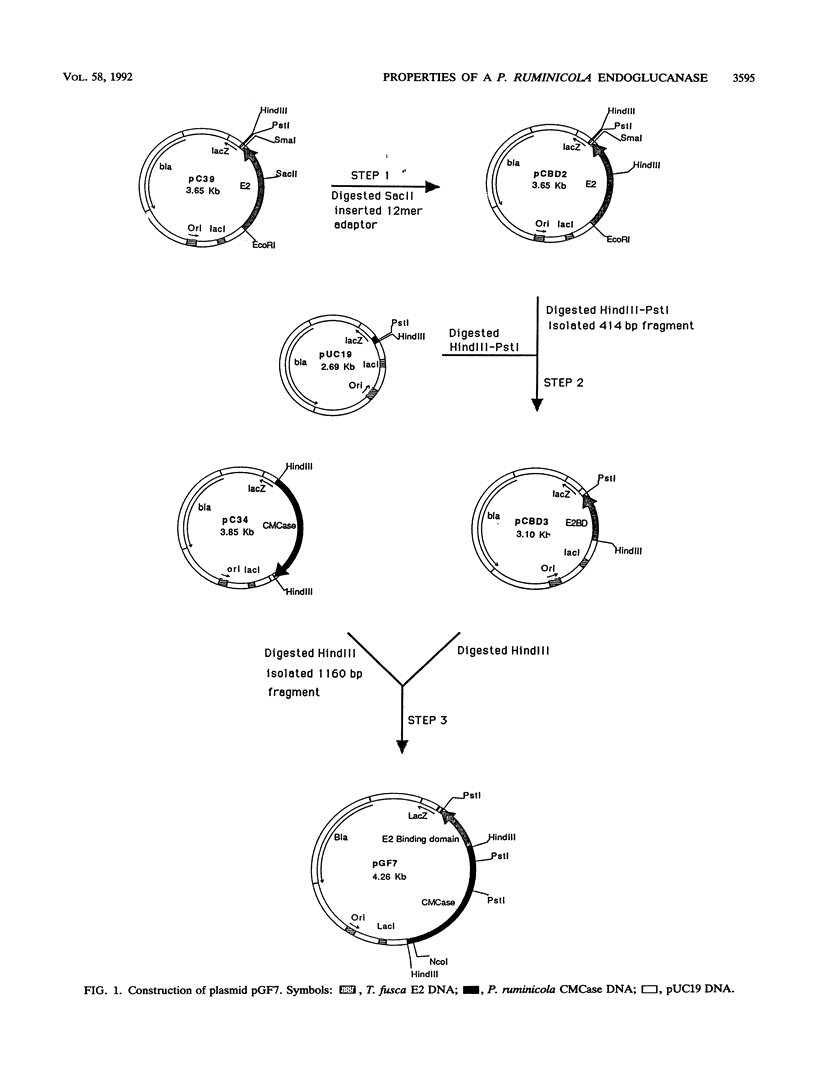
A pUC19-derived plasmid was constructed that coded for a hybrid cellulase with the Thermomonospora fusca E2 cellulose-binding domain at its C terminus joined to the Prevotella ruminicola 40.5-kDa carboxymethyl cellulase (CMCase). The hybrid enzyme was purified and characterized enzymatically. It bound tightly to cellulose, and its specific activities on carboxymethyl cellulose, amorphous cellulose, and ball-milled cellulose were 1.5, 10, and 8 times that of the 40.5-kDa CMCase, respectively. Furthermore, the modified enzyme gave synergism with an exocellulase in the degradation of filter paper, while the 40.5-kDa CMCase did not.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryant M. P. Nutritional requirements of the predominant rumen cellulolytic bacteria. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1809–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. M., Doerner K. C., White B. A. Purification and characterization of an exo-beta-1,4-glucanase from Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4581–4588. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4581-4588.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghangas G. S., Wilson D. B. Cloning of the Thermomonospora fusca Endoglucanase E2 Gene in Streptomyces lividans: Affinity Purification and Functional Domains of the Cloned Gene Product. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2521–2526. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2521-2526.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Warren R. A., Miller R. C., Jr, Kilburn D. G. Precise excision of the cellulose binding domains from two Cellulomonas fimi cellulases by a homologous protease and the effect on catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10401–10407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groleau D., Forsberg C. W. Cellulolytic activity of the rumen bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):517–530. doi: 10.1139/m81-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groleau D., Forsberg C. W. Partial characterization of the extracellular carboxymethylcellulase activity produced by the rumen bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1983 May;29(5):504–517. doi: 10.1139/m83-080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G., BRYANT M. P. THE CELLULOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF PURE STRAINS OF BACTERIA FROM THE RUMEN OF CATTLE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:441–448. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lao G., Ghangas G. S., Jung E. D., Wilson D. B. DNA sequences of three beta-1,4-endoglucanase genes from Thermomonospora fusca. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3397–3407. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3397-3407.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita O., Russell J. B., Wilson D. B. A Bacteroides ruminicola 1,4-beta-D-endoglucanase is encoded in two reading frames. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6919–6926. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6919-6926.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita O., Russell J. B., Wilson D. B. Cloning and sequencing of a Bacteroides ruminicola B(1)4 endoglucanase gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3620–3630. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3620-3630.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole D. M., Durrant A. J., Hazlewood G. P., Gilbert H. J. Characterization of hybrid proteins consisting of the catalytic domains of Clostridium and Ruminococcus endoglucanases, fused to Pseudomonas non-catalytic cellulose-binding domains. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 1;279(Pt 3):787–792. doi: 10.1042/bj2790787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Dombrowski D. B. Effect of pH on the efficiency of growth by pure cultures of rumen bacteria in continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):604–610. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.604-610.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B. Fermentation of cellodextrins by cellulolytic and noncellulolytic rumen bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):572–576. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.572-576.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Wilson D. B. Potential opportunities and problems for genetically altered rumen microorganisms. J Nutr. 1988 Feb;118(2):271–279. doi: 10.1093/jn/118.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu I., Hungate R. E. The extracellular cellulases of Ruminococcus albus. Ann Rech Vet. 1979;10(2-3):251–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]