Abstract
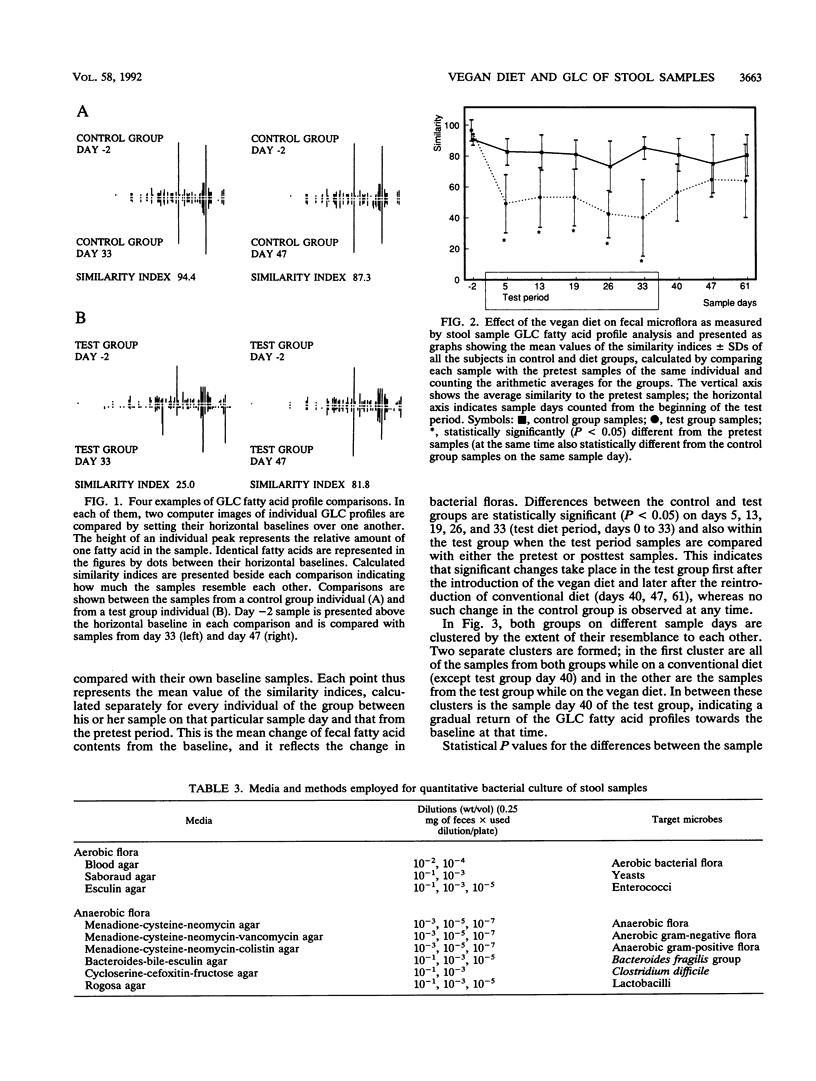
The effect of an uncooked extreme vegan diet on fecal microflora was studied by direct stool sample gas-liquid chromatography (GLC) of bacterial cellular fatty acids and by quantitative bacterial culture by using classical microbiological techniques of isolation, identification, and enumeration of different bacterial species. Eighteen volunteers were divided randomly into two groups. The test group received an uncooked vegan diet for 1 month and a conventional diet of mixed Western type for the other month of the study. The control group consumed a conventional diet throughout the study period. Stool samples were collected. Bacterial cellular fatty acids were extracted directly from the stool samples and measured by GLC. Computerized analysis of the resulting fatty acid profiles was performed. Such a profile represents all bacterial cellular fatty acids in a sample and thus reflects its microflora and can be used to detect changes, differences, or similarities of bacterial flora between individual samples or sample groups. GLC profiles changed significantly in the test group after the induction and discontinuation of the vegan diet but not in the control group at any time, whereas quantitative bacterial culture did not detect any significant change in fecal bacteriology in either of the groups. The results suggest that an uncooked extreme vegan diet alters the fecal bacterial flora significantly when it is measured by direct stool sample GLC of bacterial fatty acids.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crowther J. S., Drasar B. S., Goddard P., Hill M. J., Johnson K. The effect of a chemically defined diet on the faecal flora and faecal steroid concentration. Gut. 1973 Oct;14(10):790–793. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer J. T. Health aspects of vegetarian diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988 Sep;48(3 Suppl):712–738. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/48.3.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eerola E., Lehtonen O. P. Optimal data processing procedure for automatic bacterial identification by gas-liquid chromatography of cellular fatty acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1745–1753. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1745-1753.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evaldson G., Heimdahl A., Kager L., Nord C. E. The normal human anaerobic microflora. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;35:9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Attebery H. R., Sutter V. L. Effect of diet on human fecal flora: comparison of Japanese and American diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Dec;27(12):1456–1469. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.12.1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Sutter V. L., Sugihara P. T., Elder H. A., Lehmann S. M., Phillips R. L. Fecal microbial flora in Seventh Day Adventist populations and control subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 Nov;30(11):1781–1792. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.11.1781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin B. R., Swenson L., Dwyer J., Sexton M., Gorbach S. L. Effect of diet and Lactobacillus acidophilus supplements on human fecal bacterial enzymes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Feb;64(2):255–261. doi: 10.1093/jnci/64.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J. Does diet influence human fecal microflora composition? Nutr Rev. 1980 Oct;38(10):329–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1980.tb05934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J., Maier B. R., Burton G. C., Flynn M. A., Tsutakawa R. K. Effect of a high-beef diet on the fecal bacterial flora of humans. Cancer Res. 1977 Feb;37(2):568–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotilainen P., Huovinen P., Eerola E. Application of gas-liquid chromatographic analysis of cellular fatty acids for species identification and typing of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):315–322. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.315-322.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier B. R., Flynn M. A., Burton G. C., Tsutakawa R. K., Hentges D. J. Effects of a high-beef diet on bowel flora: a preliminary report. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Dec;27(12):1470–1474. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.12.1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Nunez-Montiel O. L. Analysis of short-chain acids from bacteria by gas-liquid chromatography with a fused-silica capillary column. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):308–311. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.308-311.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord C. E., Heimdahl A., Kager L. Antimicrobial induced alterations of the human oropharyngeal and intestinal microflora. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1986;49:64–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenvall B., Hallberg D., Larsson L., Nord C. E. The effect of clindamycin on the intestinal flora in patients with enteric hyperoxaluria. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Mar;18(2):177–181. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Weisburger J. H., Wynder E. L. Fecal bacterial beta-glucuronidase: control by diet. Science. 1974 Feb 1;183(4123):416–417. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4123.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S. The effect of quinolone antibacterials on the gastrointestinal flora compared with that of other antibacterials. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):89–102. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland I. R., Mallett A. K., Wise A. The effect of diet on the mammalian gut flora and its metabolic activities. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1985;16(1):31–103. doi: 10.3109/10408448509041324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Gastrointestinal microflora in mammalian nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr. 1986;6:155–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.06.070186.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinebaum R., Neumann V. C., Cooke E. M., Wright V. Comparison of faecal florae in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and controls. Br J Rheumatol. 1987 Oct;26(5):329–333. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/26.5.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon G. L., Gorbach S. L. Intestinal flora in health and disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jan;86(1):174–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensinck F., Custers-van Lieshout, Poppelaars-Kustermans P. A., Schröder A. M. The faecal flora of patients with Crohn's disease. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Aug;87(1):1–12. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes E., Meek E. S. Rheumatoid arthritis: review of searches for an infectious cause. Part II. Infection. 1979;7(4):192–197. doi: 10.1007/BF01640944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



