Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against Vibrio species that infect humans, fish, and shellfish were developed for application in rapid identifications. The pathogens included Vibrio alginolyticus, V. anguillarum, V. carchariae, V. cholerae, V. damsela, V. furnissii, V. harveyi, V. ordalii, V. parahaemolyticus, and V. vulnificus. Three types of MAbs were selected. The first important group included MAbs that reacted with only a single species. A second group comprised a number of MAbs that reacted with two, taxonomically closely related Vibrio species. For example, of 22 MAbs raised against V. alginolyticus, 6 recognized a 52-kDa flagellar H antigen common to both V. alginolyticus and V. parahaemolyticus; V. anguillarum and V. ordalii also shared antigens. A third group included three genus-specific MAbs that reacted with almost all Vibrio species but did not react with other members of the family Vibrionaceae (e.g., members of the Aeromonas, Photobacterium, and Plesiomonas genera) or a wide range of gram-negative bacteria representing many genera. This last group indicated the possible existence of an antigenic determinant common to Vibrio species. Two of these three genus-specific MAbs reacted with heat-stable antigenic determinants of Vibrio species as well as lipopolysaccharide extracted from Vibrio species. The use of the MAbs in blind tests and diagnosis of clinical isolates indicated that three different types of bacteria, viz., live, formalin-fixed, and sodium azide-killed bacteria, were detected consistently. Overall, it was found that the genus-specific MAbs were very useful for rapidly identifying vibrios in the screening of acute infections, while the species-specific MAbs and others were useful for completing the diagnosis.
Full text
PDF





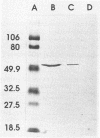
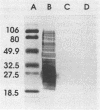
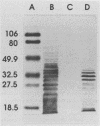
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams L. B., Henk M. C., Siebeling R. J. Detection of Vibrio cholerae with monoclonal antibodies specific for serovar O1 lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1801–1809. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1801-1809.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams L. B., Siebeling R. J. Production of Vibrio cholerae O1 and non-O1 typing sera in rabbits immunized with polysaccharide-protein carrier conjugates. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):181–186. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.181-186.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant T. N., Lee J. V., West P. A., Colwell R. R. A probability matrix for the identification of species of Vibrio and related genera. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;61(5):469–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant T. N., Lee J. V., West P. A., Colwell R. R. Numerical classification of species of Vibrio and related genera. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;61(5):437–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Trust T. J. Characterization of the surface antigens of the marine fish pathogens Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio ordalii. Can J Microbiol. 1984 May;30(5):703–710. doi: 10.1139/m84-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Antibody production by hybridomas. J Immunol Methods. 1980;39(4):285–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Rosén A., Holme T. Monoclonal antibodies against Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):449–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.449-454.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogenraad N. J., Wraight C. J. The effect of pristane on ascites tumor formation and monoclonal antibody production. Methods Enzymol. 1986;121:375–381. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)21036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Yokota T. Different types of monoclonal antibodies to Ogawa-specific and group-specific antigens of Vibrio cholerae O1. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2289–2295. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2289-2295.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. L., Rasmussen H. B., Dalsgaard I. Study of Vibrio anguillarum strains from different sources with emphasis on ecological and pathobiological properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Sep;54(9):2264–2267. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.9.2264-2267.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Heuzenroeder M. W., Yeadon J., Leavesley D. I., Reeves P. R., Rowley D. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli K-12 of the O antigens of the Inaba and Ogawa serotypes of the Vibrio cholerae O1 lipopolysaccharides and their potential for vaccine development. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.272-277.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. J., Siebeling R. J. Identification of Vibrio vulnificus O serovars with antilipopolysaccharide monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Aug;29(8):1684–1688. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.8.1684-1688.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Black R. E. Cholera and other vibrioses in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 7;312(6):343–350. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502073120604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson J. G., Siebeling R. J. Coagglutination of Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio mimicus, and Vibrio vulnificus with anti-flagellar monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):1962–1966. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.1962-1966.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. K., Sutton D. C., Fuerst J. A., Reichelt J. L. Evaluation of the genus Listonella and reassignment of Listonella damsela (Love et al.) MacDonell and Colwell to the genus Photobacterium as Photobacterium damsela comb. nov. with an emended description. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;41(4):529–534. doi: 10.1099/00207713-41-4-529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su S. D., Ward M. M., Apicella M. A., Ward R. E. Analysis of the immune response to lipopolysaccharide. Existence of an interspecies cross-reactive idiotype associated with anti-lipid A antibodies. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2994–3001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svendsen I., Larsen J. L. Monoclonal antibodies against surface antigens of Vibrio anguillarum serogroup 02. Acta Vet Scand. 1988;29(3-4):363–368. doi: 10.1186/BF03548630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassin M. G., Siebeling R. J., Roberts N. C., Larson A. D. Presumptive identification of Vibrio species with H antiserum. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):400–407. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.400-407.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Willis D. L., Berry L. J. Flagella-induced immunity against experimental cholera in adult rabbits. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):220–228. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.220-228.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]