Abstract
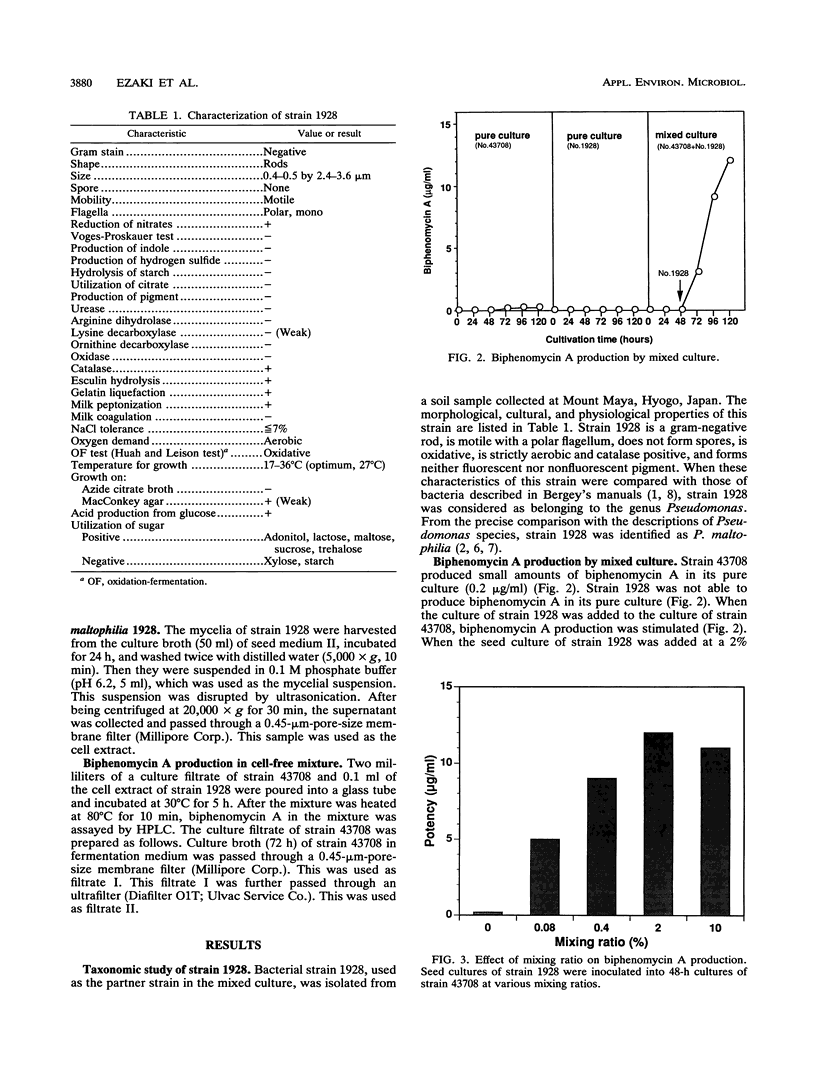
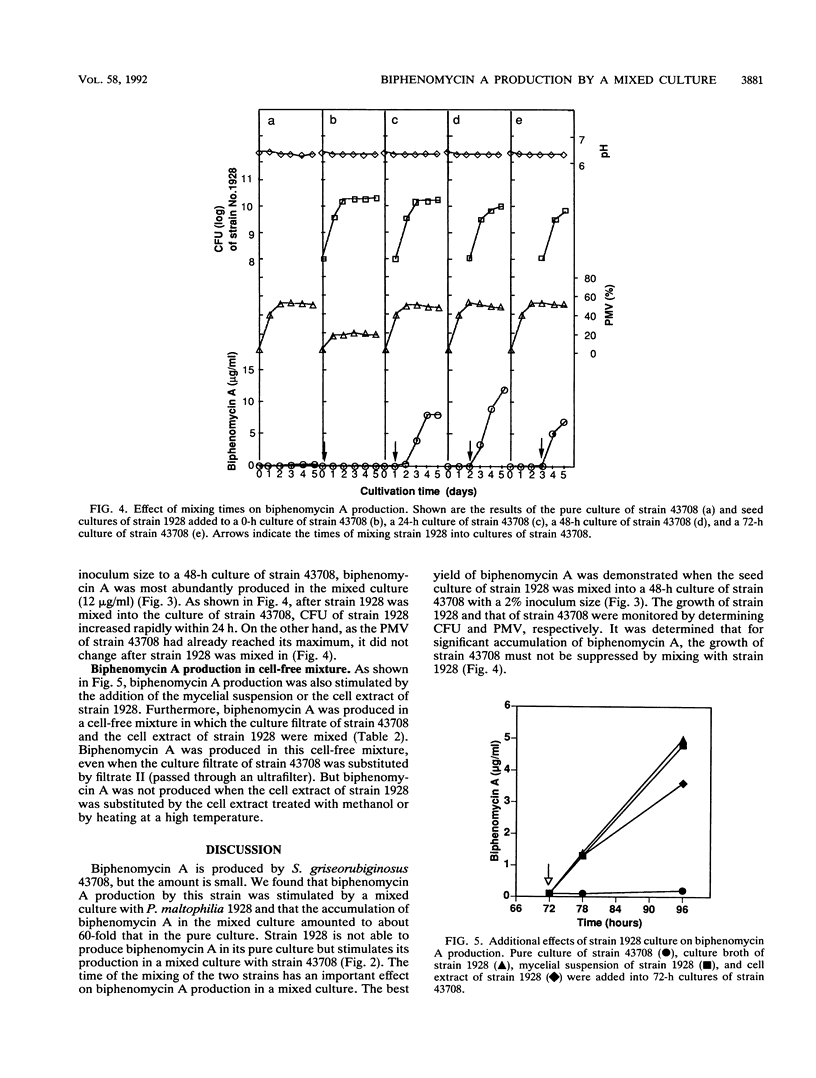
Production of biphenomycin A by Streptomyces griseorubiginosus 43708 was stimulated by a mixed culture with a partner strain, Pseudomonas maltophilia 1928. This stimulatory effect on biphenomycin A accumulation by the mixed culture was caused by the enzyme activity which strain 1928 possessed. It is suggested that in a mixed culture strain 43708 produces a precursor of biphenomycin A in culture broth and that strain 1928 converts the precursor to biphenomycin A.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dyte P. H., Gillians J. A. Pseudomonas maltophilia infection in an abattoir worker. Med J Aust. 1977 Mar 26;1(13):444–445. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb130797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki M., Iwami M., Yamashita M., Hashimoto S., Komori T., Umehara K., Mine Y., Kohsaka M., Aoki H., Imanaka H. Biphenomycins A and B, novel peptide antibiotics. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and characterization. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1985 Nov;38(11):1453–1461. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.38.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., RYSCHENKOW E. Pseudomonas maltophilia, an alcaligenes-like species. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Sep;26:123–132. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida I., Shigematsu N., Ezaki M., Hashimoto M., Aoki H., Imanaka H. Biphenomycins A and B, novel peptide antibiotics. II. Structural elucidation of biphenomycins A and B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1985 Nov;38(11):1462–1468. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.38.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



