Abstract
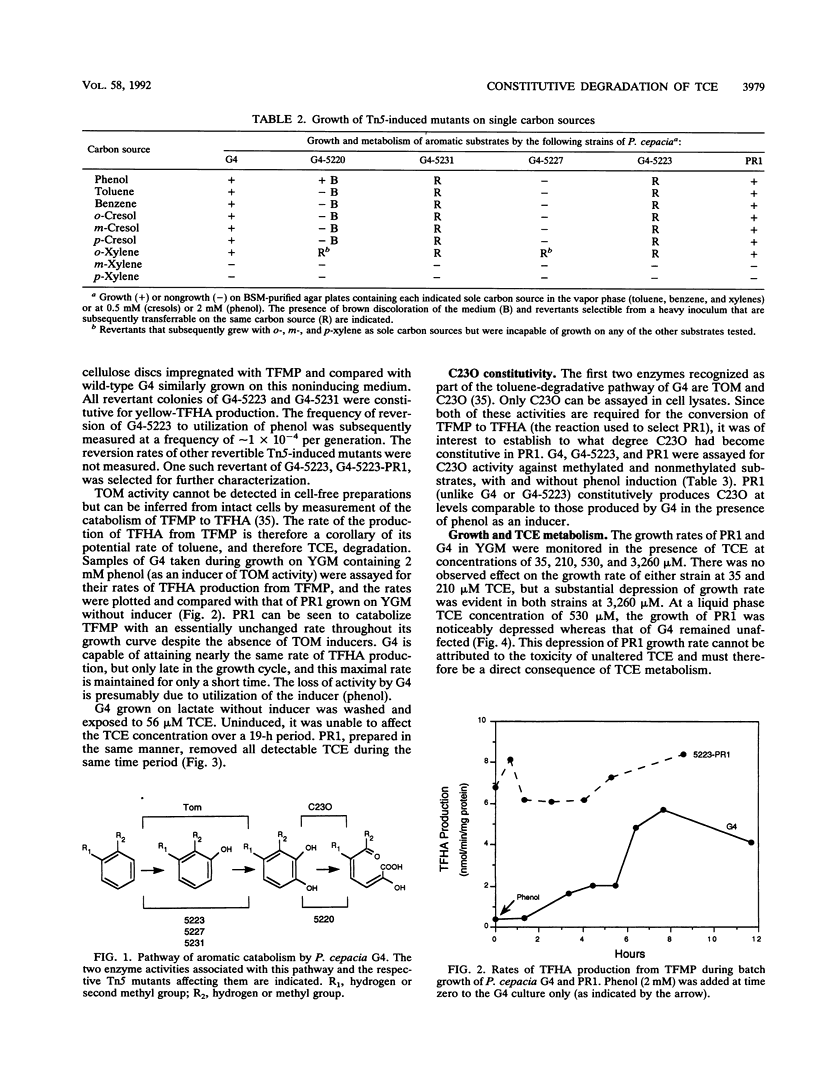
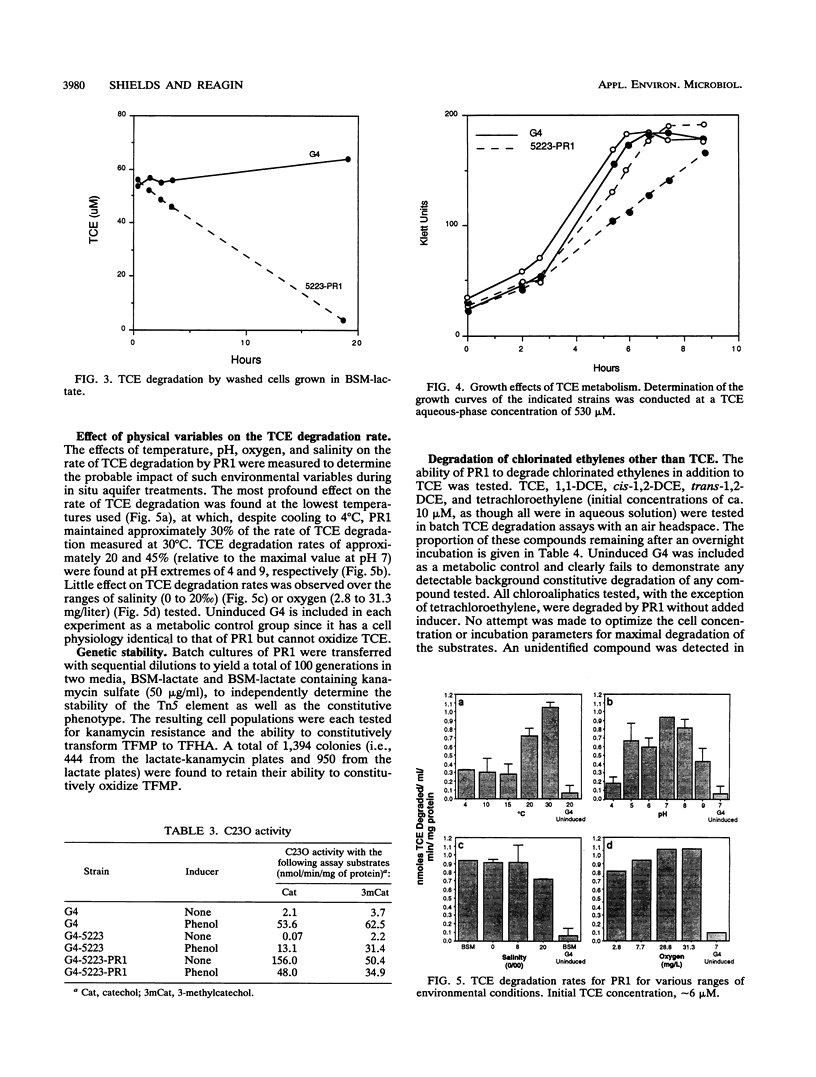
Tn5 insertion mutants of Pseudomonas cepacia G4 that were unable to degrade trichloroethylene (TCE), toluene, or phenol or to transform m-trifluoromethyl phenol (TFMP) to 7,7,7-trifluoro-2-hydroxy-6-oxo-2,4-heptadienoic acid (TFHA) were produced. Spontaneous reversion to growth on phenol or toluene as the sole source of carbon was observed in one mutant strain, G4 5223, at a frequency of approximately 1 x 10(-4) per generation. One such revertant, G4 5223-PR1, metabolized TFMP to TFHA and degraded TCE. Unlike wild-type G4, G4 5223-PR1 constitutively metabolized both TFMP and TCE without aromatic induction. G4 5223-PR1 also degraded cis-1,2-dichloroethylene, trans-1,2-dichloroethylene, and 1,1-dichloroethylene and oxidized naphthalene to alpha naphthol constitutively. G4 5223-PR1 exhibited a slight retardation in growth rate at TCE concentrations of > or = 530 microM, whereas G4 (which was unable to metabolize TCE under the same noninducing growth conditions) remained unaffected. The constitutive degradative phenotype of G4 5223-PR1 was completely stable through 100 generations of nonselective growth.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arciero D., Vannelli T., Logan M., Hooper A. B. Degradation of trichloroethylene by the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):640–643. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer E. J., McCarty P. L. Transformations of 1- and 2-carbon halogenated aliphatic organic compounds under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1286–1294. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1286-1294.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Weightman A. J., Knackmuss H. J., Timmis K. N. Transposon mutagenesis and cloning analysis of the pathways for degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 3-chlorobenzoate in Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134(pJP4). J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):85–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.85-90.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. W., Timmis K. N. Characterization of a plasmid-specified pathway for catabolism of isopropylbenzene in Pseudomonas putida RE204. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):123–131. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.123-131.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engesser K. H., Cain R. B., Knackmuss H. J. Bacterial metabolism of side chain fluorinated aromatics: cometabolism of 3-trifluoromethyl(TFM)-benzoate by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2 and Rhodococcus rubropertinctus N657. Arch Microbiol. 1988 Jan;149(3):188–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00422004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewers J., Freier-Schröder D., Knackmuss H. J. Selection of trichloroethene (TCE) degrading bacteria that resist inactivation by TCE. Arch Microbiol. 1990;154(4):410–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00276540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folsom B. R., Chapman P. J. Performance characterization of a model bioreactor for the biodegradation of trichloroethylene by Pseudomonas cepacia G4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1602–1608. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1602-1608.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folsom B. R., Chapman P. J., Pritchard P. H. Phenol and trichloroethylene degradation by Pseudomonas cepacia G4: kinetics and interactions between substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1279–1285. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1279-1285.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B. G., Borneman J. G., Wackett L. P., Lipscomb J. D. Haloalkene oxidation by the soluble methane monooxygenase from Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b: mechanistic and environmental implications. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 10;29(27):6419–6427. doi: 10.1021/bi00479a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman D. L., Gossett J. M. Biological reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene and trichloroethylene to ethylene under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2144–2151. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2144-2151.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Kim Y. Trichloroethylene degradation by two independent aromatic-degrading pathways in Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1179–1181. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1179-1181.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry S. M., Grbić-Galić D. Influence of endogenous and exogenous electron donors and trichloroethylene oxidation toxicity on trichloroethylene oxidation by methanotrophic cultures from a groundwater aquifer. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):236–244. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.236-244.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebler D. C., Guengerich F. P. Olefin oxidation by cytochrome P-450: evidence for group migration in catalytic intermediates formed with vinylidene chloride and trans-1-phenyl-1-butene. Biochemistry. 1983 Nov 22;22(24):5482–5489. doi: 10.1021/bi00293a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C. D., Palumbo A. V., Herbes S. E., Lidstrom M. E., Tyndall R. L., Gilmer P. J. Trichloroethylene biodegradation by a methane-oxidizing bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):951–956. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.951-956.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., Mahaffey W. R., Pritchard P. H. Biodegradation of trichloroethylene and involvement of an aromatic biodegradative pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):949–954. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.949-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., O'neill E. J., Pritchard P. H. Aerobic metabolism of trichloroethylene by a bacterial isolate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):383–384. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.383-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., Pritchard P. H. Trichloroethylene metabolism by microorganisms that degrade aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):604–606. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.604-606.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldenhuis R., Oedzes J. Y., van der Waarde J. J., Janssen D. B. Kinetics of chlorinated hydrocarbon degradation by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b and toxicity of trichloroethylene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.7-14.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldenhuis R., Vink R. L., Janssen D. B., Witholt B. Degradation of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b expressing soluble methane monooxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2819–2826. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2819-2826.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasche M. E., Hyman M. R., Arp D. J. Factors Limiting Aliphatic Chlorocarbon Degradation by Nitrosomonas europaea: Cometabolic Inactivation of Ammonia Monooxygenase and Substrate Specificity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):2986–2994. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.2986-2994.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scordilis G. E., Ree H., Lessie T. G. Identification of transposable elements which activate gene expression in Pseudomonas cepacia. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):8–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.8-13.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Montgomery S. O., Chapman P. J., Cuskey S. M., Pritchard P. H. Novel pathway of toluene catabolism in the trichloroethylene-degrading bacterium g4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1624–1629. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1624-1629.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields M. S., Montgomery S. O., Cuskey S. M., Chapman P. J., Pritchard P. H. Mutants of Pseudomonas cepacia G4 defective in catabolism of aromatic compounds and trichloroethylene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jul;57(7):1935–1941. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.7.1935-1941.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasek P. H., Frantz B., Sangodkar U. M., Haugland R. A., Chakrabarty A. M. Characterization and nucleotide sequence determination of a repeat element isolated from a 2,4,5-T degrading strain of Pseudomonas cepacia. Gene. 1989;76(2):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Brusseau G. A., Hanson R. S., Waclett L. P. Biodegradation of trichloroethylene by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3155–3161. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3155-3161.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannelli T., Logan M., Arciero D. M., Hooper A. B. Degradation of halogenated aliphatic compounds by the ammonia- oxidizing bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1169–1171. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1169-1171.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel T. M., McCarty P. L. Biotransformation of tetrachloroethylene to trichloroethylene, dichloroethylene, vinyl chloride, and carbon dioxide under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1080–1083. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1080-1083.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Brusseau G. A., Householder S. R., Hanson R. S. Survey of microbial oxygenases: trichloroethylene degradation by propane-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2960–2964. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2960-2964.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Degradation of trichloroethylene by toluene dioxygenase in whole-cell studies with Pseudomonas putida F1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1703–1708. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1703-1708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Householder S. R. Toxicity of Trichloroethylene to Pseudomonas putida F1 Is Mediated by Toluene Dioxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2723–2725. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2723-2725.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Wilson B. H. Biotransformation of trichloroethylene in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):242–243. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.242-243.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylstra G. J., McCombie W. R., Gibson D. T., Finette B. A. Toluene degradation by Pseudomonas putida F1: genetic organization of the tod operon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1498–1503. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1498-1503.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylstra G. J., Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Trichloroethylene degradation by Escherichia coli containing the cloned Pseudomonas putida F1 toluene dioxygenase genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3162–3166. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3162-3166.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


