Abstract
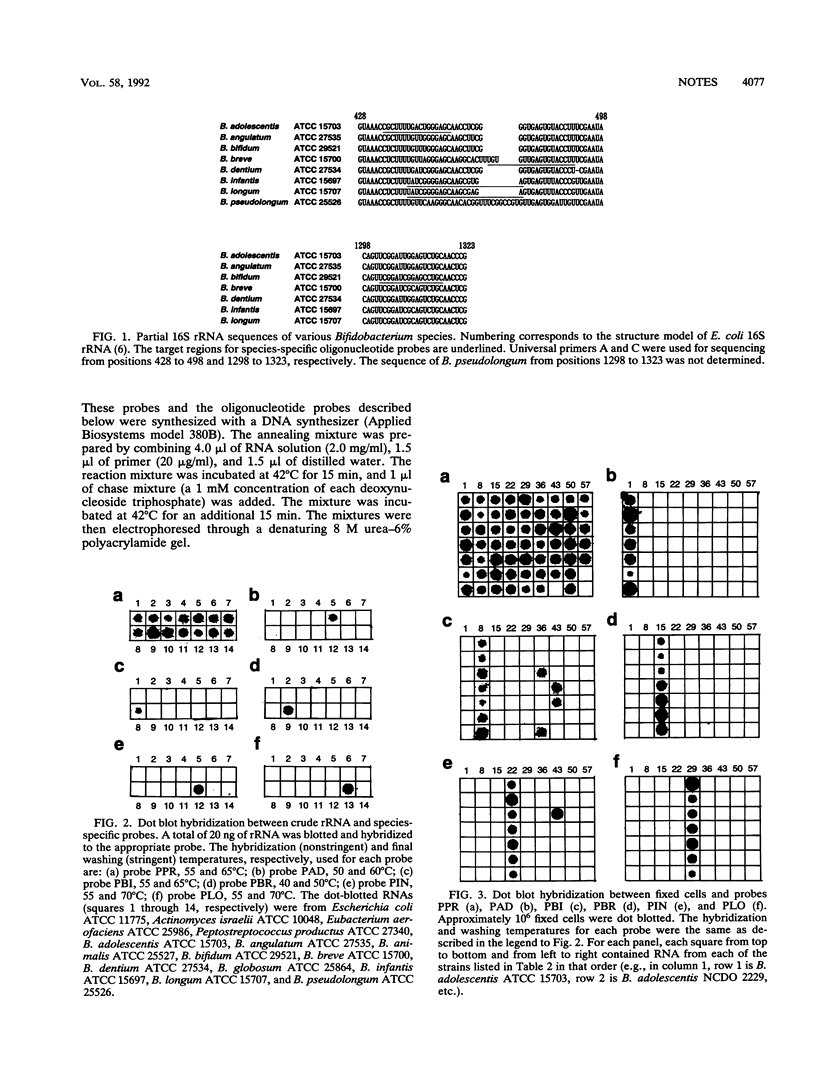
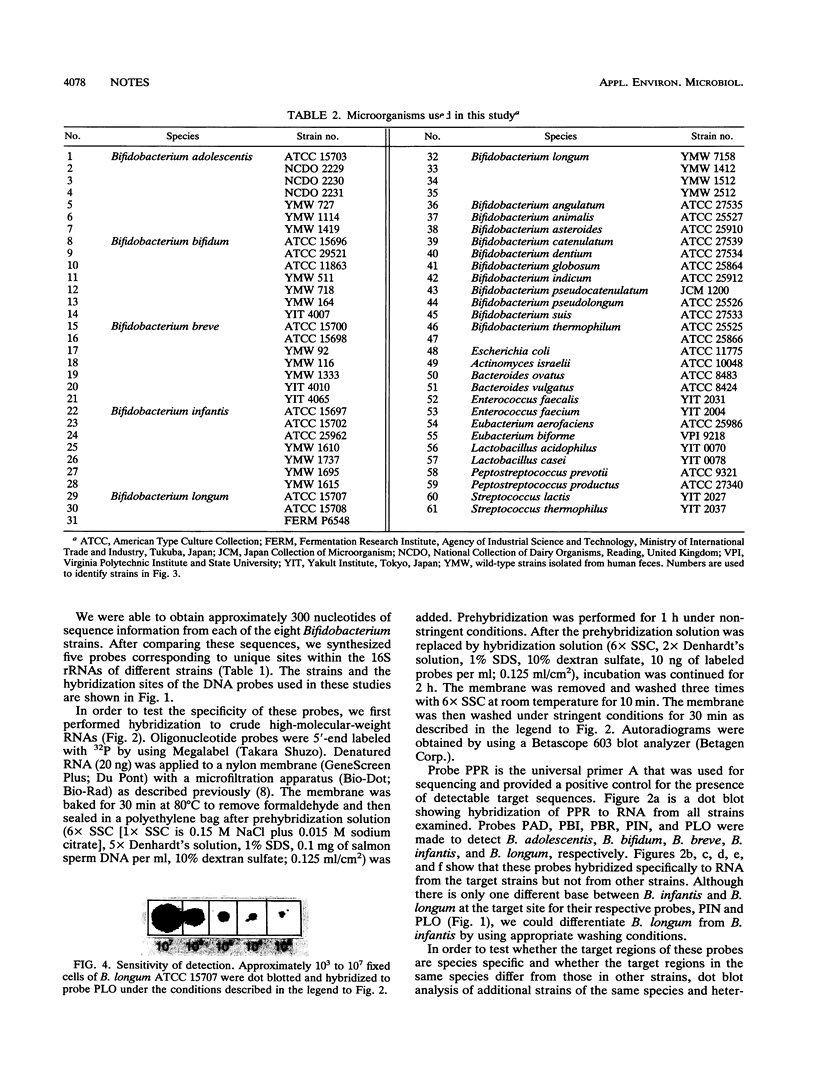
Portions of the 16S rRNA from closely related species of the genus Bifidobacterium that are found in the human intestinal microflora were sequenced in order to design species-specific oligonucleotide probes. Five oligonucleotide probes ranging from 16 to 19 bases in length and complementary to 16S rRNA sequences from Bifidobacterium adolescentis, B. bifidum, B. breve, B. infantis, and B. longum were synthesized. With crude high-molecular-weight RNA preparations as targets, these probes showed the desired species specificity, even down to a 1-nucleotide difference. For the practical evaluation of these probes, their specificity and sensitivity were tested against seven strains of the same species and 54 strains of heterologous bacteria with fixed whole cells as targets. The probes for B. adolescentis, B. breve, and B. longum showed efficient and specific hybridization. Although the probes for B. bifidum and B. infantis cross-reacted with a few bacterial strains not isolated from humans, these probes showed species specificity for human intestinal bacteria. These 16S rRNA probes should prove valuable for the identification and detection of human intestinal Bifidobacterium species.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshina S., Kahn S. M., Jiang W., Green P. H., Neu H. C., Chin N., Morotomi M., LoGerfo P., Weinstein I. B. Direct detection and amplification of Helicobacter pylori ribosomal 16S gene segments from gastric endoscopic biopsies. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Nov-Dec;13(6):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(90)90079-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morotomi M., Hoshina S., Green P., Neu H. C., LoGerfo P., Watanabe I., Mutai M., Weinstein I. B. Oligonucleotide probe for detection and identification of Campylobacter pylori. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2652–2655. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2652-2655.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Woese C. R. Secondary structure of 16S ribosomal RNA. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):403–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6163215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salama M., Sandine W., Giovannoni S. Development and application of oligonucleotide probes for identification of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1313–1318. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1313-1318.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackebrandt E., Charfreitag O. Partial 16S rRNA primary structure of five Actinomyces species: phylogenetic implications and development of an Actinomyces israelii-specific oligonucleotide probe. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jan;136(1):37–43. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. H., Blitchington R., Hindenach B., Greene R. C. Species-specific oligonucleotide probes for rRNA of Clostridium difficile and related species. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2484–2488. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2484-2488.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




