Abstract
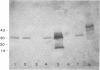
We studied the usefulness of an immunoblot technique for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) in strains and food extracts. Food samples (milk, yogurt, hot dog sausage, cheese, and mayonnaise) were artificially contaminated with SEA through SEE. Protein A did not interfere with the results; it appeared on electrophoresis gels as bands with molecular weights higher than those of the SEs. Other food proteins were not revealed by the technique. The immunoblot technique proved to be fast, specific, and sensitive for the detection of SEs in foods.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björk I., Petersson B. A., Sjöquist J. Some physiochemical properties of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):579–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASMAN E. P., BENNETT R. W. DETECTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN IN FOOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:181–189. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.181-189.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Pfister H., Rüegg O. Comparative evaluation of different enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay systems for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, C, and D. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):34–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.34-38.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa H., Igarashi H. Rapid latex agglutination test for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A to E that uses high-density latex particles. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2345–2348. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2345-2348.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Lucía E., Goyache J., Orden J. A., Blanco J. L., Ruiz-Santa-Quiteria J. A., Domínguez L., Suárez G. Production of enterotoxin A by supposedly nonenterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1447–1451. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1447-1451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLANDER H. O. PRODUCTION OF LARGE QUANTITIES OF ENTEROTOXIN B AND OTHER STAPHYLOCOCCAL TOXINS ON SOLID MEDIA. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:299–305. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Largen M. T., Newcomb J. R., Rogers T. J. Production and characterisation of monoclonal antibodies specific for staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Dec;27(4):263–270. doi: 10.1099/00222615-27-4-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. A., Reiser R. F., Bergdoll M. S. Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, C, D, and E in foods by radioimnunoassay, using staphyloccal cells containing protein A as immunoadsorbent. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):421–426. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.421-426.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orden J. A., Goyache J., Hernández F. J., Doménech A., Suárez G., Gómez-Lucía E. Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) by immunoblot combined with a semiautomated electrophoresis system. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Nov 22;144(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90086-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. E., Szabo R. Evaluation of the reversed passive latex agglutination (RPLA) test kits for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, C, and D in foods. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Sep;32(9):723–727. doi: 10.1139/m86-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser R., Conaway D., Bergdoll M. S. Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin in foods. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):83–85. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.83-85.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]