Abstract
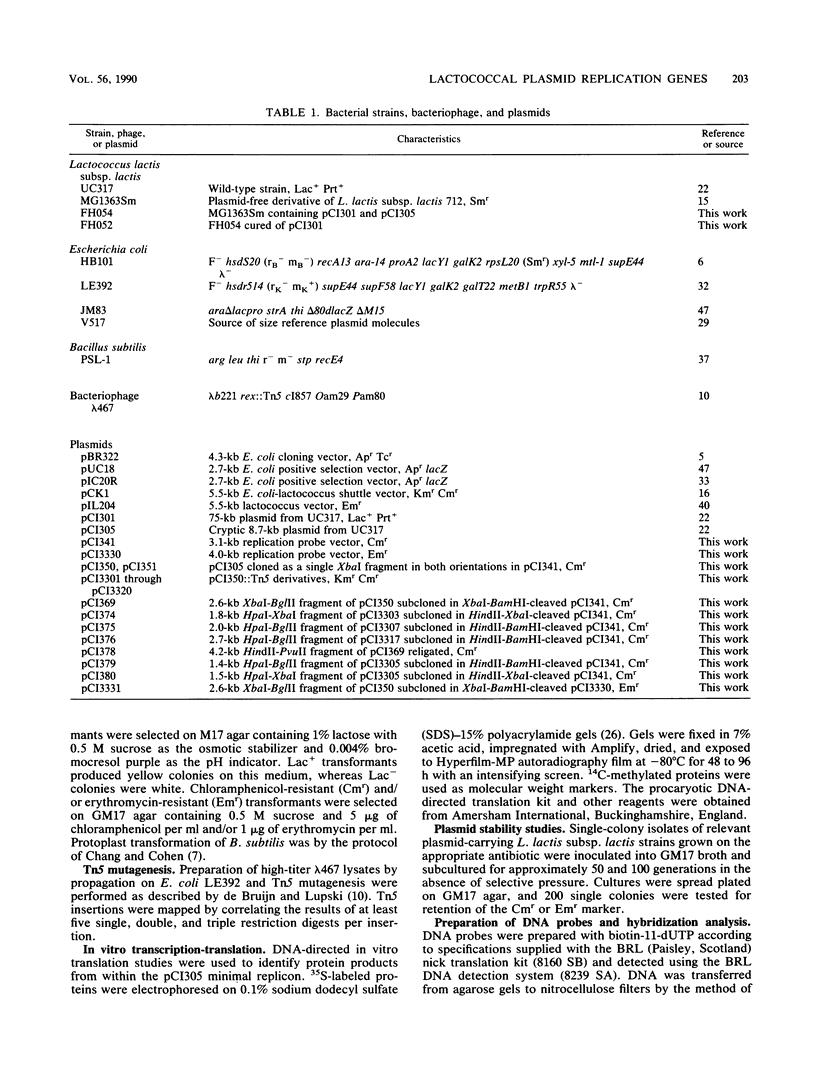
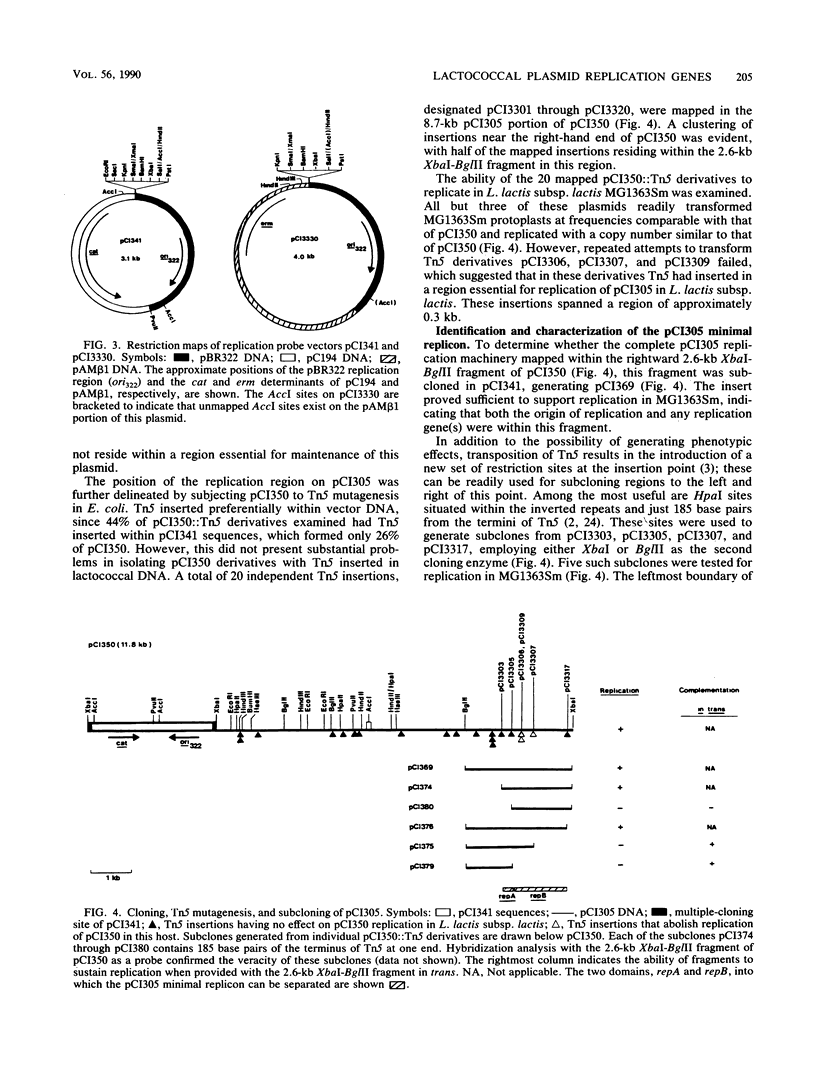
Replication functions of the stable, cryptic 8.7-kilobase (kb) plasmid pCI305 from multi-plasmid-containing Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis UC317 were studied. Analysis of this replicon was facilitated by the construction of replication probe vectors that consisted of the pBR322 replication region, a pUC18-derived multiple cloning site, and either the cat gene of pC194 (pCI341; 3.1 kb) or the erm gene of pAMβ1 (pCI3330; 4.0 kb). Plasmid pCI305 was introduced into plasmid-free L. lactis subsp. lactis MG1363Sm, a streptomycin-resistant derivative of MG1363, by a transformation procedure with the 75-kb lactose-proteinase plasmid pCI301 of UC317 as a marker plasmid. A combination of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis and subcloning in pCI341 and pCI3330 with individual Tn5 insertions around the replication region facilitated the identification of a 1.6-kb minimal replicon on pCI305. This region was separable into two domains: (i) a 1.3-kb region (repB) encoding a trans-acting function (in vitro transcription-translation studies suggested the involvement of a 48-kilodalton protein); and (ii) a 0.3-kb region (repA) sufficient to direct replication when provided with repB in trans and thus probably containing the origin of replication. Lactococcus-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors based on the pCI305 replication region were constructed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerswald E. A., Ludwig G., Schaller H. Structural analysis of Tn5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):107–113. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly C. The use of mesophilic cultures in the dairy industry. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Sep;49(3):297–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00399505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froseth B. R., Harlander S. K., McKay L. L. Plasmid-mediated reduced phage sensitivity in Streptococcus lactis KR5. J Dairy Sci. 1988 Feb;71(2):275–284. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(88)79555-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier M., Chopin M. C. Plasmid-Determined Systems for Restriction and Modification Activity and Abortive Infection in Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):923–927. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.923-927.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goze A., Ehrlich S. D. Replication of plasmids from Staphylococcus aureus in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7333–7337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes F., Caplice E., McSweeney A., Fitzgerald G. F., Daly C. pAMbeta1-Associated Mobilization of Proteinase Plasmids from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis UC317 and L. lactis subsp. cremoris UC205. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.195-201.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):815–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.815-825.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J., van der Vossen J. M., Venema G. Construction of plasmid cloning vectors for lactic streptococci which also replicate in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):726–731. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.726-731.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchansky J. B., Muriana P. M., Klaenhammer T. R. Application of electroporation for transfer of plasmid DNA to Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Leuconostoc, Listeria, Pediococcus, Bacillus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus and Propionibacterium. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):637–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag I. E., Viret J. F., Alonso J. C. Replication and incompatibility properties of plasmid pUB110 in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 May;212(2):232–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00334690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L. Functional properties of plasmids in lactic streptococci. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Sep;49(3):259–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00399502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Adler G. K., Majumder S., Khan S. A., Carleton S., Rosenblum W. D., Iordanescu S. Coding sequence for the pT181 repC product: a plasmid-coded protein uniquely required for replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4108–4112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Projan S. J., Kumar C. C., Carleton S., Gruss A., Highlander S. K., Kornblum J. Replication control for pT181, an indirectly regulated plasmid. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:299–320. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff G. R., Pène J. J. Molecular cloning with bifunctional plasmid vectors in Bacillus subtilis: isolation of a spontaneous mutant of Bacillus subtilis with enhanced transformability for Escherichia coli-propagated chimeric plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):934–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.934-936.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., de Vos W. M., Gavrieli J. Plasmid DNA in Streptococcus cremoris Wg2: Influence of pH on Selection in Chemostats of a Variant Lacking a Protease Plasmid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1272–1277. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1272-1277.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Projan S. J., Novick R. Comparative analysis of five related Staphylococcal plasmids. Plasmid. 1988 May;19(3):203–221. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Chopin A. Construction of a vector plasmid family and its use for molecular cloning in Streptococcus lactis. Biochimie. 1988 Apr;70(4):559–566. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villafane R., Bechhofer D. H., Narayanan C. S., Dubnau D. Replication control genes of plasmid pE194. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4822–4829. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4822-4829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosman B., Kooistra J., Olijve J., Venema G. Cloning in Escherichia coli of the gene specifying the DNA-entry nuclease of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosman B., Venema G. Introduction of a Streptococcus cremoris plasmid in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):920–921. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.920-921.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J., Lupski J. R. The use of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis in the rapid generation of correlated physical and genetic maps of DNA segments cloned into multicopy plasmids--a review. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Solar G. H., Puyet A., Espinosa M. Initiation signals for the conversion of single stranded to double stranded DNA forms in the streptococcal plasmid pLS1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5561–5580. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Riele H., Michel B., Ehrlich S. D. Are single-stranded circles intermediates in plasmid DNA replication? EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):631–637. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vossen J. M., Kok J., Venema G. Construction of cloning, promoter-screening, and terminator-screening shuttle vectors for Bacillus subtilis and Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):540–542. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.540-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vossen J. M., van der Lelie D., Venema G. Isolation and characterization of Streptococcus cremoris Wg2-specific promoters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2452–2457. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2452-2457.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




