Abstract
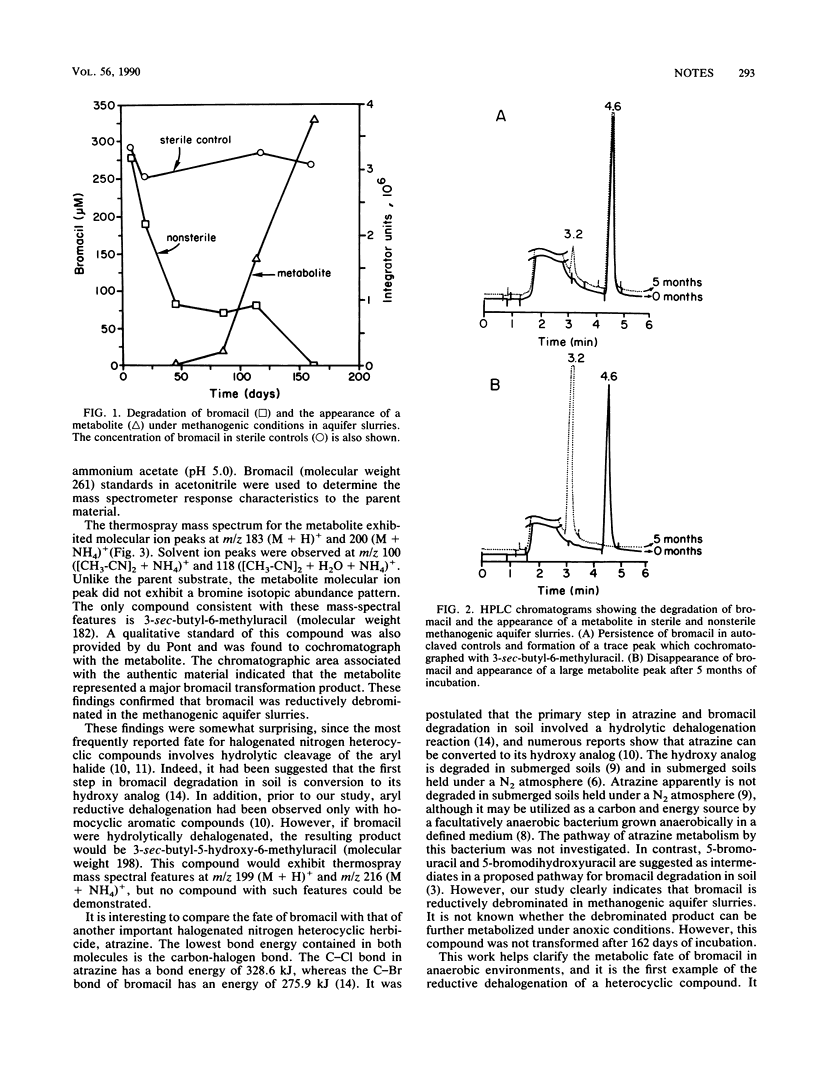
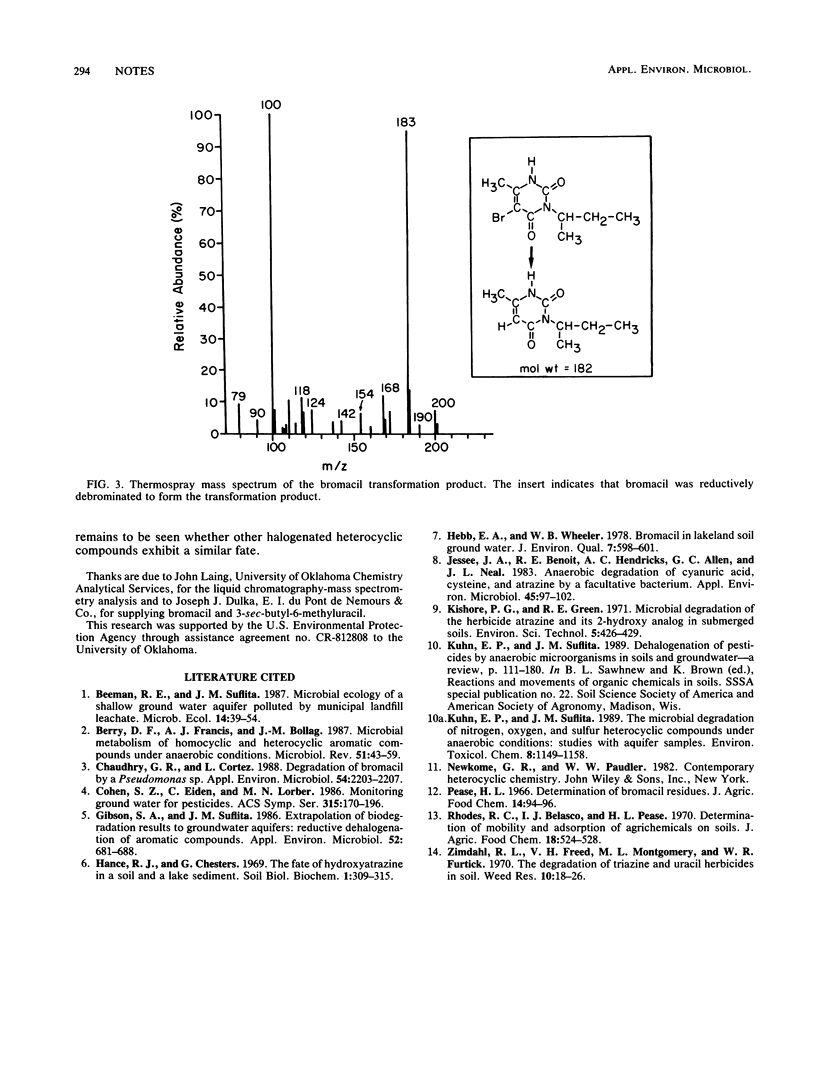
We studied the metabolic fate of bromacil in anaerobic aquifer slurries held under denitrifying, sulfate-reducing, or methanogenic conditions. Liquid chromatograhy-mass spectrometry of the slurries confirmed that bromacil was debrominated under methanogenic conditions but was not degraded under the other incubation conditions. This finding extends the range of aryl reductive dehalogenation reactions to include nitrogen heterocyclic compounds.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry D. F., Francis A. J., Bollag J. M. Microbial metabolism of homocyclic and heterocyclic aromatic compounds under anaerobic conditions. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):43–59. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.43-59.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry G. R., Cortez L. Degradation of bromacil by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Sep;54(9):2203–2207. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.9.2203-2207.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. A., Suflita J. M. Extrapolation of biodegradation results to groundwater aquifers: reductive dehalogenation of aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):681–688. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.681-688.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessee J. A., Benoit R. E., Hendricks A. C., Allen G. C., Neal J. L. Anaerobic degradation of cyanuric Acid, cysteine, and atrazine by a facultative anaerobic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.97-102.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. C., Belasco I. J., Pease H. L. Determination of mobility and adsorption of agrichemicals on soils. J Agric Food Chem. 1970 May-Jun;18(3):524–528. doi: 10.1021/jf60169a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


