Abstract
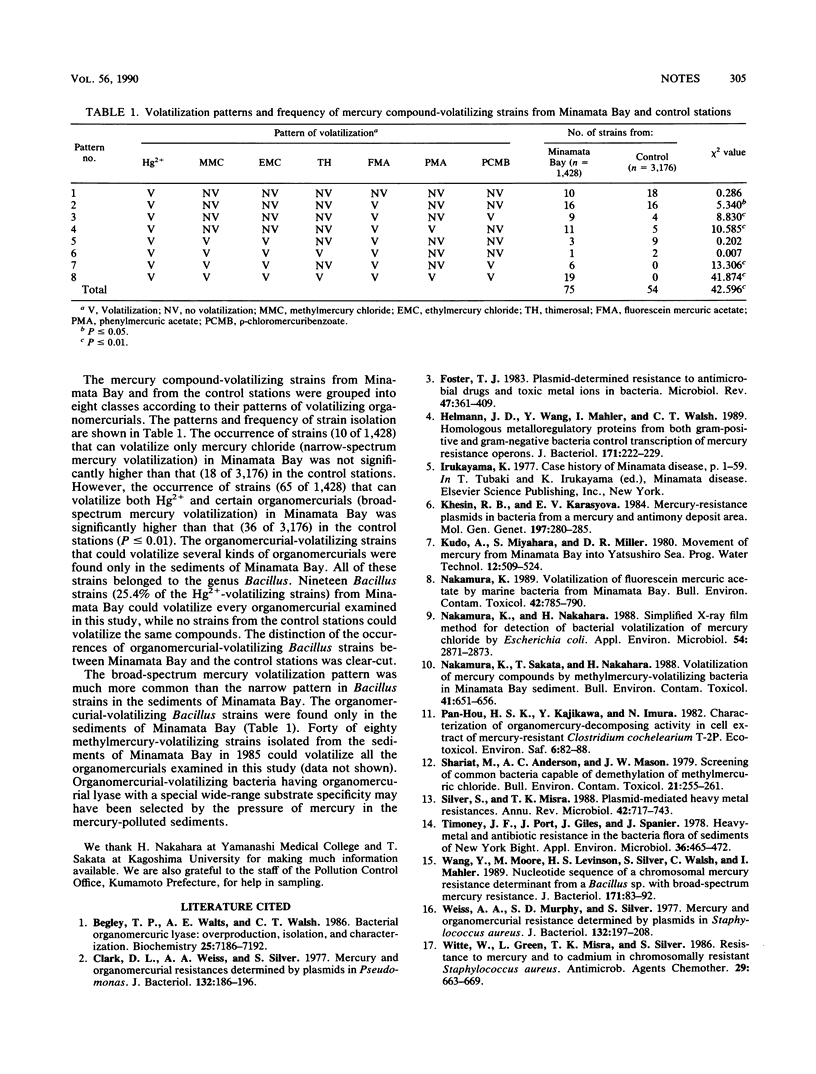
A total of 4,604 bacterial strains isolated from the sediments of Minamata Bay and nearby low-level-mercury stations (control stations) were screened for the ability to volatilize mercury from inorganic and organic mercurial compounds. The strains that volatilize mercury from several kinds of organomercurials were found only in the sediments of Minamata Bay.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Begley T. P., Walts A. E., Walsh C. T. Bacterial organomercurial lyase: overproduction, isolation, and characterization. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):7186–7192. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. L., Weiss A. A., Silver S. Mercury and organomercurial resistances determined by plasmids in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):186–196. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.186-196.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J. Plasmid-determined resistance to antimicrobial drugs and toxic metal ions in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):361–409. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.361-409.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Wang Y., Mahler I., Walsh C. T. Homologous metalloregulatory proteins from both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria control transcription of mercury resistance operons. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):222–229. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.222-229.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khesin R. B., Karasyova E. V. Mercury-resistant plasmids in bacteria from a mercury and antimony deposit area. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):280–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00330974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Nakahara H. Simplified X-ray film method for detection of bacterial volatilization of mercury chloride by Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2871–2873. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2871-2873.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Sakata T., Nakahara H. Volatilization of mercury compounds by methylmercury-volatilizing bacteria in Minamata Bay sediment. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1988 Nov;41(5):651–656. doi: 10.1007/BF02021014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K. Volatilization of fluorescein mercuric acetate by marine bacteria from Minamata Bay. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1989 May;42(5):785–790. doi: 10.1007/BF01700404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan-Hou H. S., Kajikawa Y., Imura N. Characterization of organomercury-decomposing activity in cell extract of mercury-resistant Clostridium cochlearium T-2P. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 1982 Feb;6(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0147-6513(82)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shariat M., Anderson A. C., Mason J. W. Screening of common bacteria capable of demethylation of methylmercuric chloride. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1979 Jan;21(1-2):255–261. doi: 10.1007/BF01685420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Misra T. K. Plasmid-mediated heavy metal resistances. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:717–743. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. F., Port J., Giles J., Spanier J. Heavy-metal and antibiotic resistance in the bacterial flora of sediments of New York Bight. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):465–472. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.465-472.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Moore M., Levinson H. S., Silver S., Walsh C., Mahler I. Nucleotide sequence of a chromosomal mercury resistance determinant from a Bacillus sp. with broad-spectrum mercury resistance. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):83–92. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.83-92.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Murphy S. D., Silver S. Mercury and organomercurial resistances determined by plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):197–208. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.197-208.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte W., Green L., Misra T. K., Silver S. Resistance to mercury and to cadmium in chromosomally resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):663–669. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



