Abstract
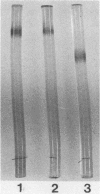
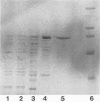
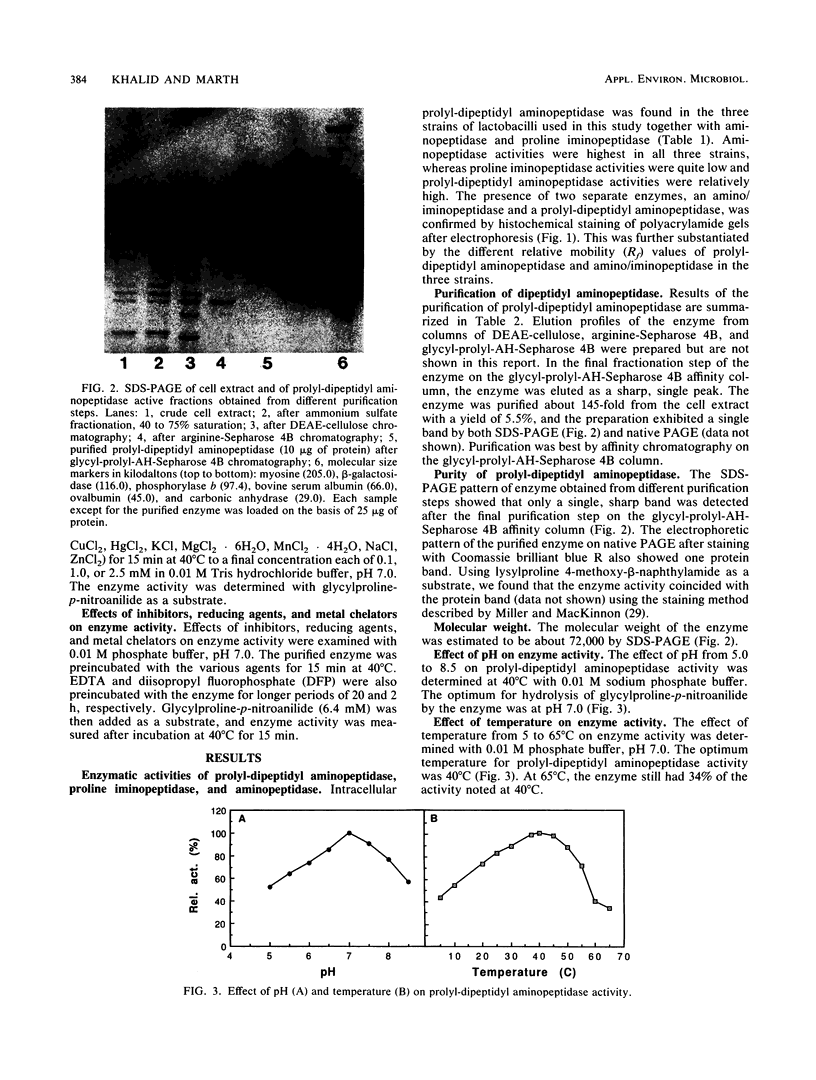
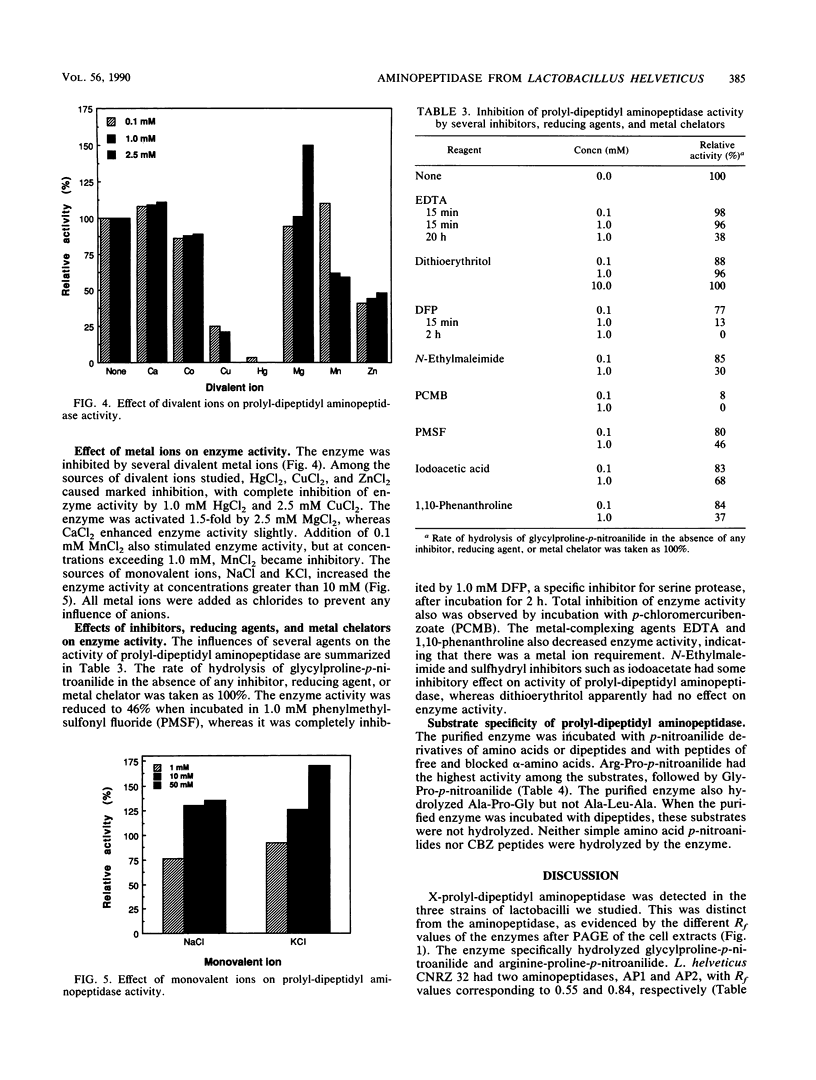
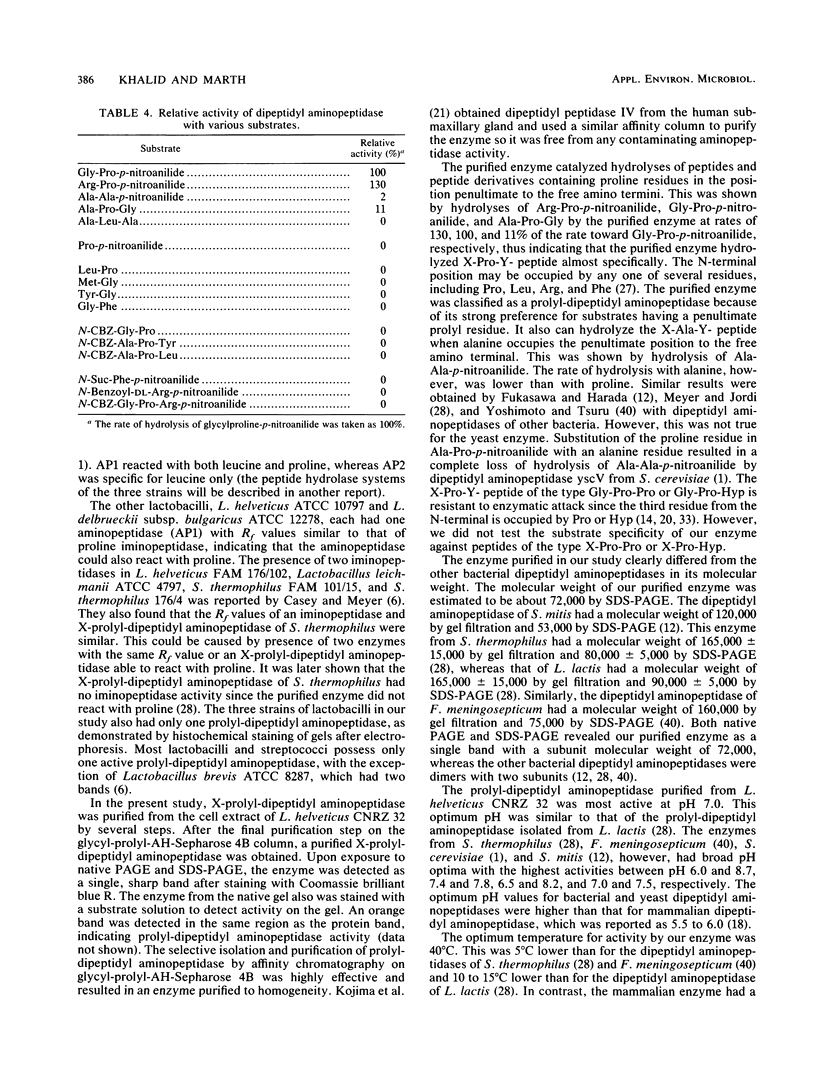
X-prolyl-dipeptidyl aminopeptidase, which hydrolyzed Gly-Pro-p-nitroanilide (relative activity [RA] = 100%) and Arg-Pro-p-nitroanilide (RA, 130%), was purified to homogeneity from the cell extract of Lactobacillus helveticus CNRZ 32. The enzyme also hydrolyzed Ala-Pro-Gly (RA, 11%) and Ala-Ala-p-nitroanilide (RA, 2%) but was not active on Ala-Leu-Ala, dipeptides, and endopeptidase and carboxypeptidase substrates. The enzyme was purified 145-fold by streptomycin sulfate precipitation, ammonium sulfate fractionation, and a series of column chromatographies on DEAE-cellulose, arginine-Sepharose 4B, and glycyl-prolyl-AH-Sepharose 4B. The purified enzyme appeared as a single band on native polyacrylamide gel and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoreses and had a molecular weight of 72,000. Optima for activity by the purified enzyme were pH 7.0 and 40°C. The enzyme was incubated at 40°C for 15 min with various metal ions. It was activated by Mg2+ (2.5 mM), Ca2+ (0.1 to 2.5 mM), Na+ (10 to 50 mM), and K+ (10 to 50 mM) and was inhibited by Hg2+ (0.1 to 2.5 mM), Cu2+ (0.1 to 2.5 mM), and Zn2+ (0.1 to 2.5 mM). Enzyme activity was partially inhibited by EDTA (1.0 mM, 20 h at 40°C), 1,10-phenanthroline (1.0 mM, 15 min at 40°C), phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (1.0 mM), N-ethylmaleimide (1.0 mM), and iodoacetate (1.0 mM). It was completely inhibited by diisopropyl fluorophosphate (1.0 mM, 2 h at 40°C) and p-chloromercuribenzoate (1.0 mM, 15 min at 40°C). The enzyme was not affected by dithioerythritol (1.0 to 10 mM).
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth A., Schulz H., Neubert K. Untersuchungen zur Reinigung und Charakterisierung der Dipeptidylaminopeptidase IV. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1974;32(2-3):157–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey M. G., Meyer J. Presence of X-prolyl-dipeptidyl-peptidase in lactic acid bacteria. J Dairy Sci. 1985 Dec;68(12):3212–3215. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(85)81229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Soda M., Desmazeaud M. J. Les peptide-hydrolases des lactobacilles du groupe Thermobacterium. I. Mise en évidence de ces activités chez Lactobacillus helveticus, L. acidophilus, L. lactis et L. bulgaricus. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Oct;28(10):1181–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa K. M., Fukasawa K., Hiraoka B. Y., Harada M. Comparison of dipeptidyl peptidase IV prepared from pig liver and kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 15;657(1):179–189. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa K. M., Harada M. Purification and properties of dipeptidyl peptidase IV from Streptococcus mitis ATCC 9811. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Aug;210(1):230–237. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonschor H., Schäfer W. Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV. Reinigung für die Verwendung zur Peptidsequenzierung. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Feb;366(2):157–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada M., Fukasawa K. M., Fukasawa K., Nagatsu T. Inhibitory action of proline-containing peptides on Xaa-Pro-dipeptidylaminopeptidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 26;705(2):288–290. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90191-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann E., Mentlein R. Complementary action of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and aminopeptidase M in the digestion of beta-casein. J Dairy Res. 1986 May;53(2):229–236. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900024833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopsu-Havu V. K., Rintola P., Glenner G. G. A hog kidney aminopeptidase liberating N-terminal dipeptides. Partial purification and characteristics. Acta Chem Scand. 1968;22(1):299–308. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.22-0299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopsu-Havu V. K., Sarimo S. R. Purification and characterization of an aminopeptidase hydrolyzing glycyl-proline-naphthylamide. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Nov;348(11):1540–1550. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1967.348.1.1540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai K., Hama T., Kato T. Purification and properties of rat brain dipeptidyl aminopeptidase. J Biochem. 1983 Feb;93(2):431–437. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Booth A. G., George S. G., Ingram J., Kershaw D., Wood E. J., Young A. R. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, a kidney brush-border serine peptidase. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):169–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1570169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima K., Hama T., Kato T., Nagatsu T. Rapid chromatographic purification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human submaxillary gland. J Chromatogr. 1980 Feb 29;189(2):233–240. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)81523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. A modified ninhydrin reagent for the photometric determination of amino acids and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):907–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Jordi R. Purification and characterization of X-prolyl-dipeptidyl-aminopeptidase from Lactobacillus lactis and from Streptococcus thermophilus. J Dairy Sci. 1987 Apr;70(4):738–745. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(87)80068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Mackinnon K. Peptidase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):355–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.355-363.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita T., Deguchi Y., Yajima M., Sakurai T., Yura T. Multiple nutritional requirements of lactobacilli: genetic lesions affecting amino acid biosynthetic pathways. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):64–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.64-71.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oya H., Harada M., Nagatsu T. Peptidase activity of glycylprolyl beta-naphthylamidase from human submaxillary gland. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Jun;19(6):489–491. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Fischl M., Orlowski R. C., Walter R. Post-proline cleaving enzyme and post-proline dipeptidyl aminopeptidase. Comparison of two peptidases with high specificity for proline residues. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3708–3716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Tsuru D. Proline-specific dipeptidyl aminopeptidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum. J Biochem. 1982 Jun;91(6):1899–1906. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]