Abstract
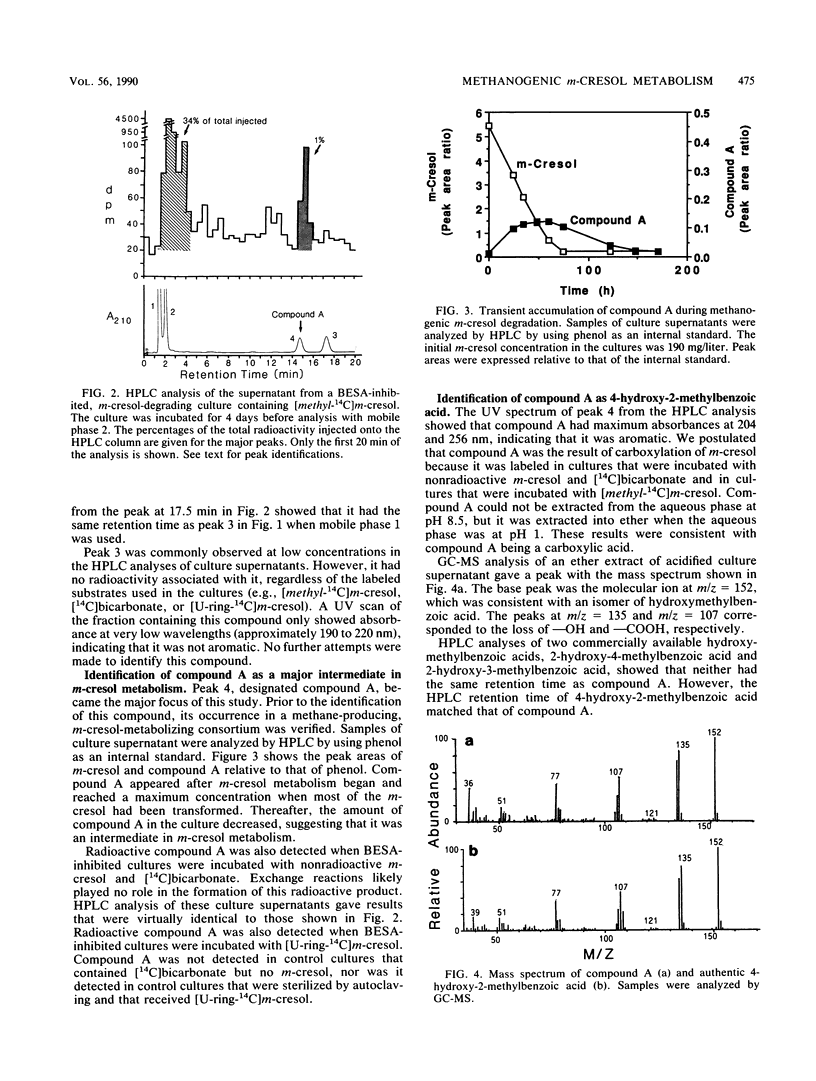
The metabolism of m-cresol by methanogenic cultures enriched from domestic sewage sludge was investigated. In the initial studies, bromoethanesulfonic acid was used to inhibit methane production. This led to the accumulation of 4.0 ± 0.8 mol of acetate per mol of m-cresol metabolized. These results suggested that CO2 incorporation occurred because each molecule of m-cresol contained seven carbon atoms, whereas four molecules of acetate product contained a total of eight carbon atoms. To verify this, [14C]bicarbonate was added to bromoethanesulfonic acid-inhibited cultures, and those cultures yielded [14C]acetate. Of the label recovered as acetate, 89% was found in the carboxyl position. Similar cultures fed [methyl-14C]m-cresol yielded methyl-labeled acetate. A 14C-labeled transient intermediate was detected in cultures given either m-cresol and [14C]bicarbonate or bicarbonate and [methyl-14C]m-cresol. The intermediate was identified as 4-hydroxy-2-methylbenzoic acid. In addition, another metabolite was detected and identified as 2-methylbenzoic acid. This compound appeared to be produced only sporadically, and it accumulated in the medium, suggesting that the dehydroxylation of 4-hydroxy-2-methylbenzoic acid led to an apparent dead-end product.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boone D. R. Terminal reactions in the anaerobic digestion of animal waste. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):57–64. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.57-64.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossert I. D., Young L. Y. Anaerobic oxidation of p-cresol by a denitrifying bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1117–1122. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1117-1122.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd S. A., Shelton D. R., Berry D., Tiedje J. M. Anaerobic biodegradation of phenolic compounds in digested sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.50-54.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Fuchs G. Anaerobic degradation of aromatic compounds. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:289–317. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINA L. R., FISKIN A. M. The anaerobic decomposition of benzoic acid during methane fermentation. II. Fate of carbons one and seven. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Dec;91:163–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorak P. M., Westlake D. W. Fungal Metabolism of n-Alkylbenzenes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):435–437. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.435-437.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith C. L., Bridges R. L., Fina L. R., Iverson K. L., Cloran J. A. The anaerobic decomposition of benzoic acid during methane fermentation. IV. Dearomatization of the ring and volatile fatty acids formed on ring rupture. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Aug 1;118(2):173–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00415726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. P., Zeyer J., Eicher P., Schwarzenbach R. P. Anaerobic degradation of alkylated benzenes in denitrifying laboratory aquifer columns. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.490-496.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHARES E. F. Degradation of labeled propionic and acetic acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Sep;33(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolenski W. J., Suflita J. M. Biodegradation of cresol isomers in anoxic aquifers. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):710–716. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.710-716.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Rupprecht E., Jungermann K. Separation of 14C-formate from CO2 fixation metabolites by isoionic-exchange chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1970 Dec;38(2):461–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschech A., Fuchs G. Anaerobic degradation of phenol by pure cultures of newly isolated denitrifying pseudomonads. Arch Microbiol. 1987 Sep;148(3):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00414814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



