Abstract
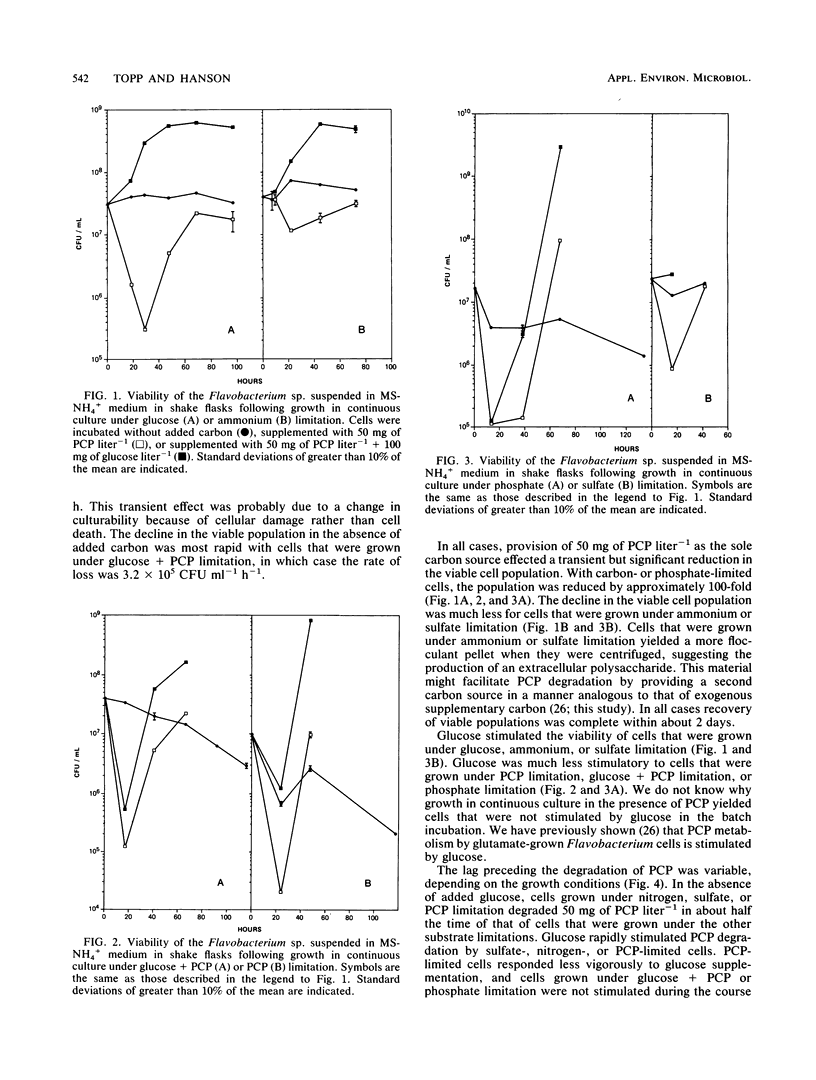
A Flavobacterium sp. was grown in continuous culture limited for growth with ammonium, phosphate, sulfate, glucose, glucose + pentachlorophenol (PCP) (0.065 h -1), or PCP. Cells ere harvested, washed, and suspended to 3 x 10(7) cells ml (-1) in shake flasks containing a complete mineral salts medium without added carbon or supplemented with 50 mg of PCP ml(-1) or 50 mg of PCP ml(-1) + 100 mg of glucose ml(-1). The PCP concentration and the viable cell density were determined periodically. Cells that were grown under phosphate, glucose, or glucose + PCP limitation were more sensitive to PCP and took longer to degrade 50 mg of PCP ml(-1) than did cells that very were grown under ammonium, sulfate, or PCP limitation. Glucose stimulated viability and PCP degradation in all cases except when the cells were grown under carbon limitation with glucose and PCP added together as the carbon source. These results indicate that there is a relationship between nutrient limitation, phenotypic variation, and the sensitivity to and degradation of PCP by this organism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown M. R., Williams P. Influence of substrate limitation and growth phase on sensitivity to antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):7–14. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu J. P., Kirsch E. J. Metabolism of pentachlorophenol by an axenic bacterial culture. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):1033–1035. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.1033-1035.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgehill R. U., Finn R. K. Microbial treatment of soil to remove pentachlorophenol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1122–1125. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.1122-1125.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P., Brown M. R. Influence of growth rate and nutrient limitation on the gross cellular composition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its resistance to 3- and 4-chlorophenol. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1066–1072. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1066-1072.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder W., Dijkhuizen L. Physiological responses to nutrient limitation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbane J. J., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Detoxification of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid from contaminated soil by Pseudomonas cepacia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1697–1700. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1697-1700.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnikin D. E., Abdolrahimzadeh H., Baddiley J. Replacement of acidic phosphates by acidic glycolipids in Pseudomonas diminuta. Nature. 1974 May 17;249(454):268–269. doi: 10.1038/249268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnikin D. E., Abdolrahimzadeh H. The replacement of phosphatidylethanolamine and acidic phospholipids by an ornithine-amide lipid and a minor phosphorus-free lipid in Pseudomonas fluorescens NCMB 129. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 1;43(3):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80655-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatello J. J., Martinson M. M., Steiert J. G., Carlson R. E., Crawford R. L. Biodegradation and photolysis of pentachlorophenol in artificial freshwater streams. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1024–1031. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1024-1031.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Tempest D. W. Phenotypic variability of the envelope proteins of Klebsiella aerogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):361–370. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saber D. L., Crawford R. L. Isolation and characterization of Flavobacterium strains that degrade pentachlorophenol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1512–1518. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1512-1518.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanlake G. J., Finn R. K. Isolation and characterization of a pentachlorophenol-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1421–1427. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1421-1427.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert J. G., Pignatello J. J., Crawford R. L. Degradation of chlorinated phenols by a pentachlorophenol-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):907–910. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.907-910.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T. Metabolism of pentachlorophenol by a soil microbe. J Environ Sci Health B. 1977;12(2):113–127. doi: 10.1080/03601237709372057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp E., Crawford R. L., Hanson R. S. Influence of readily metabolizable carbon on pentachlorophenol metabolism by a pentachlorophenol-degrading Flavobacterium sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2452–2459. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2452-2459.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. E., Finn R. K. Growth rates of a pseudomonad on 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4-dichlorophenol. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.181-184.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



