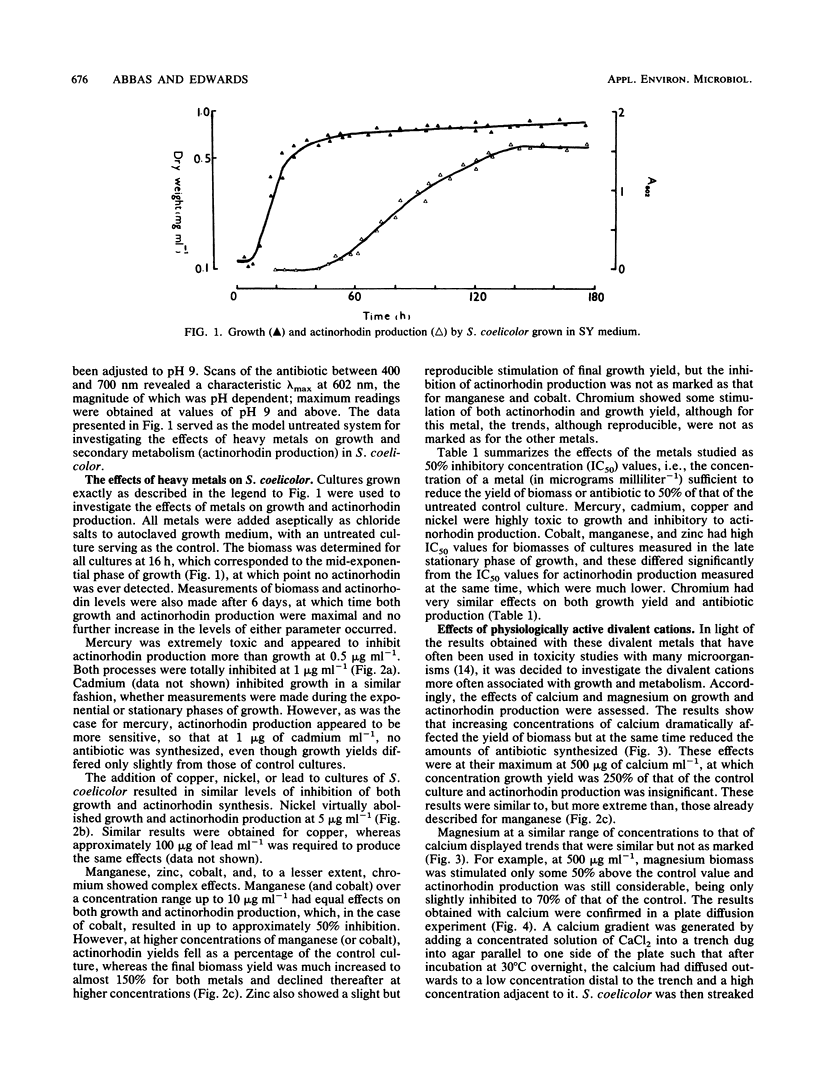
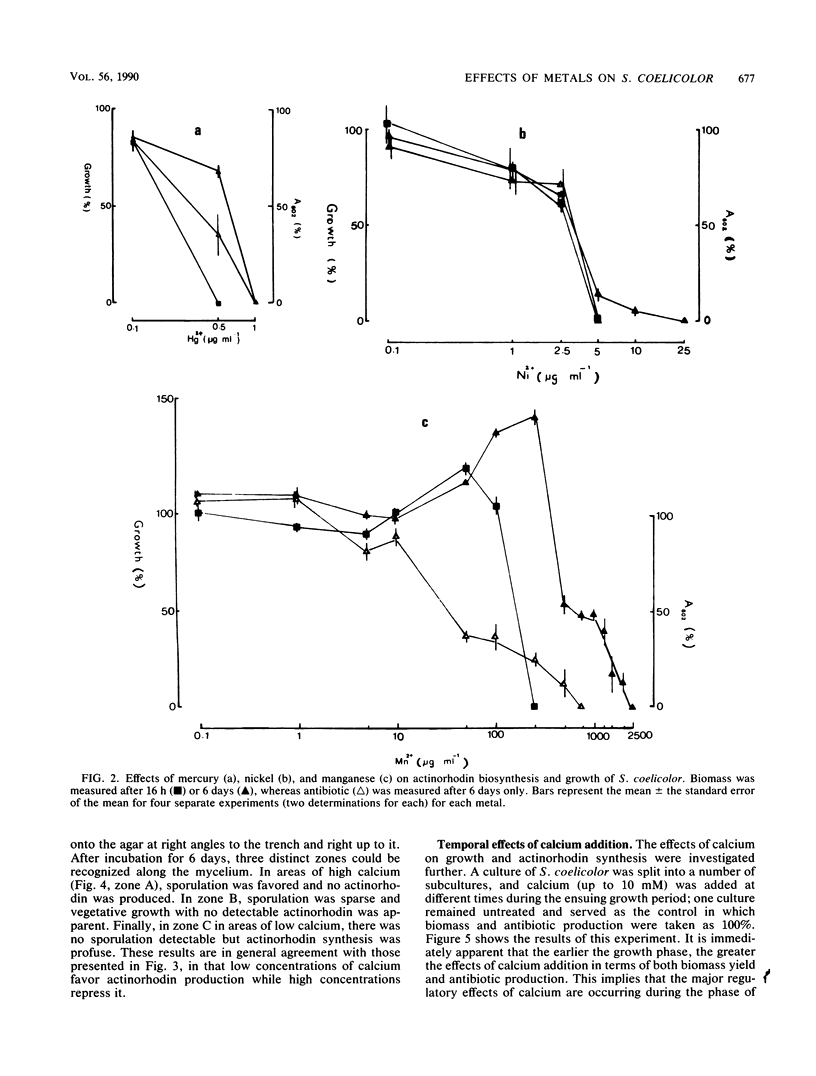
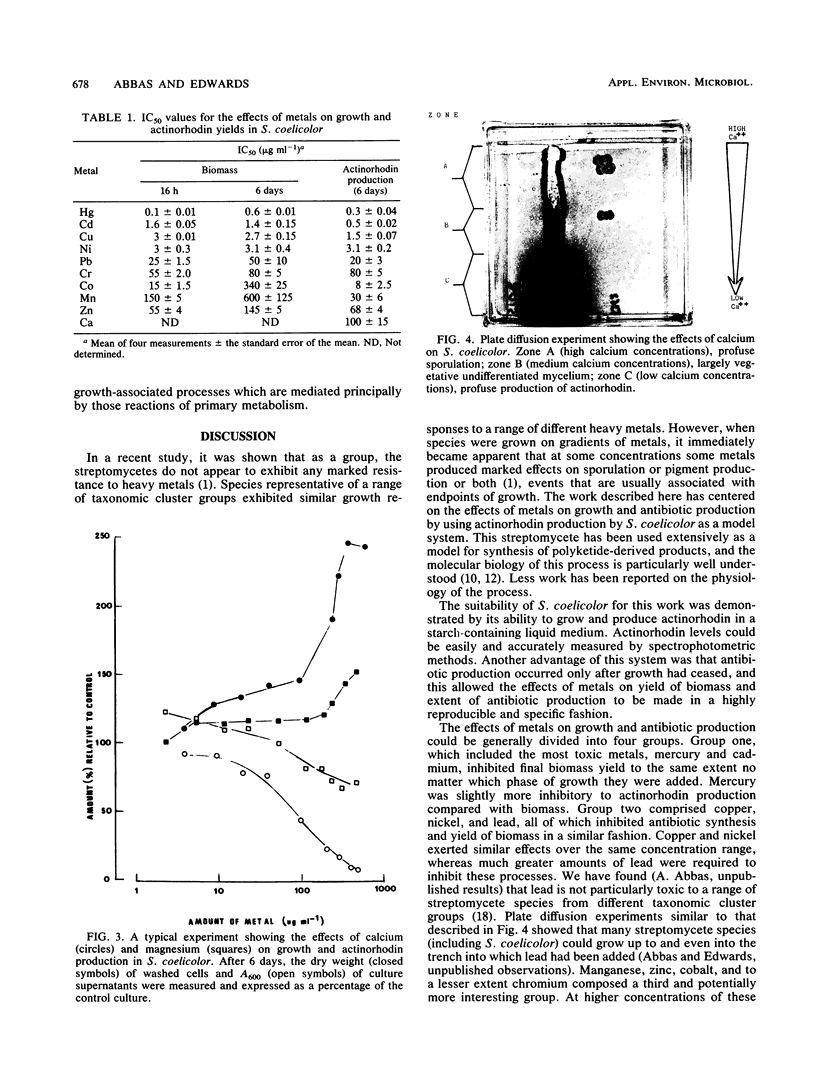
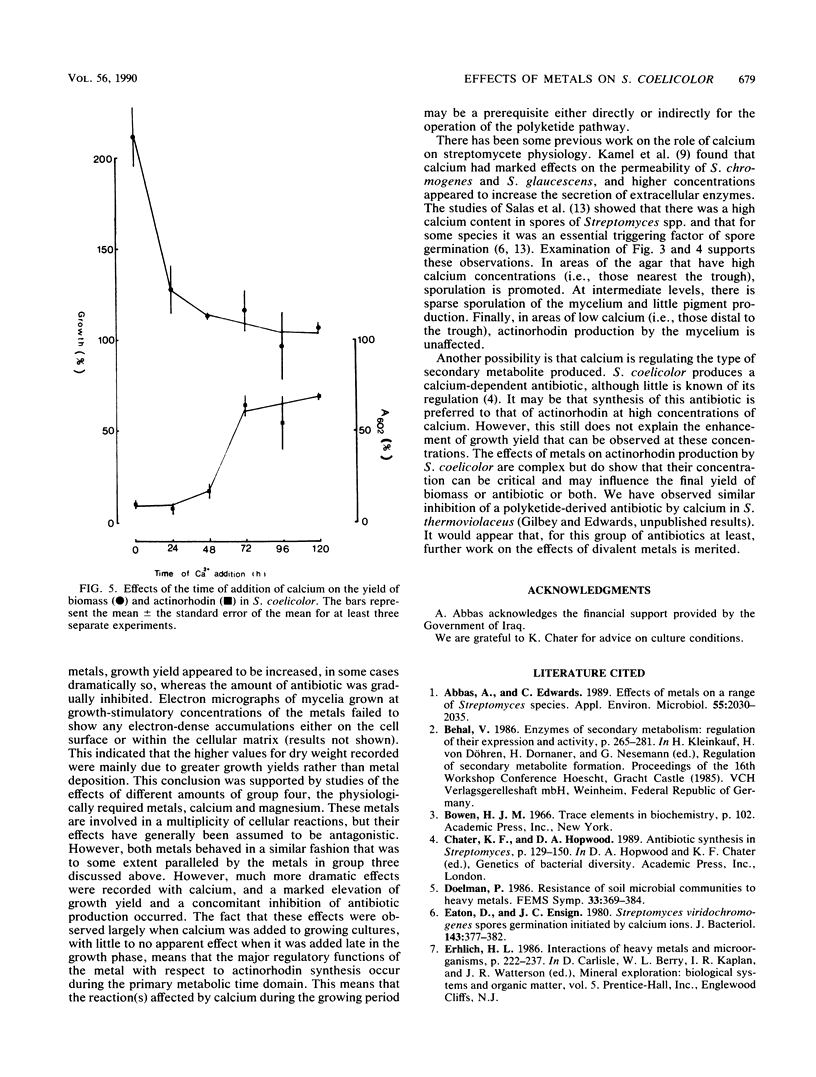
Abstract
Actinorhodin production by Streptomyces coelicolor was used as a model system to study the effects of metals on growth and polyketide synthesis in a streptomycete. Numerous metals were tested in cultures grown in liquid media. Mercury and cadmium were highly toxic, and copper, nickel, and lead were less so, but all tended to inhibit both growth and antibiotic synthesis to a similar extent. Unexpectedly, manganese, cobalt, zinc, and, to a lesser extent, chromium caused complex effects that in general resulted in some enhancement of growth yield but a reduction in antibiotic titers. These complex effects meant that cobalt, manganese, and zinc had lower 50% inhibitory concentrations for antibiotic yields compared with those for biomass. The physiologically active divalent cations calcium and magnesium were also tested. Calcium at high concentrations was particularly effective in reducing antibiotic titers and enhancing growth yields. By adding calcium at different phases of growth, it could be demonstrated that it was most effective in reducing the antibiotic yield when added during the early growth phase. Addition during the antibiotic-producing phase resulted in little reduction of final actinorhodin titers.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas Ala, Edwards Clive. Effects of Metals on a Range of Streptomyces Species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):2030–2035. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.2030-2035.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D., Ensign J. C. Streptomyces viridochromogenes spore germination initiated by calcium ions. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):377–382. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.377-382.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpartida F., Hopwood D. A. Physical and genetic characterisation of the gene cluster for the antibiotic actinorhodin in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):66–73. doi: 10.1007/BF02428033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd B. A., Hopwood D. A. Genetics of actinorhodin biosynthesis by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):35–43. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas J. A., Guijarro J. A., Hardisson C. High calcium content in Streptomyces spores and its release as an early event during spore germination. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1316–1323. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1316-1323.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Ulmer D. D. Biochemical effects of mercury, cadmium, and lead. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41(10):91–128. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. T., Goodfellow M., Alderson G., Wellington E. M., Sneath P. H., Sackin M. J. Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jun;129(6):1743–1813. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-6-1743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




