Abstract
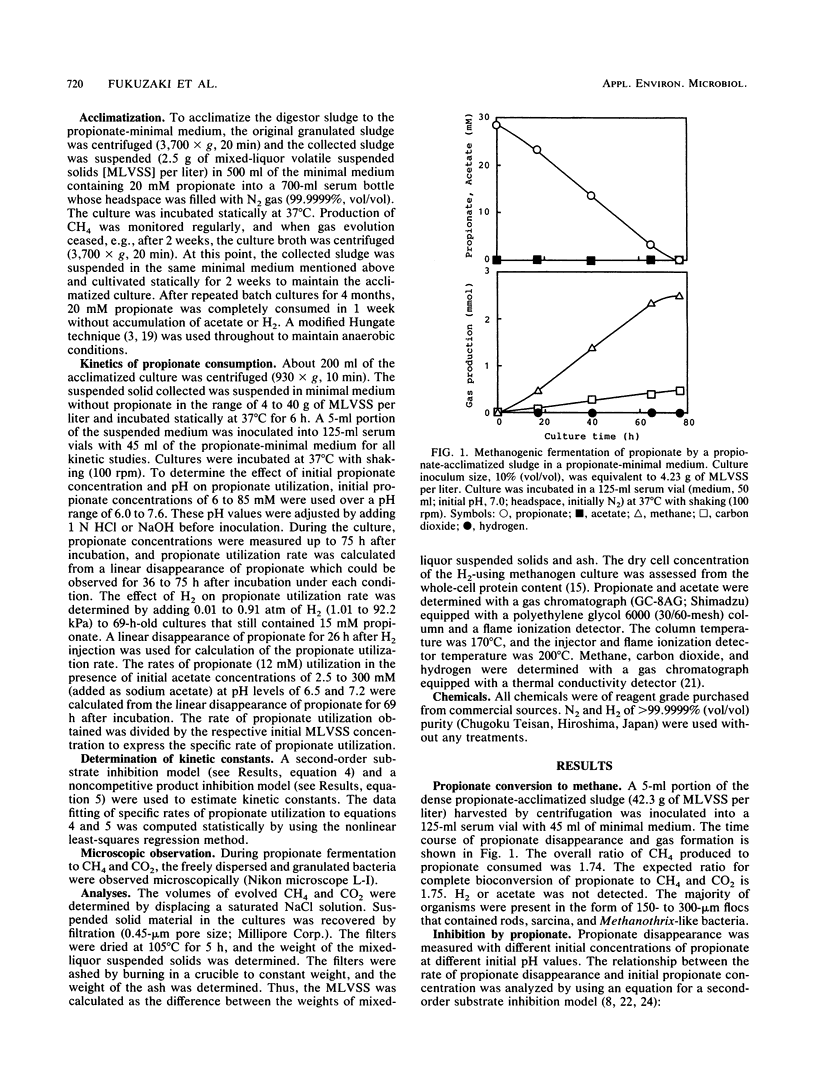
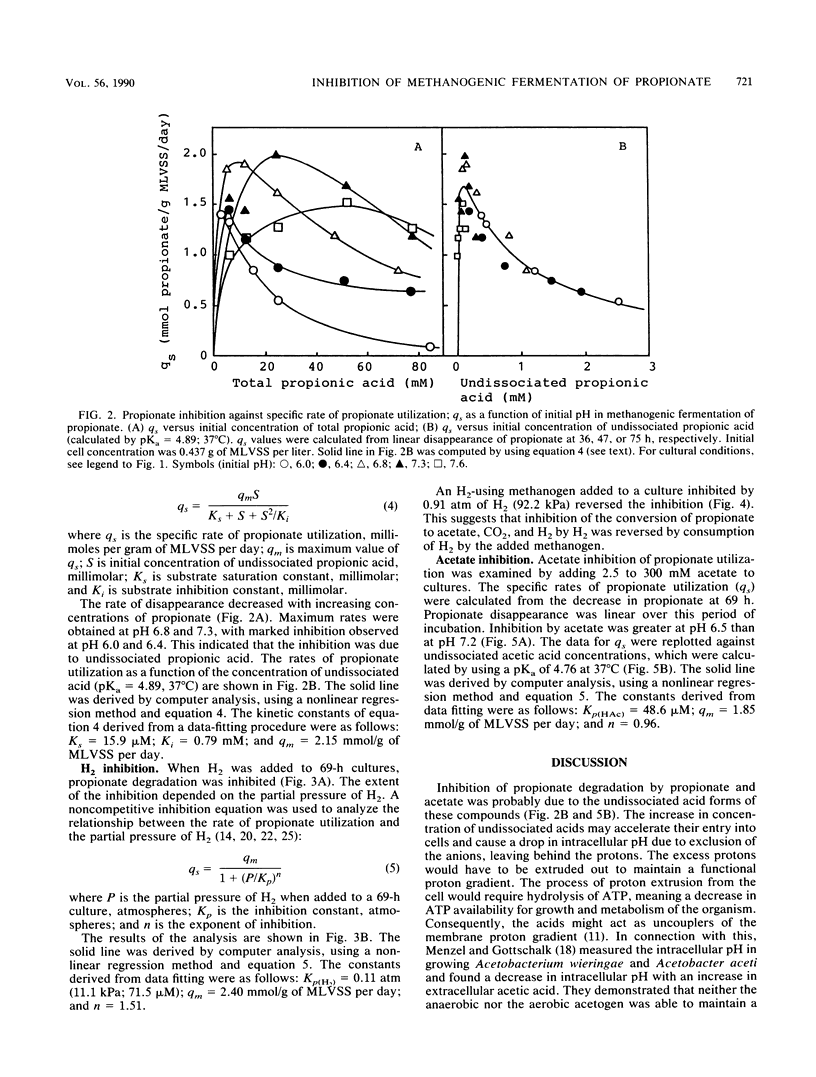
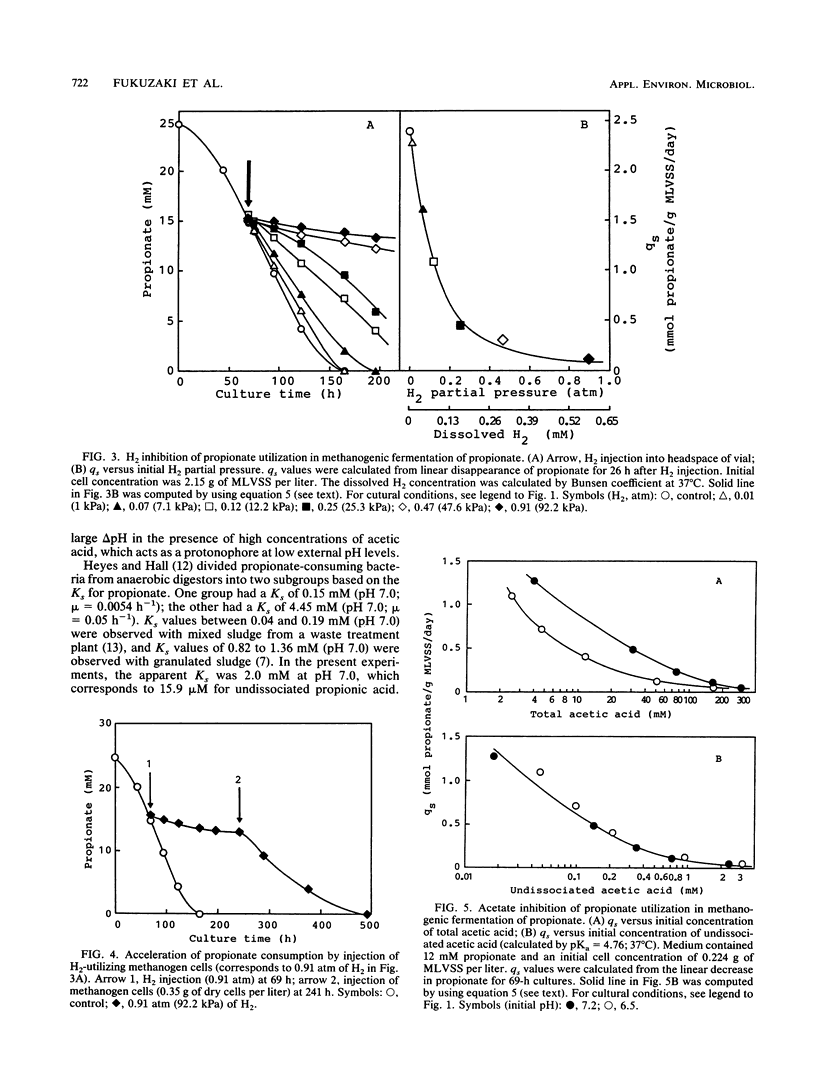
Inhibition of the fermentation of propionate to methane and carbon dioxide by hydrogen, acetate, and propionate was analyzed with a mesophilic propionate-acclimatized sludge that consisted of numerous flocs (size, 150 to 300 μm). The acclimatized sludge could convert propionate to methane and carbon dioxide stoichiometrically without accumulating hydrogen and acetate in a propionate-minimal medium. Inhibition of propionate utilization by propionate could be analyzed by a second-order substrate inhibition model (shown below) given that the substrate saturation constant, Ks, was 15.9 μM; the substrate inhibition constant, Ki, was 0.79 mM; and the maximum specific rate of propionate utilization, qm, was 2.15 mmol/g of mixed-liquor volatile suspended solids (MLVSS) per day: qs = qmS/[Ks + S + (S2/Ki)], where qs is the specific rate of propionate utilization and S is the initial concentration of undissociated propionic acid. For inhibition by hydrogen and acetate to propionate utilization, a noncompetitive product inhibition model was used: qs = qm/[1 + (P/Kp)n], where P is the initial concentration of hydrogen or undissociated acetic acid and Kp is the inhibition constant. Kinetic analysis gave, for hydrogen inhibition, Kp(H2) = 0.11 atm (= 11.1 kPa, 71.5 μM), qm = 2.40 mmol/g of MLVSS per day, and n = 1.51 and, for acetate inhibition, Kp(HAc) = 48.6 μM, qm = 1.85 mmol/g of MLVSS per day, and n = 0.96. It could be concluded that the increase in undissociated propionic acid concentration was a key factor in inhibition of propionate utilization and that hydrogen and acetate cooperatively inhibited propionate degradation, suggesting that hydrogenotrophic and acetoclastic methanogens might play an important role in enhancing propionate degradation to methane and carbon dioxide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahring B. K., Westermann P. Thermophilic anaerobic degradation of butyrate by a butyrate-utilizing bacterium in coculture and triculture with methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):429–433. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.429-433.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R., Bryant M. P. Propionate-Degrading Bacterium, Syntrophobacter wolinii sp. nov. gen. nov., from Methanogenic Ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):626–632. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.626-632.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Commentary on the Hungate technique for culture of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1324–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Wolin E. A., Wolin M. J., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacillus omelianskii, a symbiotic association of two species of bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):20–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00406313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad R., Phelps T. J., Zeikus J. G. Gas metabolism evidence in support of the juxtaposition of hydrogen-producing and methanogenic bacteria in sewage sludge and lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):595–601. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.595-601.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards V. H. The influence of high substrate concentrations on microbial kinetics. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1970 Sep;12(5):679–712. doi: 10.1002/bit.260120504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyes R. H., Hall R. J. Kinetics of two subgroups of propionate-using organisms in anaerobic digestion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):710–715. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.710-715.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar H. F., Wuhrmann K. Kinetic parameters and relative turnovers of some important catabolic reactions in digesting sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.1-7.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder T. K., Nishio N., Fukuzaki S., Nagai S. Effect of Sulfur-Containing Compounds on Growth of Methanosarcina barkeri in Defined Medium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):617–622. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.617-622.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInerney M. J., Bryant M. P., Hespell R. B., Costerton J. W. Syntrophomonas wolfei gen. nov. sp. nov., an Anaerobic, Syntrophic, Fatty Acid-Oxidizing Bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):1029–1039. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.1029-1039.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. L., Wolin M. J. A serum bottle modification of the Hungate technique for cultivating obligate anaerobes. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):985–987. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.985-987.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter J. U., Wolfe R. S. Methane formation from fructose by syntrophic associations of Acetobacterium woodii and different strains of methanogens. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Jan;124(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00407031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


