Abstract
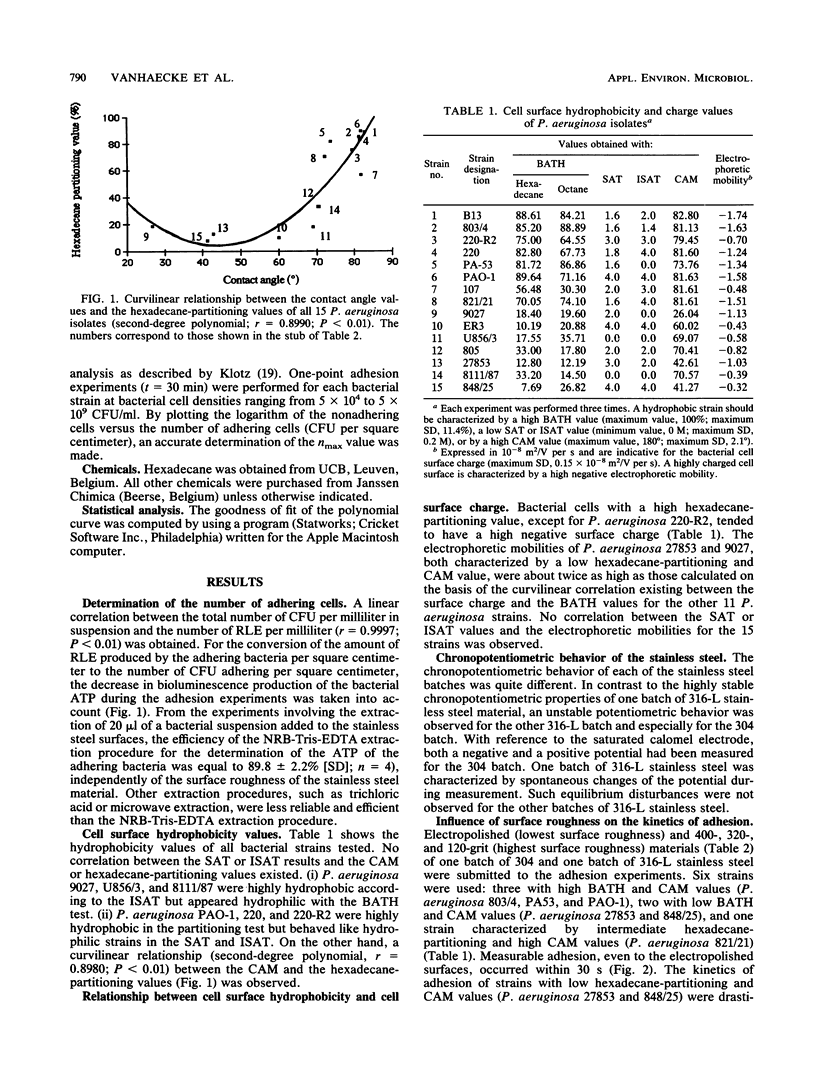
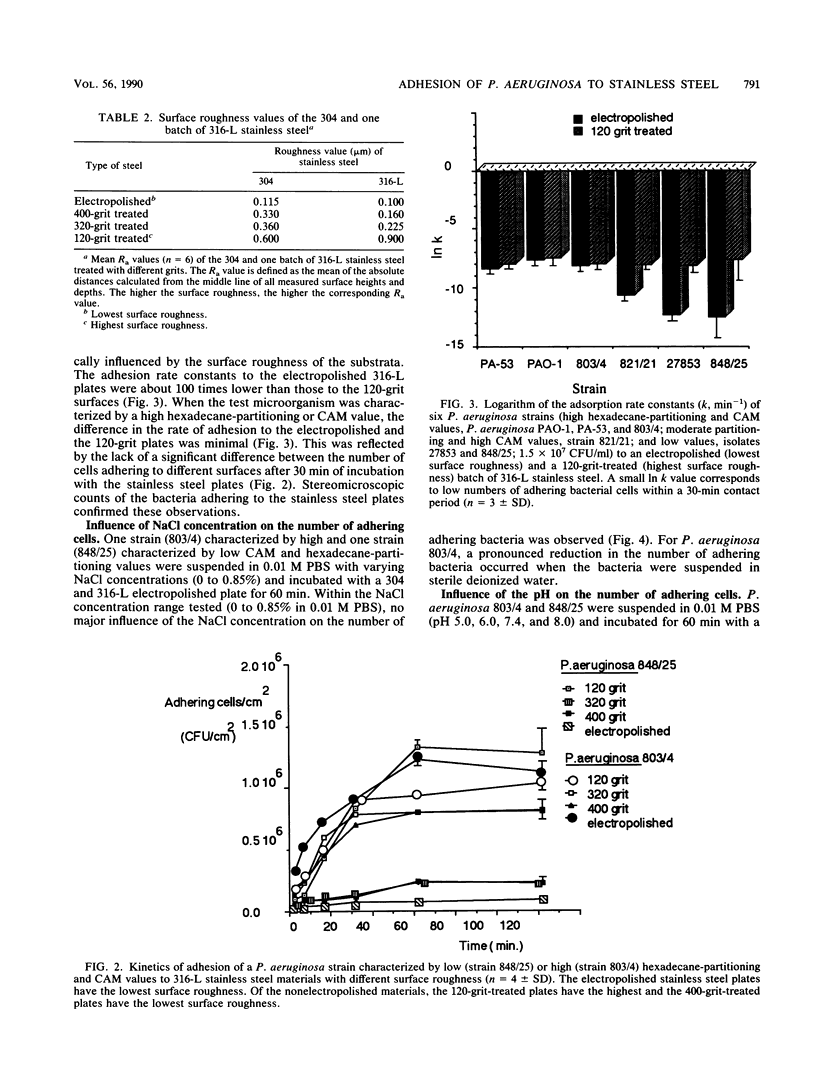
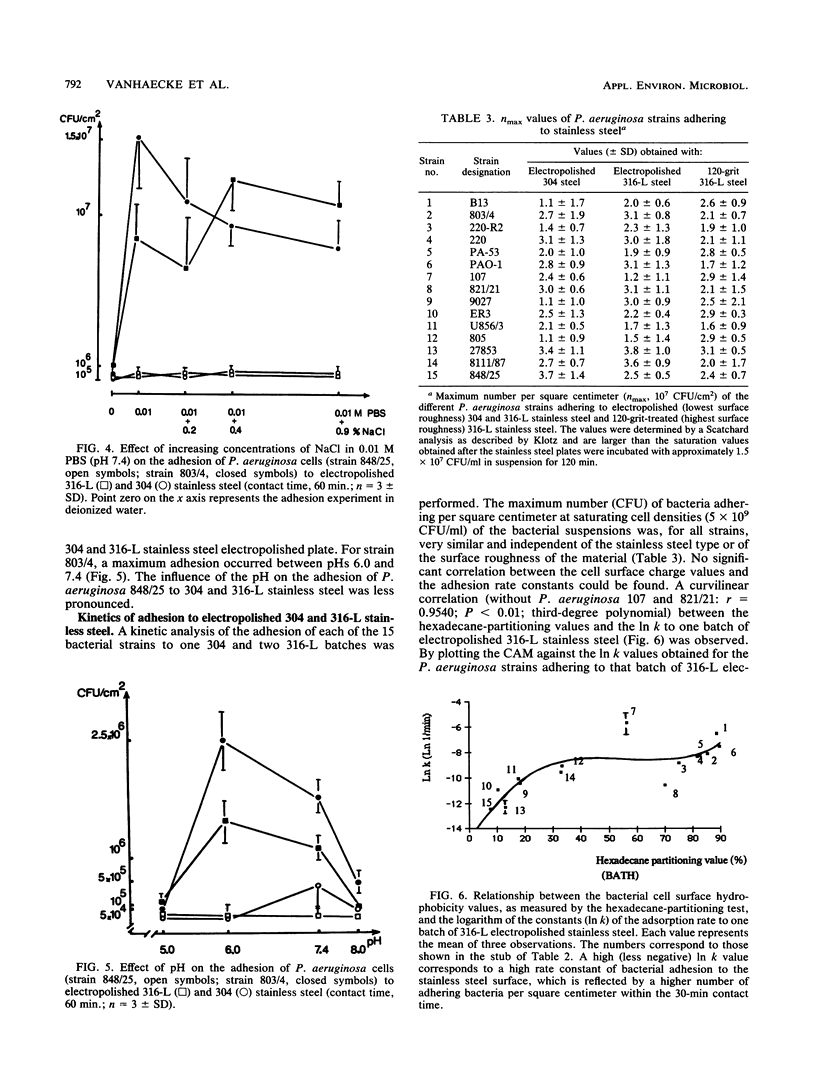
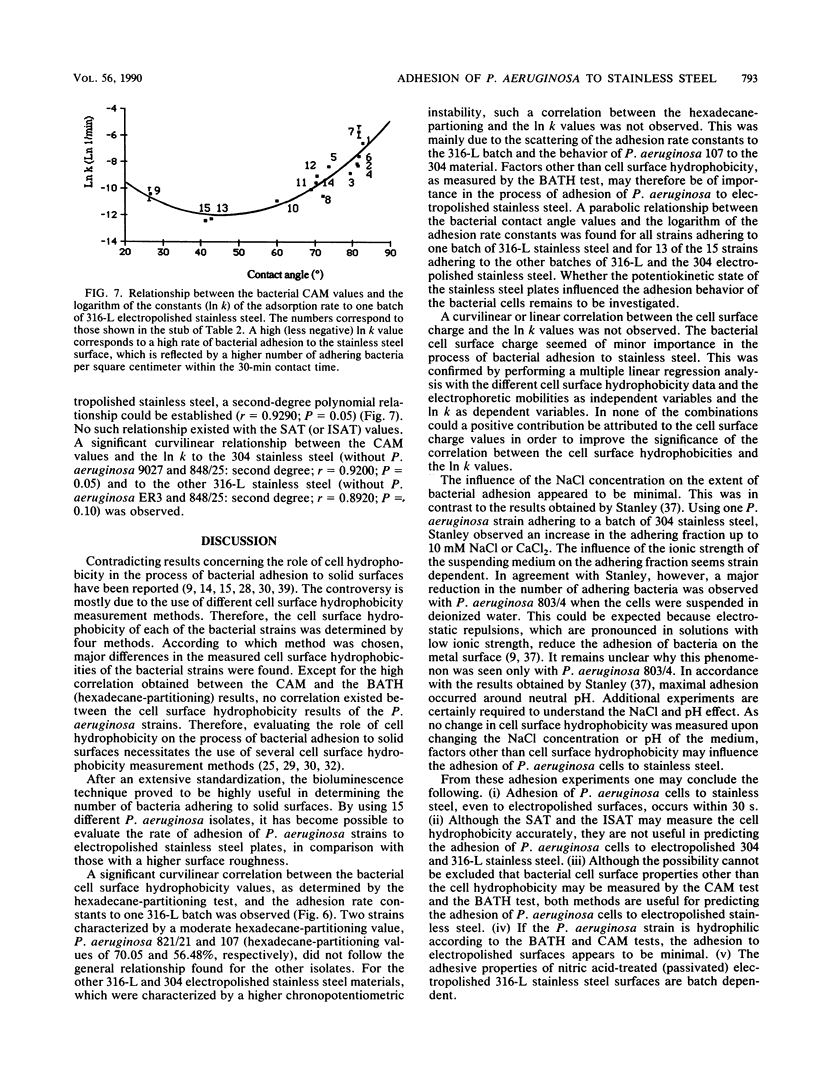
Fifteen different isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa were used to study the kinetics of adhesion to 304 and 316-L stainless steel. Stainless steel plates were incubated with approximately 1.5 X 10(7) CFU/ml in 0.01 M phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.4). After the plates were rinsed with the buffer, the number of adhering bacteria was determined by a bioluminescence assay. Measurable adhesion, even to the electropolished surfaces, occurred within 30 s. Bacterial cell surface hydrophobicity, as determined by the bacterial adherence to hydrocarbons test and the contact angle measurement test, was the major parameter influencing the adhesion rate constant for the first 30 min of adhesion. A parabolic relationship between the CAM values and the logarithm of the adhesion rate constants (In k) was established. No correlation between either the salt aggregation or the improved salt aggregation values and the bacterial adhesion rate constants could be found. Since there was no significant correlation between the bacterial electrophoretic mobilities and the In k values, the bacterial cell surface charge seemed of minor importance in the process of adhesion of P. aeruginosa to 304 and 316-L stainless steel.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baier R. E. Comments on cell adhesion to biomaterial surfaces: conflicts and concerns. J Biomed Mater Res. 1982 Mar;16(2):173–175. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820160210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J., Geesey G. G., Ladd T. I., Nickel J. C., Dasgupta M., Marrie T. J. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:435–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einolf C. W., Jr, Carstensen E. L. Bacterial conductivity in the determination of surface charge by microelectrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):506–516. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exner M., Tuschewitzki G. J., Scharnagel J. Influence of biofilms by chemical disinfectants and mechanical cleaning. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1987 Apr;183(5-6):549–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattom A., Shilo M. Hydrophobicity as an adhesion mechanism of benthic cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.135-143.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S. Influence of Alginate on Attachment of Vibrio spp. to Stainless Steel Surfaces in Seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1175–1177. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1175-1177.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gristina A. G., Costerton J. W. Bacterial adherence to biomaterials and tissue. The significance of its role in clinical sepsis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985 Feb;67(2):264–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herson D. S., McGonigle B., Payer M. A., Baker K. H. Attachment as a factor in the protection of Enterobacter cloacae from chlorination. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1178–1180. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1178-1180.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogt A. H., Dankert J., Feijen J. Adhesion of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus to a hydrophobic biomaterial. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2485–2491. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogt A. H., Dankert J., Feijen J. Adhesion of coagulase-negative staphylococci to methacrylate polymers and copolymers. J Biomed Mater Res. 1986 Apr;20(4):533–545. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820200409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M. Numbers of receptor sites from Scatchard graphs: facts and fantasies. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1247–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.6287580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leake E. S., Gristina A. G., Wright M. J. Use of chemotaxis chambers for studying in vitro bacterial colonization of biomaterials. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):320–323. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.320-323.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. J., Gilmour A. Microflora associated with the internal surfaces of rubber and stainless steel milk transfer pipeline. J Appl Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;62(4):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1987.tb04928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl M., Faris A., Wadström T., Hjertén S. A new test based on 'salting out' to measure relative surface hydrophobicity of bacterial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):471–476. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamo W., Rozgonyi F., Brown A., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Cell surface hydrophobicity and charge of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci from bovine mastitis. J Appl Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;62(3):241–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1987.tb02405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer K. H., Zinner S. H. Bacterial pathogens of increasing significance in hospital-acquired infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7 (Suppl 3):S371–S379. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.supplement_3.s371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWalter P. W. Determination of susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus to methicillin by luciferin-luciferase assay of bacterial adenosine triphosphate. J Appl Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;56(1):145–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1984.tb04706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minagi S., Miyake Y., Fujioka Y., Tsuru H., Suginaka H. Cell-surface hydrophobicity of Candida species as determined by the contact-angle and hydrocarbon-adherence methods. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Apr;132(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-4-1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L. K., Taylor D. E., Stiles M. E. Estimation of Campylobacter spp. in broth culture by bioluminescence assay of ATP. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):730–731. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.730-731.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozgonyi F., Szitha K. R., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Standardization of salt aggregation test for reproducible determination of cell-surface hydrophobicity with special reference to Staphylococcus species. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;59(5):451–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb03345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. C., Bramhill B., Wardlaw N. C., Costerton J. W. Bacterial fouling in a model core system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):693–701. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.693-701.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. M. Factors affecting the irreversible attachment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to stainless steel. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Nov;29(11):1493–1499. doi: 10.1139/m83-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaecke E., Pijck J. Bioluminescence Assay for Measuring the Number of Bacteria Adhering to the Hydrocarbon Phase in the BATH Test. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1436–1439. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1436-1439.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., Busscher H. J. The surface free energy of oral streptococci after being coated with saliva and its relation to adhesion in the mouth. J Dent Res. 1985 Oct;64(10):1204–1210. doi: 10.1177/00220345850640100501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vicente A., Borrego J. J., Arrabal F., Romero P. Comparative study of selective media for enumeration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from water by membrane filtration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):832–840. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.832-840.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loosdrecht M. C., Lyklema J., Norde W., Schraa G., Zehnder A. J. Electrophoretic mobility and hydrophobicity as a measured to predict the initial steps of bacterial adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1898–1901. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1898-1901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loosdrecht M. C., Lyklema J., Norde W., Schraa G., Zehnder A. J. The role of bacterial cell wall hydrophobicity in adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1893–1897. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1893-1897.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



