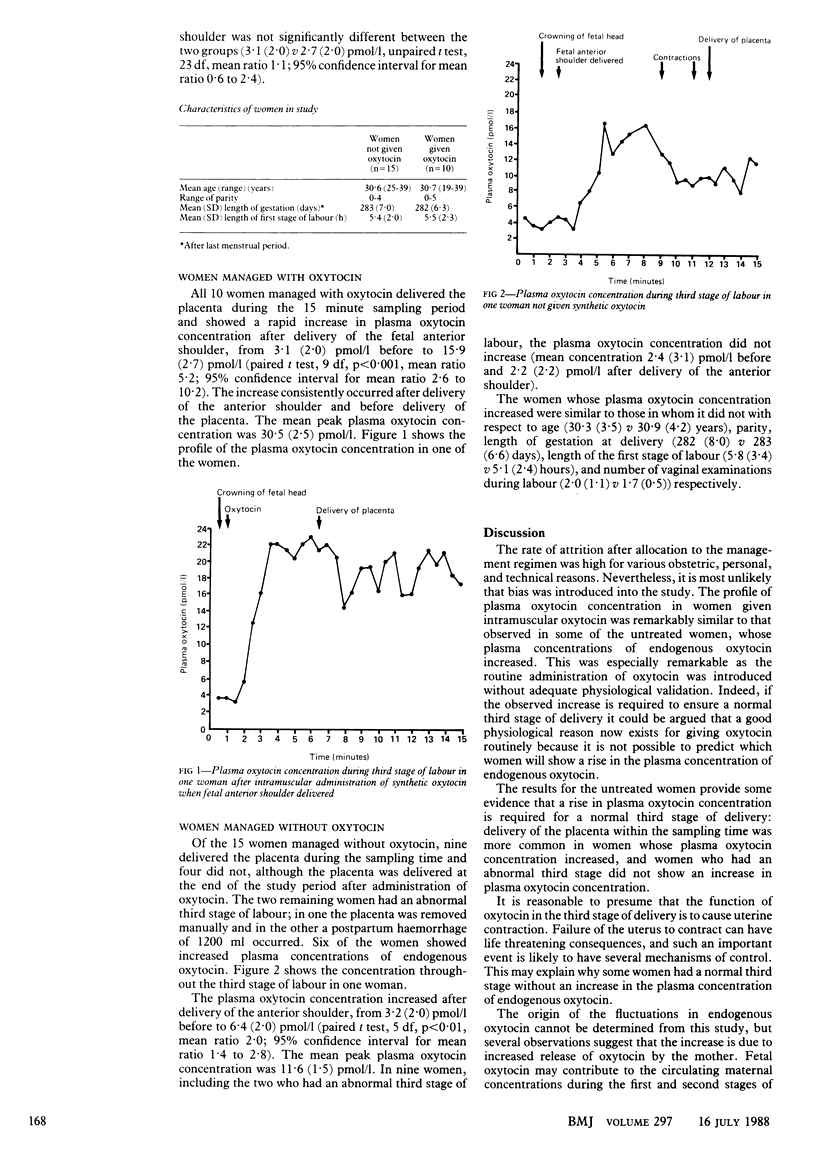
Abstract
The incidences of postpartum haemorrhage and retained placenta have decreased with the use of synthetic oxytocin and controlled cord traction. Whether such treatment is valuable is open to question because of the lack of clinical and physiological studies. The physiological effects of synthetic oxytocin on plasma concentrations of oxytocin and events during delivery were assessed. Plasma oxytocin concentration was determined in serial samples during the late second stage and throughout the third stage of labour in 25 women. Ten women received combined ergotamine and synthetic oxytocin intramuscularly and 15 were not treated. The geometric mean plasma oxytocin concentration significantly increased in the women given oxytocin when measured before and after delivery of the fetal anterior shoulder (3.1 (SD 2.0) pmol/l before and 15.9 (2.7) pmol/l after). Six of the women who did not receive treatment showed a significant increase in geometric mean plasma oxytocin concentration before and after delivery of the fetal shoulder (3.2 (2.0) pmol/l before and 6.4 (2.0) pmol/l after) and nine did not show an increase (geometric mean 2.4 (3.1) pmol/l before and 2.2 (2.2) pmol/l after). Of these nine women, two had an abnormal third stage of delivery; one woman had a postpartum haemorrhage and one required manual removal of the placenta. As it is impossible to predict which women will show a rise in the plasma concentration of endogenous oxytocin, intramuscular oxytocin should be given routinely.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amico J. A., Seitchik J., Robinson A. G. Studies of oxytocin in plasma of women during hypocontractile labor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Feb;58(2):274–279. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-2-274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beardwell C. G. Radioimmunoassay of arginine vasopressin in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):254–260. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd J. M., Davison J., Weightman D. R., Baylis P. H. Evaluation of enzyme inhibitors of pregnancy associated oxytocinase: application to the measurement of plasma immunoreactive oxytocin during human labour. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1987 Mar;114(3):458–464. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1140458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd J. M., Weightman D. R., Baylis P. H. Solid phase radioimmunoassay for direct measurement of human plasma oxytocin. J Immunoassay. 1985;6(3):227–243. doi: 10.1080/01971528508063031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chard T., Boyd N. R., Forsling M. L., McNeilly A. S., Landon J. The development of a radioimmunoassay for oxytocin: the extraction of oxytocin from plasma, and its measurement during parturition in human and goat blood. J Endocrinol. 1970 Oct;48(2):223–234. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0480223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chard T., Hudson C. N., Edwards C. R., Boyd N. R. Release of oxytocin and vasopressin by the human foetus during labour. Nature. 1971 Dec 10;234(5328):352–354. doi: 10.1038/234352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chard T. The radioimmunoassay of oxytocin and vasopressin. J Endocrinol. 1973 Jul;58(1):143–160. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0580143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbourne D., Prendiville W., Chalmers I. Choice of oxytocic preparation for routine use in the management of the third stage of labour: an overview of the evidence from controlled trials. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1988 Jan;95(1):17–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1988.tb06476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbens D., Boyd N. R., Crocker S., Baumber S., Chard T. The circulating levels of oxytocin following intravenous and intramuscular administration of Syntometrine. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1972 Jul;79(7):644–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1972.tb14215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaresan P., Anandarangam P. B., Dianzon W., Vasicka A. Plasma oxytocin levels during human pregnancy and labor as determined by radioimmunoassay. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 May 15;119(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(74)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooke P., Baylis P. H. A new sensitive radioimmunoassay for plasma arginine vasopressin. J Immunoassay. 1982;3(2):115–131. doi: 10.1080/15321818208056990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerlee A. J. Extracellular recordings from oxytocin neurones during the expulsive phase of birth in unanaesthetized rats. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:1–9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


