Abstract
The luciferin-luciferase bioluminescence method was used to estimate the number of bacteria retained in neutral and amphiphilic gels and those in the eluate to determine the hydrophobic surface properties of bacteria by using hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Good correlations were found between viable counts and ATP content for Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas fragi, and Listeria monocytogenes. ATP determination was more rapid than viable counts for characterizing the relative hydrophobicity of L. monocytogenes. Quantitative estimations of adsorption of L. monocytogenes on octyl-Sepharose indicate that this microorganism is hydrophilic.
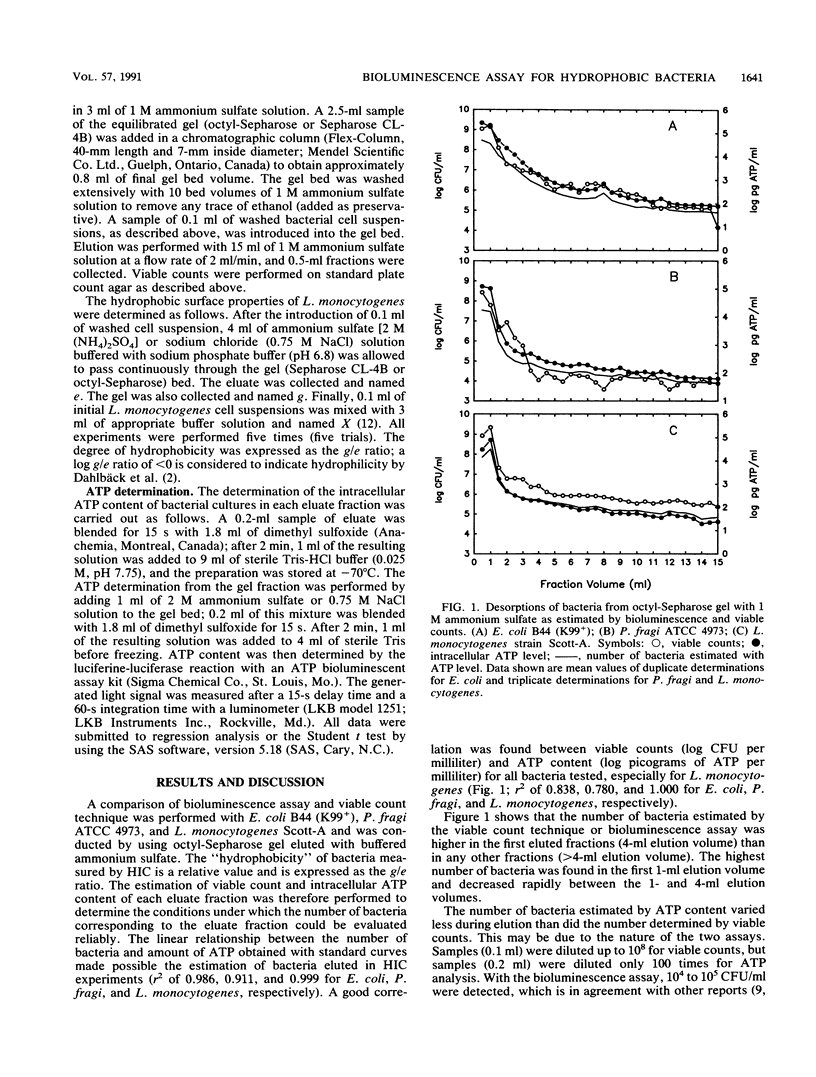
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dahlbäck B., Hermansson M., Kjelleberg S., Norkrans B. The hydrophobicity of bacteria - an important factor in their initial adhesion at the air-water interface. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Jan;128(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00422527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubczak E., Leclerc H. Mesure de l'ATP bactérien par bioluminescence: étude critique des méthodes d'extraction. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1980;38(5):297–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl D. M. Cellular nucleotide measurements and applications in microbial ecology. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):739–796. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.739-796.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leps W. T., Ensign J. C. Adenosine triphosphate pool levels and endogenous metabolism in Arthrobacter crystallopoietes during growth and starvation. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Jul;122(1):61–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00408047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E. Hydrophobic interaction--a mechanism of bacterial binding. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;33:32–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L. K., Taylor D. E., Stiles M. E. Estimation of Campylobacter spp. in broth culture by bioluminescence assay of ATP. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):730–731. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.730-731.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda Y., Kanemasa Y. Determination of hydrophobicity on bacterial surfaces by nonionic surfactants. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):1016–1019. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.1016-1019.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Jonsson P., Olsson E., Soderlind O., Rosengren J., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Differences in hydrophobic surface characteristics of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with or without K88 antigen as revealed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.462-472.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaecke E., Pijck J. Bioluminescence Assay for Measuring the Number of Bacteria Adhering to the Hydrocarbon Phase in the BATH Test. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1436–1439. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1436-1439.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaecke E., Remon J. P., Moors M., Raes F., De Rudder D., Van Peteghem A. Kinetics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa adhesion to 304 and 316-L stainless steel: role of cell surface hydrophobicity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Mar;56(3):788–795. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.3.788-795.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



