Abstract
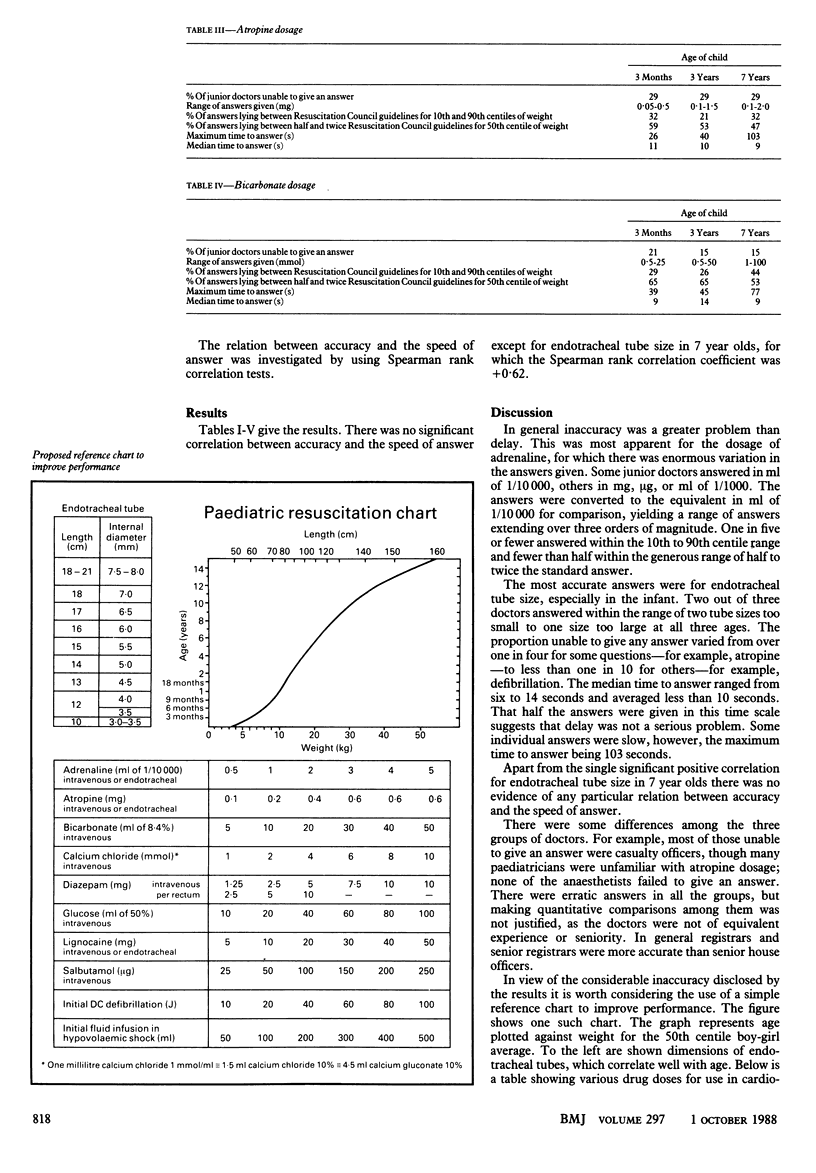
Several surveys have noted the poor performance of junior hospital doctors in simulated cardiorespiratory arrest in adults. A further survey was undertaken to investigate inaccuracy and delay in the resuscitation of children. The results suggested that inaccuracy was a greater problem than delay. Because of the variation in size of children and the comparative infrequency of cardiorespiratory arrest in this age group a simple, versatile, and readily available reference chart is needed to aid rapid and accurate decisions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casey W. F. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a survey of standards among junior hospital doctors. J R Soc Med. 1984 Nov;77(11):921–924. doi: 10.1177/014107688407701105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein S. R., Hansbrough J. F., Libby L. S., Hill D. M., Mountain R. D., Scoggin C. H. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation by medical and surgical house-officers. Lancet. 1981 Sep 26;2(8248):679–681. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. V., Camm A. J., Miles S. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation skills of preregistration house officers. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 May 25;290(6481):1549–1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6481.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zideman D. ABC of resuscitation. Resuscitation of infants and children. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Jun 14;292(6535):1584–1588. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6535.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


