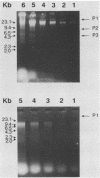
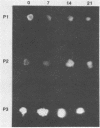
Abstract
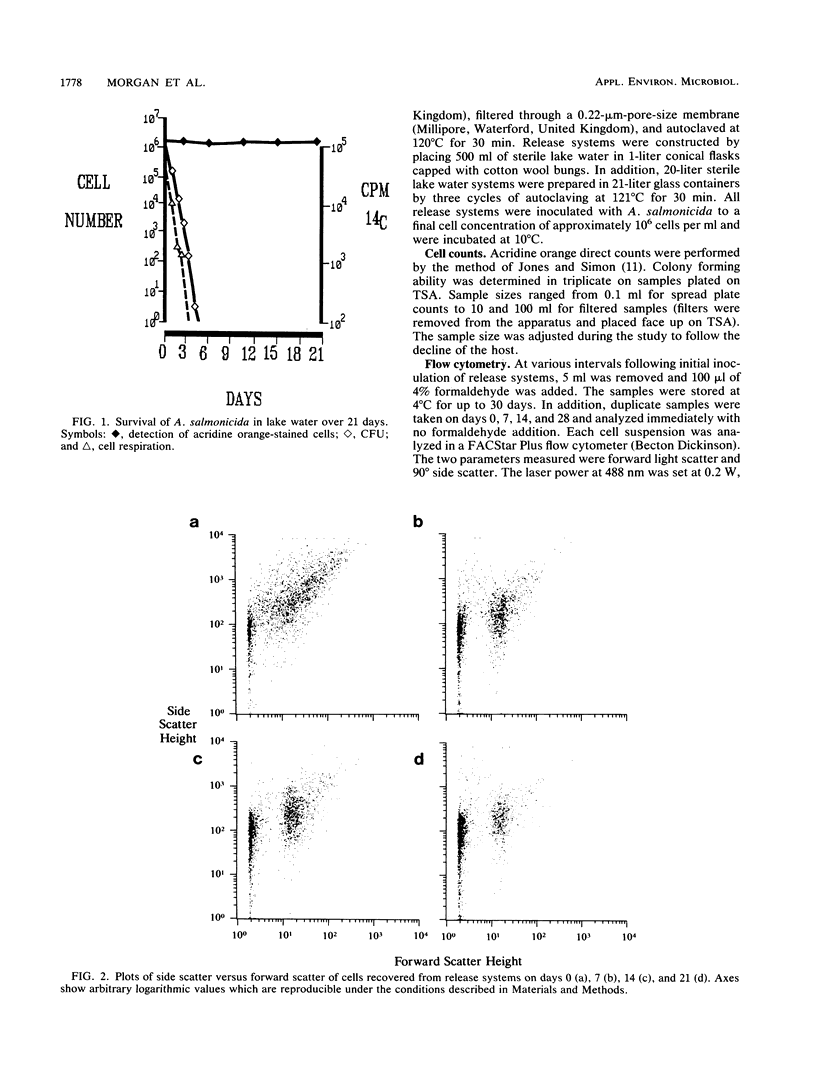
The survival of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida in lake water was investigated by using a variety of techniques. They included acridine orange epifluorescence, respiration, cell culture, cell revival, flow cytometry, plasmid maintenance, and membrane fatty acid analysis. During a 21-day study, A. salmonicida became nonculturable in sterile lake water samples. Flow cytometry and direct microscopy indicated that cells were present. Although the nonculturable cells could not be revived, the recovery method did indicate that the presence of low numbers of culturable cells within samples could produce misleading results. Plasmid DNA, genomic DNA, and RNA were maintained in the nonculturable cells; in addition, changes in the fatty acid profiles were also detected. Although viability could not be proven, it was shown that the morphological integrity of nonculturable cells was maintained.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker K. H., Mills A. L. Determination of the Number of Respiring Thiobacillus ferrooxidans Cells in Water Samples by Using Combined Fluorescent Antibody-2-(p-Iodophenyl)-3-(p-Nitrophenyl)-5-Phenyltetrazolium Chloride Staining. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):338–344. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.338-344.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. M., Singleton F. L., Hood M. A. Effects of nutrient deprivation on Vibrio cholerae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Oct;46(4):930–940. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.4.930-940.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcina I., González J. M., Iriberri J., Egea L. Effect of visible light on progressive dormancy of Escherichia coli cells during the survival process in natural fresh water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):246–251. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.246-251.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd J. J., Colwell R. R. Maintenance of plasmids pBR322 and pUC8 in nonculturable Escherichia coli in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2104–2107. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2104-2107.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. G., Simon B. M. An investigation of errors in direct counts of aquatic bacteria by epifluorescence microscopy, with reference to a new method for dyeing membrane filters. J Appl Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;39(3):317–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1975.tb00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogure K., Simidu U., Taga N. A tentative direct microscopic method for counting living marine bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):415–420. doi: 10.1139/m79-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang L. N., Sinclair J. L., Mallory L. M., Alexander M. Fate in model ecosystems of microbial species of potential use in genetic engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):708–714. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.708-714.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder K., Oliver J. D. Membrane fatty acid and virulence changes in the viable but nonculturable state of Vibrio vulnificus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2837–2842. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2837-2842.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel C., Dubois-Darnaudpeys A. Persistence of the virulence of Aeromonas salmonicida strains kept in river sediments. Ann Rech Vet. 1980;11(4):375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. A., Winstanley C., Pickup R. W., Jones J. G., Saunders J. R. Direct phenotypic and genotypic detection of a recombinant pseudomonad population released into lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2537–2544. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2537-2544.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. S., Ellis A. E., Munro A. L. Evidence against dormancy in the bacterial fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 1;56(1-2):105–107. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90133-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Colwell R. R. Survival strategies of bacteria in the natural environment. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):365–379. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.365-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Grimes D. J., Colwell R. R. Viable but nonrecoverable stage of Salmonella enteritidis in aquatic systems. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Mar;30(3):334–338. doi: 10.1139/m84-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai D. K. Electrostatic mechanism of survival of virulent Aeromonas salmonicida strains in river water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1343–1349. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1343-1349.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcroft R., Williams P. A. Rapid methods for the study of both stable and unstable plasmids in Pseudomonas. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jun;124(2):433–437. doi: 10.1099/00221287-124-2-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstanley C., Morgan J. A., Pickup R. W., Jones J. G., Saunders J. R. Differential regulation of lambda pL and pR promoters by a cI repressor in a broad-host-range thermoregulated plasmid marker system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):771–777. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.771-777.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R., Iturriaga R., Becker-Birck J. Simultaneous determination of the total number of aquatic bacteria and the number thereof involved in respiration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):926–935. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.926-935.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]