Abstract
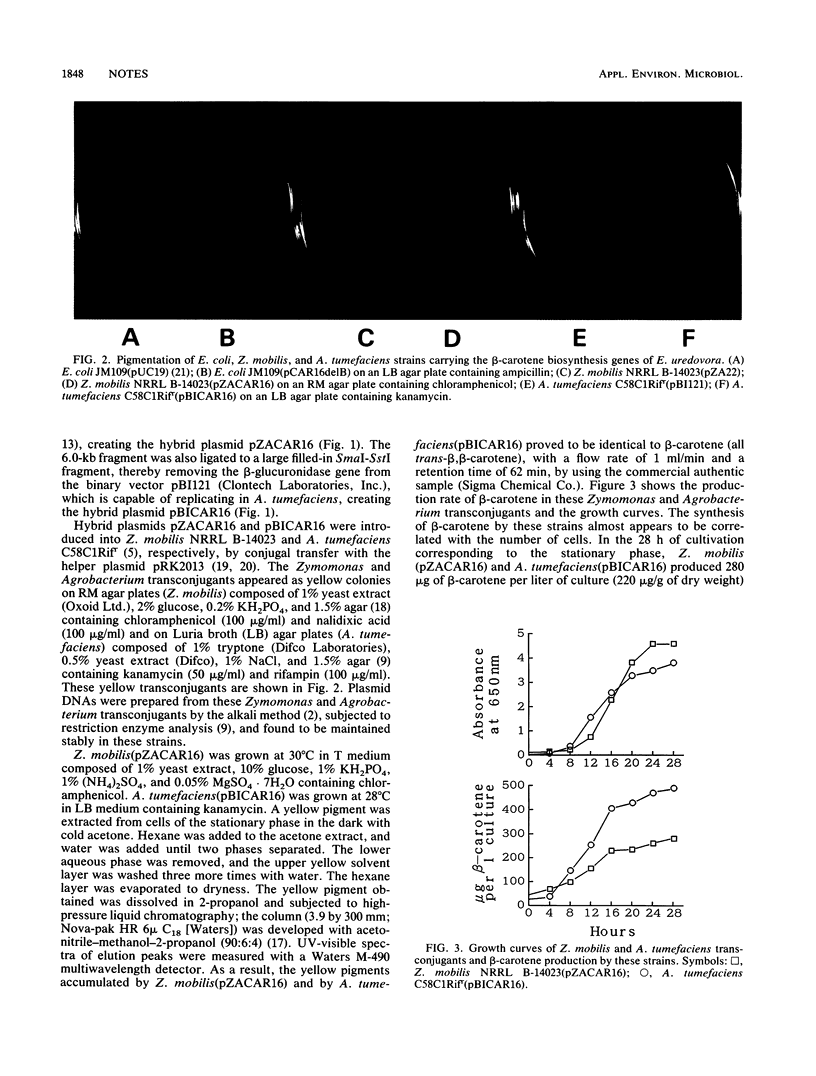
The Erwinia uredovora crtB, crtE, crtI, and crtY genes required for beta-carotene biosynthesis were introduced by conjugal transfer into an ethanol-producing bacterium, Zymomonas mobilis, and a phytopathogenic bacterium, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, in which no carotenoid is synthesized. The transconjugants of Z. mobilis and A. tumefaciens carrying these genes appeared as yellow colonies and produced 220 and 350 micrograms of beta-carotene per g of dry weight, respectively, in the stationary phase in liquid culture.
Full text
PDF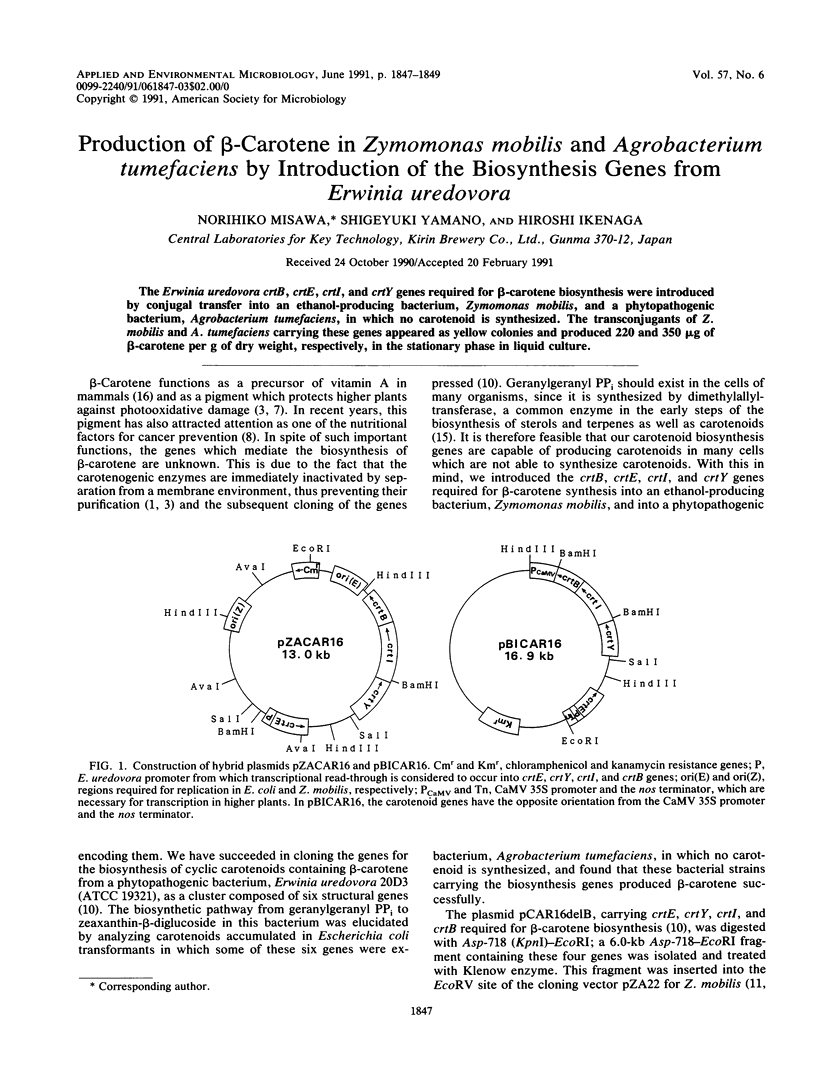

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beyer P., Weiss G., Kleinig H. Solubilization and reconstitution of the membrane-bound carotenogenic enzymes from daffodil chromoplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 2;153(2):341–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey V. C., Walia S. K., Ingram L. O. Expression of a Lactose Transposon (Tn951) in Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1163–1168. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1163-1168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deblaere R., Bytebier B., De Greve H., Deboeck F., Schell J., Van Montagu M., Leemans J. Efficient octopine Ti plasmid-derived vectors for Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer to plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4777–4788. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert L. A., Koch W. H., Wamer W. G., Kornhauser A. Antitumor activity in skin of Skh and Sencar mice by two dietary beta-carotene formulations. Nutr Cancer. 1990;13(4):213–221. doi: 10.1080/01635589009514063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misawa N., Nakagawa M., Kobayashi K., Yamano S., Izawa Y., Nakamura K., Harashima K. Elucidation of the Erwinia uredovora carotenoid biosynthetic pathway by functional analysis of gene products expressed in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6704–6712. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6704-6712.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura K., Shinka T., Seto S. The purification and properties of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthetase from pumpkin fruit. J Biochem. 1972 Nov;72(5):1101–1108. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmann G., Woods W. S., Tuveson R. W. Identification of carotenoids in Erwinia herbicola and in a transformed Escherichia coli strain. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Sep 1;59(1-2):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90035-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skotnicki M. L., Tribe D. E., Rogers P. L. R-Plasmid Transfer in Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.7-12.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuy J. H. Plasmid transfer in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):520–529. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.520-529.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



