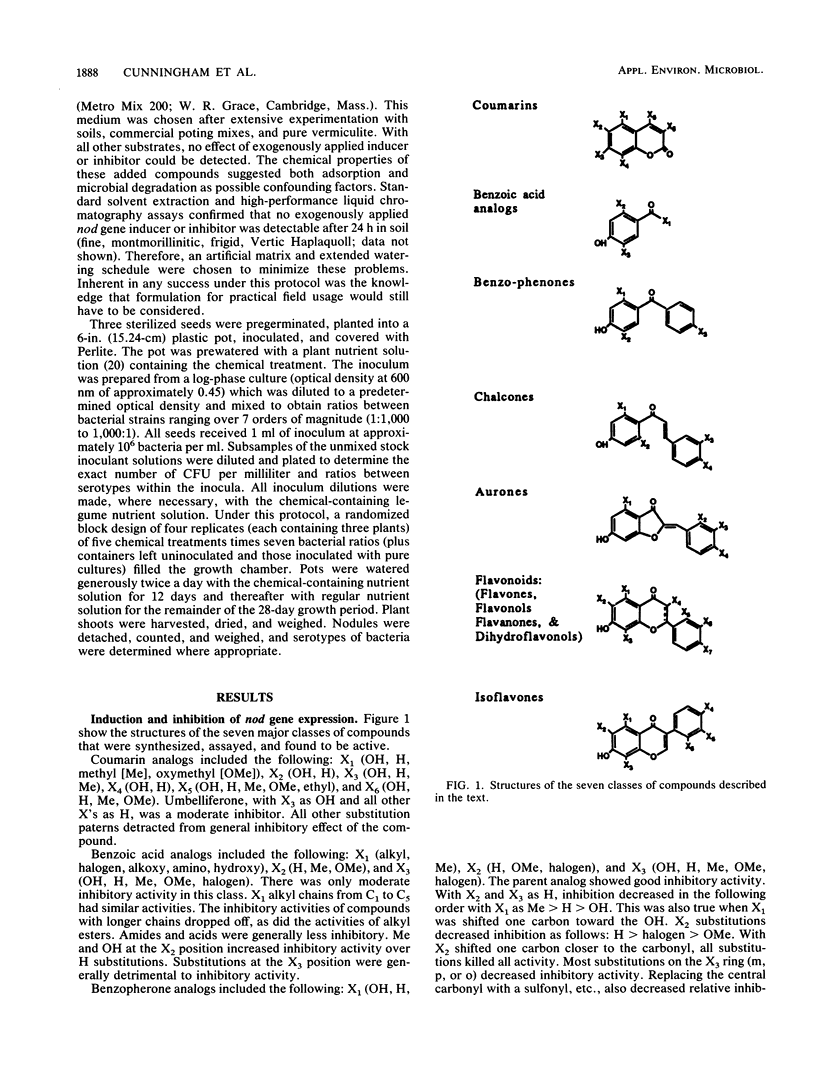
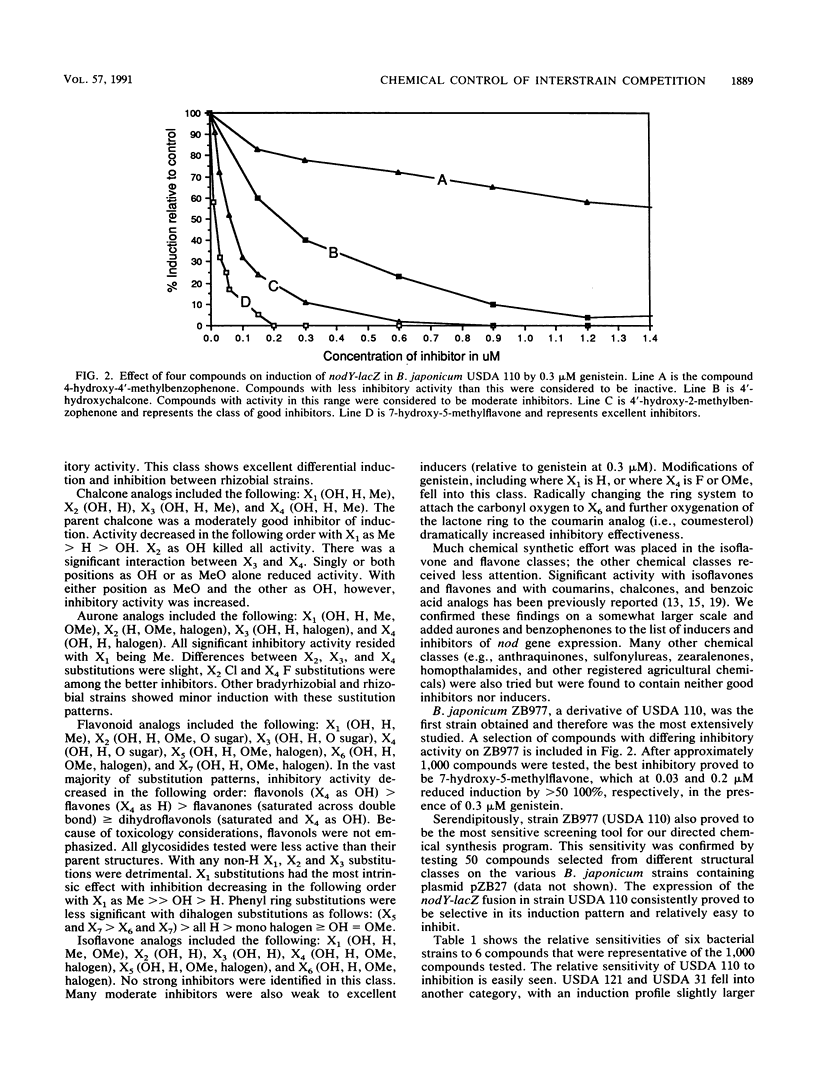
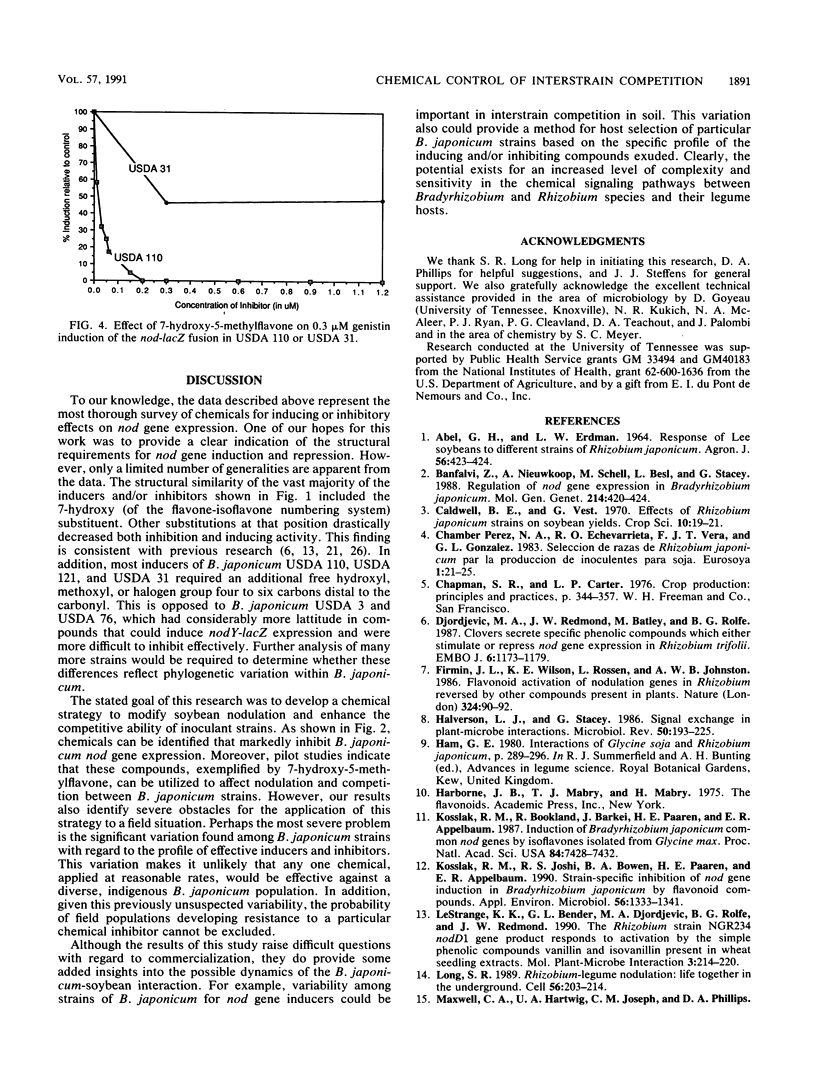
Abstract
Previous research has shown that a significant limitation to the agricultural use of improved rhizobial inoculant strains is competition from the indigenous soil population. In this work, we sought to test whether chemical inhibitors of flavonoid-induced nod gene expression in Bradyrhizobium japonicum could be identified and utilized to affect interstrain competition for nodulation of soybeans. Approximately 1,000 structural and functional analogs of the known, natural inducers of nod gene expression were tested on six strains of B. japonicum containing a nodY-lacZ fusion. We successfully identified effective inhibitors of nodY expression. The addition of the inhibitor 7-hydroxy-5-methylflavone significantly inhibited nodulation by a sensitive strain and could be used to effectively manipulate the competition between strains for soybean nodulation. However, this work also uncovered significant limitations for the practical use of this methodology. For example, despite the almost universal induction response to the identified natural inducers, there was a wide variability among strains in their response to any specific inhibitor. Given this unexpected variability, the cost of registration of an agronomic chemical, and the potential for the development of resistant field populations, it is unlikely that chemical inhibitors can be successfully applied to a field situation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banfalvi Z., Nieuwkoop A., Schell M., Besl L., Stacey G. Regulation of nod gene expression in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):420–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00330475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic M. A., Redmond J. W., Batley M., Rolfe B. G. Clovers secrete specific phenolic compounds which either stimulate or repress nod gene expression in Rhizobium trifolii. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1173–1179. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halverson L. J., Stacey G. Signal exchange in plant-microbe interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Jun;50(2):193–225. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.2.193-225.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bookland R., Barkei J., Paaren H. E., Appelbaum E. R. Induction of Bradyrhizobium japonicum common nod genes by isoflavones isolated from Glycine max. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Joshi R. S., Bowen B. A., Paaren H. E., Appelbaum E. R. Strain-Specific Inhibition of nod Gene Induction in Bradyrhizobium japonicum by Flavonoid Compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1333–1341. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1333-1341.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Induction of Rhizobium meliloti nodC expression by plant exudate requires nodD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6609–6613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Frost J. W., Long S. R. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Long S. R. Alfalfa Root Exudates and Compounds which Promote or Inhibit Induction of Rhizobium meliloti Nodulation Genes. Plant Physiol. 1988 Oct;88(2):396–400. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So J. S., Hodgson A. L., Haugland R., Leavitt M., Banfalvi Z., Nieuwkoop A. J., Stacey G. Transposon-induced symbiotic mutants of Bradyrhizobium japonicum: isolation of two gene regions essential for nodulation. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):15–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00331485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaat S. A., Schripsema J., Wijffelman C. A., van Brussel A. A., Lugtenberg B. J. Analysis of the major inducers of the Rhizobium nodA promoter from Vicia sativa root exudate and their activity with different nodD genes. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Aug;13(2):175–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00016136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



