Abstract
Activity of the lactococcal cell envelope-located serine proteinase depends on the presence of membrane-associated lipoprotein PrtM. To differentiate between the action of the proteinase and the action of PrtM in the process of proteinase maturation, an inactive form of the lactococcal proteinase was constructed. This was done by mutating one of the three amino acids thought to constitute the active site of the enzyme. The secreted form of this inactivated proteinase was the same size as the inactive secreted form of the proteinase produced in the absence of PrtM. Both inactive proteinases are larger than the active proteinase. Isolation of proteinase by washing lactococcal cells carrying the complete proteinase gene in a Ca(2+)-free buffer was prevented by the absence of prtM or the absence of a functional active site. We propose that PrtM, during or after membrane translocation of the proteinase, effects the autoproteolytic removal of the N-terminal pro region of the proteinase. Subsequent C-terminal autodigestion results in the release of the enzyme from the lactococcal cells.
Full text
PDF


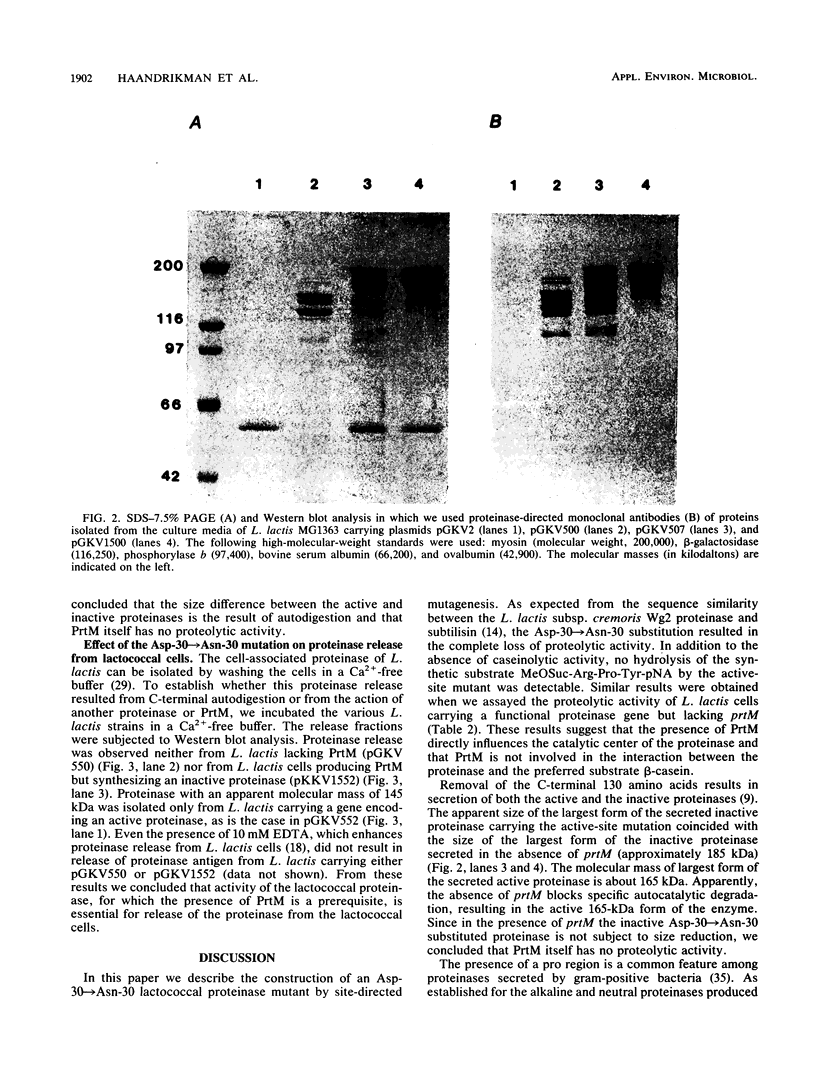


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P., Wells J. A. Dissecting the catalytic triad of a serine protease. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):564–568. doi: 10.1038/332564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A. Differences in short peptide-substrate cleavage by two cell-envelope-located serine proteinases of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris are related to secondary binding specificity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1990 Jul;33(4):401–406. doi: 10.1007/BF00176654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A., de Veer G. J. Partial Isolation and Degradation of Caseins by Cell Wall Proteinase(s) of Streptococcus cremoris HP. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.328-332.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haandrikman A. J., Kok J., Laan H., Soemitro S., Ledeboer A. M., Konings W. N., Venema G. Identification of a gene required for maturation of an extracellular lactococcal serine proteinase. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2789–2794. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2789-2794.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura H., Inouye M. In vitro processing of pro-subtilisin produced in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12959–12963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiwaki M., Ikemura H., Shimizu-Kadota M., Hirashima A. Molecular characterization of a cell wall-associated proteinase gene from Streptococcus lactis NCDO763. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Mar;3(3):359–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J. Genetics of the proteolytic system of lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Sep;7(1-2):15–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J., Hill D., Haandrikman A. J., de Reuver M. J., Laan H., Venema G. Deletion analysis of the proteinase gene of Streptococcus cremoris Wg2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.239-244.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J., Leenhouts K. J., Haandrikman A. J., Ledeboer A. M., Venema G. Nucleotide sequence of the cell wall proteinase gene of Streptococcus cremoris Wg2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):231–238. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.231-238.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok J., van Dijl J. M., van der Vossen J. M., Venema G. Cloning and expression of a Streptococcus cremoris proteinase in Bacillus subtilis and Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):94–101. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.94-101.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer B., Kramer W., Fritz H. J. Different base/base mismatches are corrected with different efficiencies by the methyl-directed DNA mismatch-repair system of E. coli. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laan H., Konings W. N. Mechanism of Proteinase Release from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris Wg2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3101–3106. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3101-3106.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laan H., Smid E. J., de Leij L., Schwander E., Konings W. N. Monoclonal Antibodies to the Cell-Wall-Associated Proteinase of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris Wg2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Sep;54(9):2250–2256. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.9.2250-2256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenhouts K. J., Kok J., Venema G. Stability of Integrated Plasmids in the Chromosome of Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2726–2735. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2726-2735.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff G. R., Pène J. J. Molecular cloning with bifunctional plasmid vectors in Bacillus subtilis: isolation of a spontaneous mutant of Bacillus subtilis with enhanced transformability for Escherichia coli-propagated chimeric plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):934–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.934-936.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silen J. L., Agard D. A. The alpha-lytic protease pro-region does not require a physical linkage to activate the protease domain in vivo. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):462–464. doi: 10.1038/341462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos P., Simons G., Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M. Primary structure and organization of the gene for a procaryotic, cell envelope-located serine proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13579–13585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos P., van Asseldonk M., van Jeveren F., Siezen R., Simons G., de Vos W. M. A maturation protein is essential for production of active forms of Lactococcus lactis SK11 serine proteinase located in or secreted from the cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2795–2802. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2795-2802.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C. Secretion, processing and activation of bacterial extracellular proteases. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1825–1831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Asseldonk M., Rutten G., Oteman M., Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M., Simons G. Cloning of usp45, a gene encoding a secreted protein from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis MG1363. Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90428-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vossen J. M., Kok J., Venema G. Construction of cloning, promoter-screening, and terminator-screening shuttle vectors for Bacillus subtilis and Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):540–542. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.540-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]