Abstract
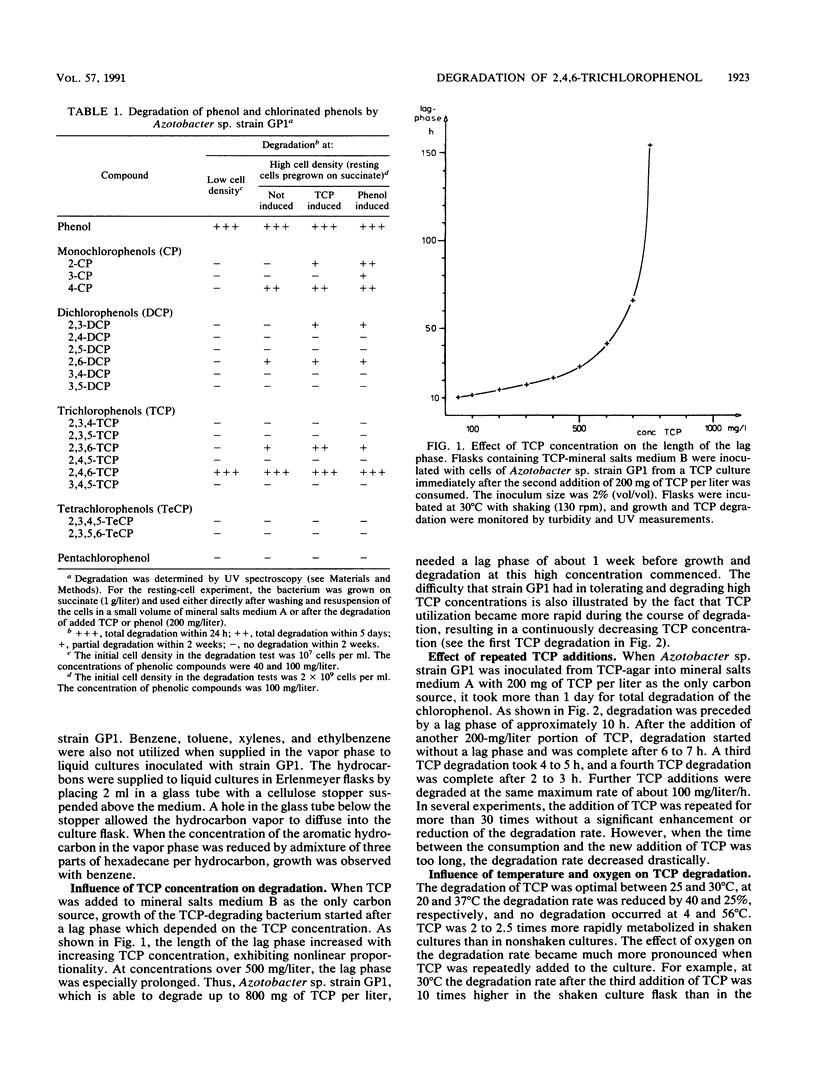
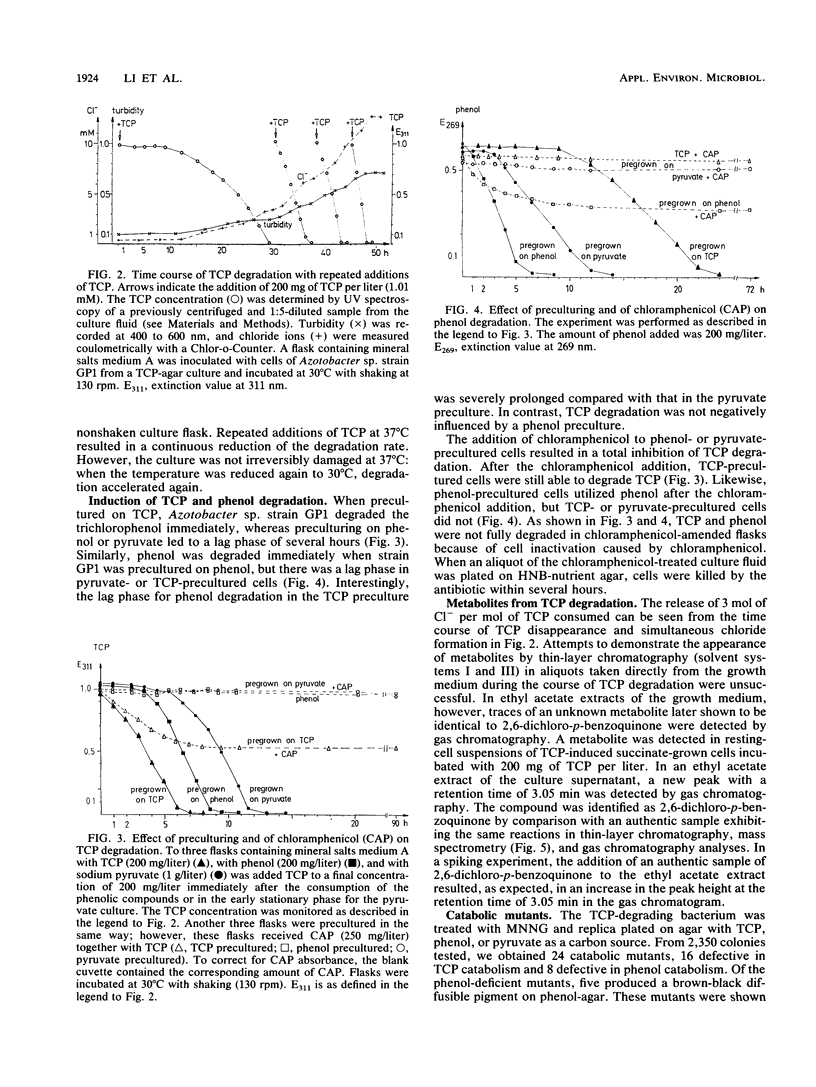
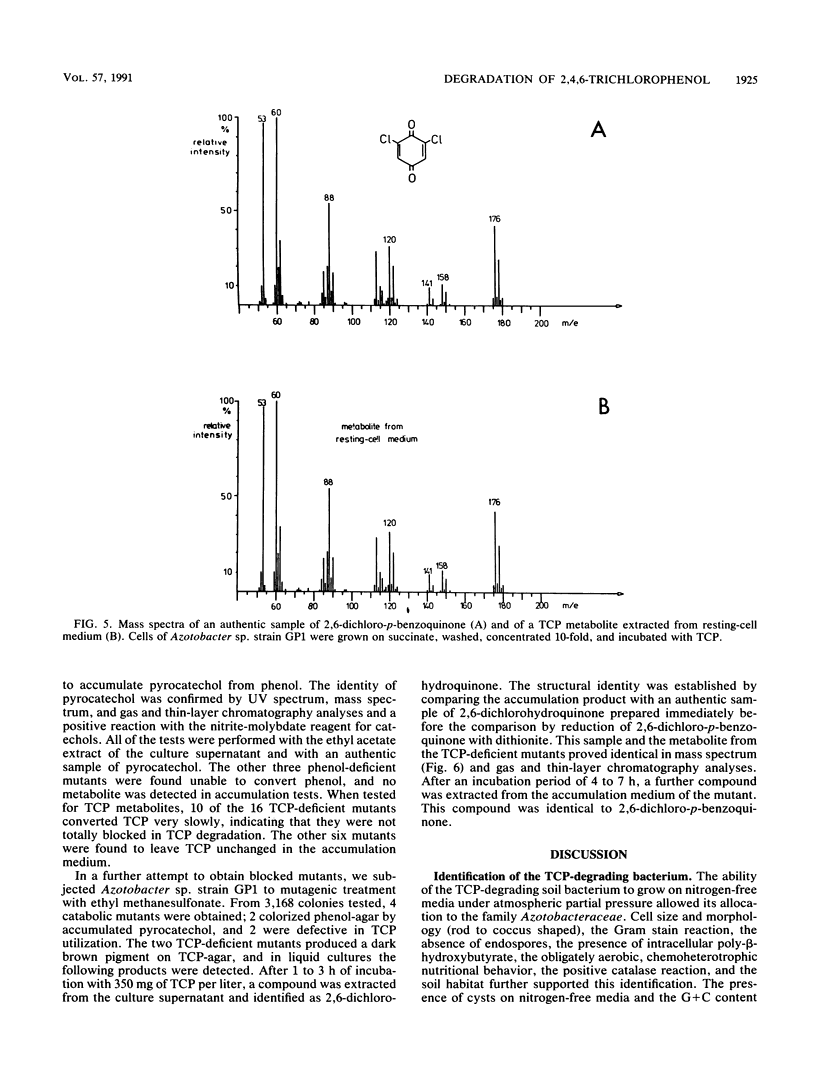
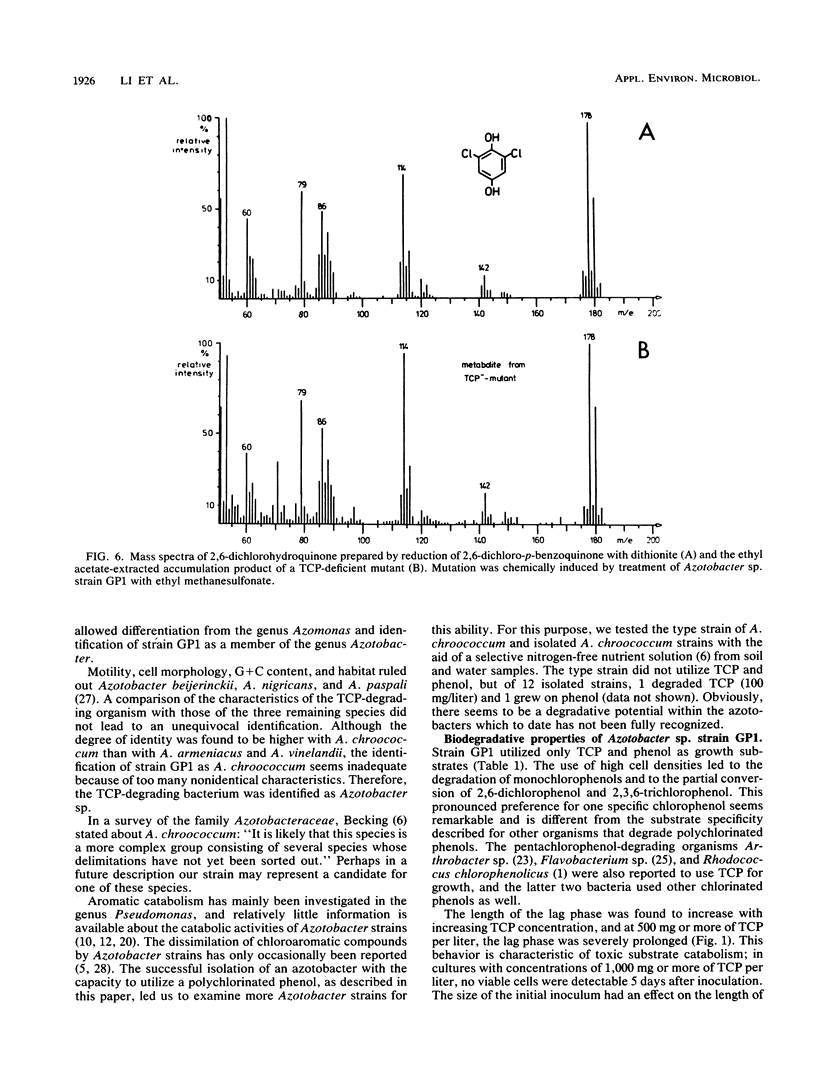
A bacterium which utilizes 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (TCP) as a sole source of carbon and energy was isolated from soil. The bacterium, designated strain GP1, was identified as an Azotobacter sp. TCP was the only chlorinated phenol which supported the growth of the bacterium. Resting cells transformed monochlorophenols, 2,6-dichlorophenol, and 2,3,6-trichlorophenol. Phenol and a number of phenolic compounds, including 4-methylphenol, all of the monohydroxybenzoates, and several dihydroxybenzoates, were very good carbon sources for Azotobacter sp. strain GP1. The organism utilized up to 800 mg of TCP per liter; the lag phase and time for degradation, however, were severely prolonged at TCP concentrations above 500 mg/liter. Repeated additions of 200 mg of TCP per liter led to accelerated degradation, with an optimum value of 100 mg of TCP per liter per h. TCP degradation was significantly faster in shaken than in nonshaken cultures. The optimum temperature for degradation was 25 to 30 degrees C. Induction studies, including treatment of the cells with chloramphenicol prior to TCP or phenol addition, revealed that TCP induced TCP degradation but not phenol degradation and that phenol induced only its own utilization. Per mol of TCP, 3 mol of Cl- was released. 2,6-Dichloro-p-benzoquinone was detected in the resting-cell medium of Azotobacter sp. strain GP1. By chemical mutagenesis, mutants blocked in either TCP degradation or phenol degradation were obtained. No mutant defective in the degradation of both phenols was found, indicating separate pathways for the dissimilation of the compounds. In some of the phenol-deficient mutants, pyrocatechol was found to accumulate, and in some of the TCP-deficient mutants, 2,6-dichlorohydroquinone was found to accumulate.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apajalahti J. H., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Complete dechlorination of tetrachlorohydroquinone by cell extracts of pentachlorophenol-induced Rhodococcus chlorophenolicus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5125–5130. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5125-5130.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apajalahti J. H., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Dechlorination and para-hydroxylation of polychlorinated phenols by Rhodococcus chlorophenolicus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):675–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.675-681.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balajee S., Mahadevan A. Dissimilation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by Azotobacter chroococcum. Xenobiotica. 1990 Jun;20(6):607–617. doi: 10.3109/00498259009046876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groseclose E. E., Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of resorcinylic compounds by bacteria: new pathway for resorcinol catabolism in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):460–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.460-466.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugland R. A., Schlemm D. J., Lyons R. P., 3rd, Sferra P. R., Chakrabarty A. M. Degradation of the chlorinated phenoxyacetate herbicides 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid by pure and mixed bacterial cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1357–1362. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1357-1362.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggblom M. M., Janke D., Salkinoja-Salonen M. S. Hydroxylation and Dechlorination of Tetrachlorohydroquinone by Rhodococcus sp. Strain CP-2 Cell Extracts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):516–519. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.516-519.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knackmuss H. J., Hellwig M. Utilization and cooxidation of chlorinated phenols by Pseudomonas sp. B 13. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00689343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikesell M. D., Boyd S. A. Complete reductive dechlorination and mineralization of pentachlorophenol by anaerobic microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):861–865. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.861-865.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Evans W. C. The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):400–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk T., Müller R., Mörsberger F., Otto M. K., Lingens F. Enzymatic dehalogenation of pentachlorophenol by extracts from Arthrobacter sp. strain ATCC 33790. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5487–5491. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5487-5491.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanlake G. J., Finn R. K. Isolation and characterization of a pentachlorophenol-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1421–1427. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1421-1427.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert J. G., Crawford R. L. Catabolism of pentachlorophenol by a Flavobacterium sp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):825–830. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiert J. G., Pignatello J. J., Crawford R. L. Degradation of chlorinated phenols by a pentachlorophenol-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):907–910. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.907-910.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



