Abstract
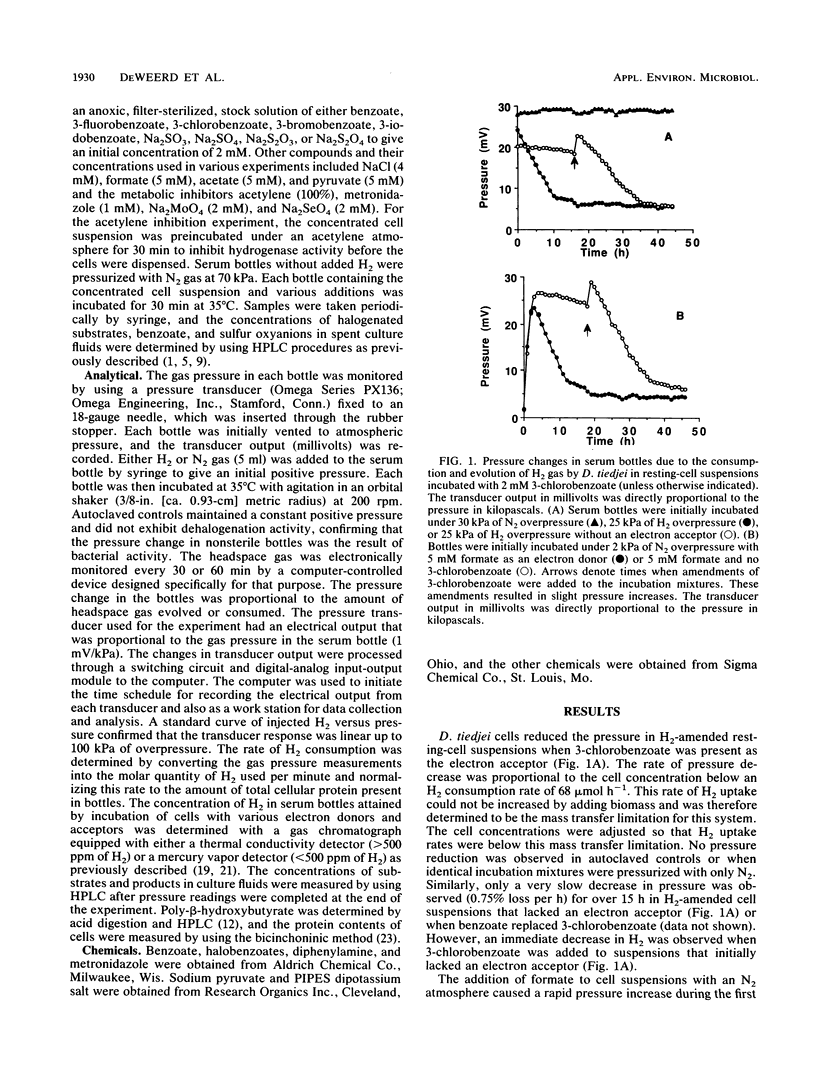
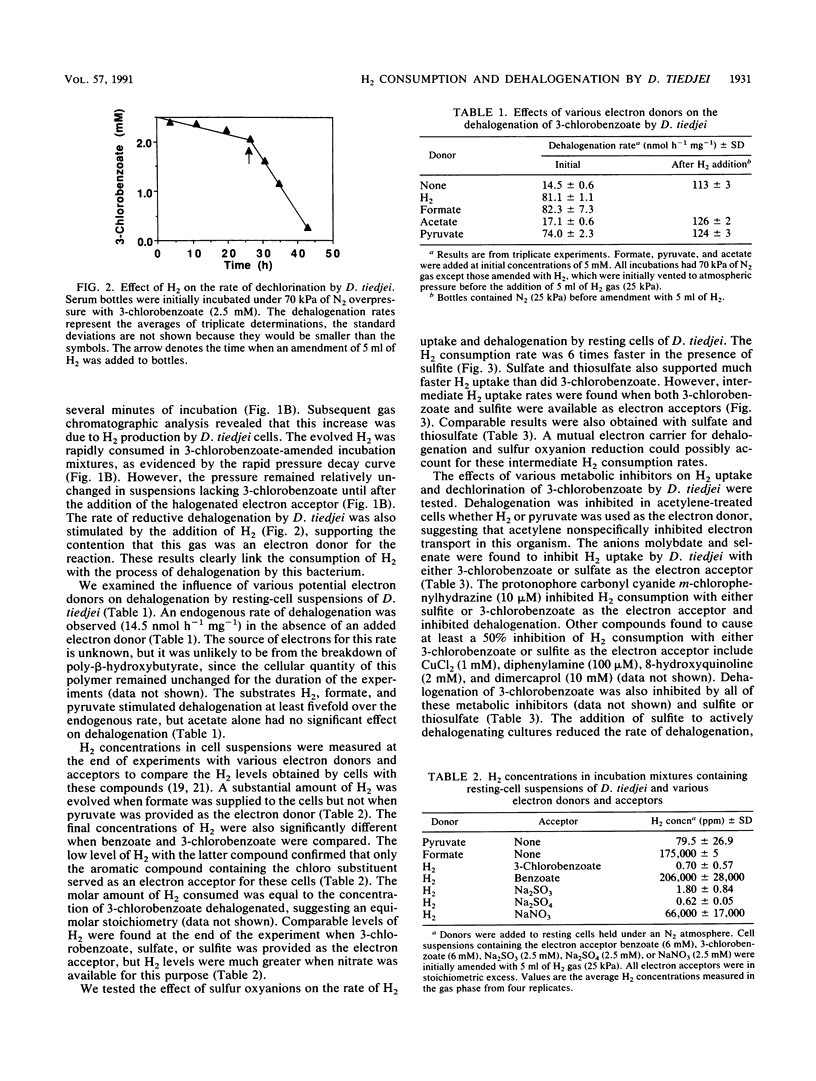
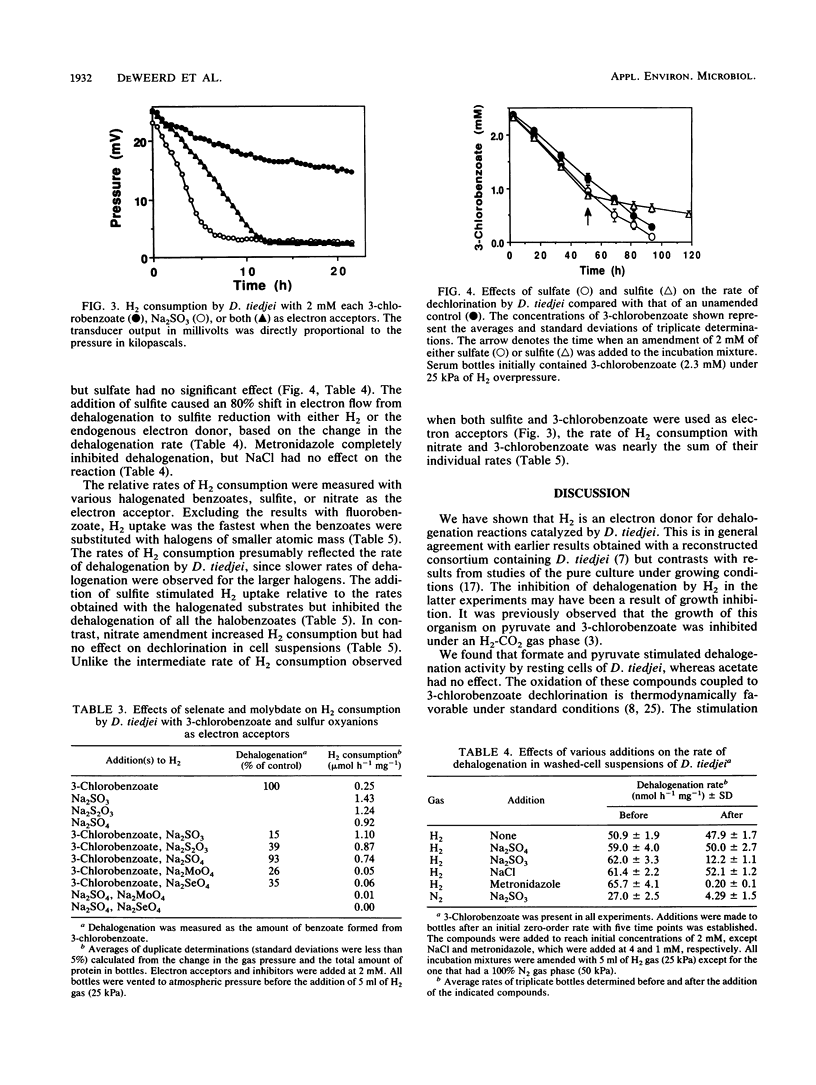
Resting-cell suspensions of Desulfomonile tiedjei consumed H2 with 3-chloro-, 3-bromo-, and 3-iodobenzoate as electron acceptors with rates of 0.50, 0.44, and 0.04 mumol h-1 mg-1, respectively. However, benzoate and 3-fluorobenzoate were not metabolized by this bacterium. In addition, H2 uptake was at least fourfold faster when sulfate, sulfite, or thiosulfate was available as the electron acceptor instead of a haloaromatic substrate. When sulfite and 3-chlorobenzoate were both available for this purpose, the rate of H2 uptake by D. tiedjei was intermediate between that obtained with either electron acceptor alone. Hydrogen concentrations were reduced to comparably low levels when either 3-chlorobenzoate, sulfate, or sulfite was available as an electron acceptor, but significantly less H2 depletion was evident with benzoate or nitrate. Rates of 3-chlorobenzoate dechlorination increased from an endogenous rate of 14.5 to 17.1, 74.0, 81.1, and 82.3 nmol h-1 mg-1 with acetate, pyruvate, H2, and formate, respectively, as the electron donors. Sulfite and thiosulfate inhibited dehalogenation, but sulfate and NaCl had no effect. Dehalogenation and H2 metabolism were also inhibited by acetylene, molybdate, selenate, and metronidazole. Sulfite reduction and dehalogenation were inhibited by the same respiratory inhibitors. These results suggest that the reduction of sulfite and dehalogenation may share part of the same electron transport chain. The kinetics of H2 consumption and the direct inhibition of dehalogenation by sulfite and thiosulfate in D. tiedjei cells clearly indicate that the reduction of sulfur oxyanions is favored over aryl dehalogenation for the removal of reducing equivalents under anaerobic conditions.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deweerd K. A., Suflita J. M. Anaerobic Aryl Reductive Dehalogenation of Halobenzoates by Cell Extracts of "Desulfomonile tiedjei". Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Oct;56(10):2999–3005. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.10.2999-3005.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J. Reductive dechlorination of 3-chlorobenzoate is coupled to ATP production and growth in an anaerobic bacterium, strain DCB-1. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(3):264–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00249079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J., Tiedje J. M. Growth yield increase linked to reductive dechlorination in a defined 3-chlorobenzoate degrading methanogenic coculture. Arch Microbiol. 1987;149(2):102–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00425073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Price W. A., Pritchard P. H. Anaerobic Degradation of Chloroaromatic Compounds in Aquatic Sediments under a Variety of Enrichment Conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1466–1471. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1466-1471.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. A., Suflita J. M. Anaerobic biodegradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic Acid in samples from a methanogenic aquifer: stimulation by short-chain organic acids and alcohols. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1825–1832. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1825-1832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. A., Suflita J. M. Extrapolation of biodegradation results to groundwater aquifers: reductive dehalogenation of aromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):681–688. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.681-688.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggblom M. M., Young L. Y. Chlorophenol degradation coupled to sulfate reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3255–3260. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3255-3260.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr D. B., Waters J. K., Emerich D. W. Analysis of Poly-beta-Hydroxybutyrate in Rhizobium japonicum Bacteroids by Ion-Exclusion High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography and UV Detection. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Dec;46(6):1339–1344. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.6.1339-1344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. M. Dehalogenation in marine sediments containing natural sources of halophenols. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3079–3085. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3079-3085.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohring G. W., Zhang X. M., Wiegel J. Anaerobic dechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol in freshwater sediments in the presence of sulfate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2735–2737. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2735-2737.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. P., Townsend G. T., Suflita J. M. Effect of sulfate and organic carbon supplements on reductive dehalogenation of chloroanilines in anaerobic aquifer slurries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2630–2637. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2630-2637.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linkfield T. G., Tiedje J. M. Characterization of the requirements and substrates for reductive dehalogenation by strain DCB-1. J Ind Microbiol. 1990 Jan;5(1):9–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01569601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohn W. W., Tiedje J. M. Strain DCB-1 conserves energy for growth from reductive dechlorination coupled to formate oxidation. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(3):267–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00249080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zeikus J. G. Rapid method for the radioisotopic analysis of gaseous end products of anaerobic metabolism. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):258–261. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.258-261.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. A., Smolenski W. J., Ogilvie M. L., Peters J. P. In vitro total-gas, CH4, H2, volatile fatty acid, and lactate kinetics studies on luminal contents from the small intestine, cecum, and colon of the pig. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2460–2467. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2460-2467.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarlett N., Gorrell T. E., Marczak R., Müller M. Reduction of nitroimidazole derivatives by hydrogenosomal extracts of Trichomonas vaginalis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Jan;14(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



